7-1 Panda and PP Milk (20 分)

PP milk (盆盆奶)is Pandas’ favorite. They would line up to enjoy it as show in the picture. On the other hand, they could drink in peace only if they believe that the amount of PP milk is fairly distributed, that is, fatter panda can have more milk, and the ones with equal weight may have the same amount. Since they are lined up, each panda can only compare with its neighbor(s), and if it thinks this is unfair, the panda would fight with its neighbor.
Given that the minimum amount of milk a panda must drink is 200 ml. It is only when another bowl of milk is at least 100 ml more than its own that a panda can sense the difference.
Now given the weights of a line of pandas, your job is to help the breeder(饲养员)to decide the minimum total amount of milk that he/she must prepare, provided that the pandas are lined up in the given order.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, first a positive integer n (≤10[HTML_REMOVED]4[HTML_REMOVED]) is given as the number of pandas. Then in the next line, n positive integers are given as the weights (in kg) of the pandas, each no more than 200. the numbers are separated by spaces.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line the minimum total amount of milk that the breeder must prepare, to make sure that all the pandas can drink in peace.
Sample Input:
10
180 160 100 150 145 142 138 138 138 140
Sample Output:
3000
Hint:
The distribution of milk is the following:
400 300 200 500 400 300 200 200 200 300
Tag:
思维
Meaning:
有n个排好队的熊猫,给出他们的体重,现在要求为每一只熊猫分配牛奶。
要求最少分配200ml,并且每只熊猫会观察与其相邻的熊猫奶量,体重更重的需要喝更多奶(至少多100ml)
要求输出n只熊猫最小的奶量总和
Thought:
类似于两遍的最长上升子序列问题
其实有很简单的思路,先让所有的熊猫向左看,调整奶量后再让所有的熊猫向右看,此时奶量需要和上一次的结果取max
以向左看为例:
- 当前熊猫体重 > 左边的熊猫,当前熊猫奶量 = 左边熊猫奶量 + 100
- 当前熊猫体重 = 左边的熊猫,当前熊猫奶量 = 左边熊猫奶量
- 当前熊猫体重 < 左边的熊猫,当前熊猫奶量 = 200(取最小值)
最后对奶量求和输出即可
算法的时间复杂度是O(n)的,n最大为10[HTML_REMOVED]4[HTML_REMOVED],完全可行
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010;
int n;
int weight[N], num[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
cin >> weight[i];
num[0] = 2;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i ++ )
{
if(weight[i] > weight[i - 1])
num[i] = num[i - 1] + 1;
else if(weight[i] == weight[i - 1])
num[i] = num[i - 1];
else
num[i] = 2;
}
num[n - 1] = max(2, num[n - 1]);
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i -- )
{
if(weight[i] > weight[i + 1])
num[i] = max(num[i + 1] + 1, num[i]);
else if(weight[i] == weight[i + 1])
num[i] = max(num[i + 1], num[i]);
else
num[i] = max(2, num[i]);
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
res += num[i] * 100;
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
```
7-2 How Many Ways to Buy a Piece of Land (25 分)
The land is for sale in CyberCity, and is divided into several pieces. Here it is assumed that each piece of land has exactly two neighboring pieces, except the first and the last that have only one. One can buy several contiguous(连续的) pieces at a time. Now given the list of prices of the land pieces, your job is to tell a customer in how many different ways that he/she can buy with a certain amount of money.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case first gives in a line two positive integers: N (≤10[HTML_REMOVED]4[HTML_REMOVED]), the number of pieces of the land (hence the land pieces are numbered from 1 to N in order), and M (≤10[HTML_REMOVED]9[HTML_REMOVED]), the amount of money that your customer has.
Then in the next line, N positive integers are given, where the i-th one is the price of the i-th piece of the land.
It is guaranteed that the total price of the land is no more than 10[HTML_REMOVED]9[HTML_REMOVED].
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the number of different ways that your customer can buy. Notice that the pieces must be contiguous.
