6 Thrift
6.1 引言
Thrift是一个跨语言的RPC框架(Remote Procedure Call),用于服务之间的通信。它把过程封装到一个函数中,它可以让不同编程语言无缝结合,使得调用者像调用本地服务一样方便。
Thrift优势
- 开发速度快:用户只需编写IDL,编译器自动生成服务端骨架和客户端桩(Stubs)
- 接口维护简单:只需维护IDL
- 学习成本低:面向对象风格
- 支持多种语言:Java、Python、C++等
- 稳定且广泛使用:Hadoop
6.2 架构
Thrift自顶向下可分为5层
- 传输层(Transport Layer):负责从网络中读取数据和写入数据,定义了具体的网络传输协议,例如TCP/IP
- 协议层(Protocol Layer):定义了数据传输格式,负责网络传输数据的序列化和反序列化,例如JSON、XML、二进制数据等
- 处理层(Processor Layer):由具体的接口描述语言IDL生成,封装了具体的底层网络传输和序列化方式,委托给用户实现的
Handler处理 - 服务层(Server Layer):整合上述组件,提供具体的网络IO模型(单线程/多线程/事件驱动),形成最终服务
- 底层(Underlying Layer):包含
socket、http等内容