Sample Input:
5 85
38 42 15 24 9
Sample Output:
11
Hint:
The 11 different ways are:
38
42
15
24
9
38 42
42 15
42 15 24
15 24
15 24 9
24 9
Tag:
前缀和,枚举
Meaning:
给出n块土地的价格,并且给出总钱数m
只能购买连续相邻的土地,并且总花费不能超过m,问总共有多少种购买方案
Thought:
看到contiguous(连续的)这个关键字,就要想到前缀和了
虽然n最大是10[HTML_REMOVED]4[HTML_REMOVED],但这题似乎只能双重循环去暴力枚举区间首尾,因为这题没有单调性,不能用双指针优化
时间复杂度O(n[HTML_REMOVED]2[HTML_REMOVED]),pta的数据还是一如既往的
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010;
int n, m;
int s[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
cin >> s[i];
s[i] += s[i - 1];
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = i; j <= n; j ++ )
if(s[j] - s[i - 1] <= m)
res++;
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
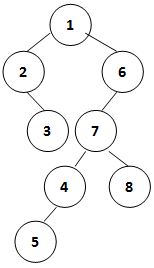
7-3 Left-View of Binary Tree (25 分)
The left-view of a binary tree is a list of nodes obtained by looking at the tree from left hand side and from top down. For example, given a tree shown by the figure, its left-view is { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }
Given the inorder and preorder traversal sequences of a binary tree, you are supposed to output its left-view.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤20), which is the total number of nodes in the tree. Then given in the following 2 lines are the inorder and preorder traversal sequences of the tree, respectively. All the keys in the tree are distinct positive integers in the range of int.
Output Specification:
For each case, print in a line the left-view of the tree. All the numbers in a line are separated by exactly 1 space, and there must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line.
Sample Input:
8
2 3 1 5 4 7 8 6
1 2 3 6 7 4 5 8
Sample Output:
1 2 3 4 5
Tag:
树的遍历,重建二叉树
Meaning:
给出一颗二叉树的中序遍历和前序遍历,要求输出树的“左视图”
即输出每一层的第一个节点
Thought:
经典重建二叉树,直接套模板就行了
提供两种思路:
- 真的重建好这颗树,通过层序遍历存下每一层的值,最后输出每一层的第一个数即可
- 不需要重建(保存)这颗树,在建树的过程中顺带记录每个节点的高度,每次保存每个高度下第一次出现的值(这两种遍历都是先遍历左子树后遍历右子树,所以每个高度下第一次出现的值一定是这一层最左边的节点),同理如果是“右视图”,只需要保存这一高度下最后出现的节点值(一直覆盖即可)
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 25;
int n;
int in[N], pre[N], max_deep, d[N];
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
void build(int pl, int pr, int il, int ir, int deep)
{
int root = pre[pl];
int k = mp[root];
if(deep == max_deep)
d[max_deep++] = root;
if(il < k)
build(pl + 1, pl + 1 + (k - 1 - il), il, k - 1, deep + 1);
if(k < ir)
build(pl + 1 + (k - 1 - il) + 1, pr, k + 1, ir, deep + 1);
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
cin >> in[i];
mp[in[i]] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
cin >> pre[i];
build(0, n - 1, 0, n - 1, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < max_deep; i++)
cout << d[i] << (i == max_deep - 1 ? '\n' : ' ');
return 0;
}
7-4 Professional Ability Test (30 分)
Professional Ability Test (PAT) consists of several series of subject tests. Each test is divided into several levels. Level A is a prerequisite (前置要求) of Level B if one must pass Level A with a score no less than S in order to be qualified to take Level B. At the mean time, one who passes Level A with a score no less than S will receive a voucher(代金券)of D yuans (Chinese dollar) for taking Level B.
At the moment, this PAT is only in design and hence people would make up different plans. A plan is NOT consistent if there exists some test T so that T is a prerequisite of itself. Your job is to test each plan and tell if it is a consistent one, and at the mean time, find the easiest way (with minimum total S) to obtain the certificate of any subject test. If the easiest way is not unique, find the one that one can win the maximum total value of vouchers.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives two positive integers N (≤1000) and M, being the total numbers of tests and prerequisite relations, respectively. Then M lines follow, each describes a prerequisite relation in the following format:
T1 T2 S D
where T1 and T2 are the indices (from 0 to N−1) of the two distinct tests; S is the minimum score (in the range (0, 100]) required to pass T1 in order to be qualified to take T2; and D is the value of the voucher (in the range (0, 500]) one can receive if one passes T1 with a score no less than S and plan to take T2. It is guaranteed that at most one pair of S and D are defined for a prerequisite relation.
Then another positive integer K (≤N) is given, followed by K queries of tests. All the numbers in a line are separated by spaces.
Output Specification:
Print in the first line Okay. if the whole plan is consistent, or Impossible. if not.
If the plan is consistent, for each query of test T, print in a line the easiest way to obtain the certificate of this test, in the format:
T0->T1->...->T
However, if T is the first level of some subject test (with no prerequisite), print You may take test T directly. instead.
If the plan is impossible, for each query of test T, check if one can take it directly or not. If the answer is yes, print in a line You may take test T directly.; or print Error. instead.
Sample Input 1:
8 15
0 1 50 50
1 2 20 20
3 4 90 90
3 7 90 80
4 5 20 20
7 5 10 10
5 6 10 10
0 4 80 60
3 1 50 45
1 4 30 20
1 5 50 20
2 4 10 10
7 2 10 30
2 5 30 20
2 6 40 60
8
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Sample Output 1:
Okay.
You may take test 0 directly.
0->1
0->1->2
You may take test 3 directly.
0->1->2->4
0->1->2->4->5
0->1->2->6
3->7
Sample Input 2:
4 5
0 1 1 10
1 2 2 10
3 0 4 10
3 2 5 10
2 0 3 10
2
3 1
Sample Output 2:
Impossible.
You may take test 3 directly.
Error.
Tag:
拓扑排序,堆优化dijkstra,多源汇最短路径
Meaning:
给定n个点,m条边的有向图
每条边除首尾节点编号外,额外携带值s和值d
对于每个询问:
- 首先判断是否有入度,若入度为零,则直接到达
- 如果整个图无合法拓扑排序,或者该点无法找到一条拓扑路径,则输出error
- 输出一条以s值第一关键字,以d值为第二关键字的拓扑路径(最小化s,最大化d)
Thought:
首先说拓扑排序,这里我们可以再开一个数组,记录某一点是否无法到达(成环,即正常拓扑排序没能遍历到的点)
然后是求解最短路径,这里可能会出现多个起点(多源最短路径),所以每次求解最短路径,都需要从每个节点都遍历一遍,即便是采用堆优化的dijkstra也会超时
这里我们可以建立一个超级源点,这个点是图中不存在的点,假定编号为n,我们可以为每一个起点,都添加上一条从n点到起点,s值和d值都为0的有向边,这样问题又转化为了单源最短路径,n最大为10[HTML_REMOVED]3[HTML_REMOVED],由于只需要执行一遍dijkstra算法,所以采用朴素版dijkstra也是可以的,时间复杂度为O(n[HTML_REMOVED]2[HTML_REMOVED])
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010, M = N * N;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
int n, m, k;
vector<int> a;
int h[N], e[M], S[M], D[M], ne[M], idx;
int d[N], q[N], hh, rr;
bool hasFront[N], inLoop[N], vis[N];
int minS[N], maxD[N], pre[N];
void add(int a, int b, int T1, int T2)
{
e[idx] = b;
S[idx] = T1;
D[idx] = T2;
ne[idx] = h[a];
h[a] = idx++;
}
bool topSort()
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
if(d[i] == 0)
q[rr++] = i;
while(hh < rr)
{
int t = q[hh++];
for(int i = h[t]; ~i; i = ne[i])
if(--d[e[i]] == 0)
q[rr++] = e[i];
}
return rr == n;
}
void dijkstra()
{
priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> q;
memset(minS, 0x3f, sizeof minS);
q.push({0, n});
minS[n] = 0;
while(q.size())
{
PII top = q.top();
q.pop();
int t = top.second;
if(vis[t])
continue;
vis[t] = true;
for (int i = h[t]; ~i; i = ne[i])
{
int j = e[i];
if(minS[j] > minS[t] + S[i])
{
pre[j] = t;
minS[j] = minS[t] + S[i];
maxD[j] = maxD[t] + D[i];
q.push({minS[j], j});
}
else if(minS[j] == minS[t] + S[i])
{
if(maxD[j] < maxD[t] + D[i])
{
pre[j] = t;
maxD[j] = maxD[t] + D[i];
q.push({minS[j], j});
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
while(m--)
{
int a, b, T1, T2;
scanf("%d %d %d %d", &a, &b, &T1, &T2);
add(a, b, T1, T2);
hasFront[b] = true;
d[b]++;
}
scanf("%d", &k);
a.resize(k);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i ++ )
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
bool flag = topSort();
flag ? puts("Okay.") : puts("Impossible.");
for(int i = rr; i < n; i++)
inLoop[i] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
if(!hasFront[i])
add(n, i, 0, 0);
dijkstra();
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
int u = a[i];
if(!hasFront[u])
printf("You may take test %d directly.\n", u);
else if(!flag || inLoop[u])
puts("Error.");
else
{
string str = to_string(u);
for(int i = pre[u]; i != n; i = pre[i])
str = to_string(i) + "->" + str;
printf("%s\n", str.c_str());
}
}
return 0;
}


so cute
%%%
%%%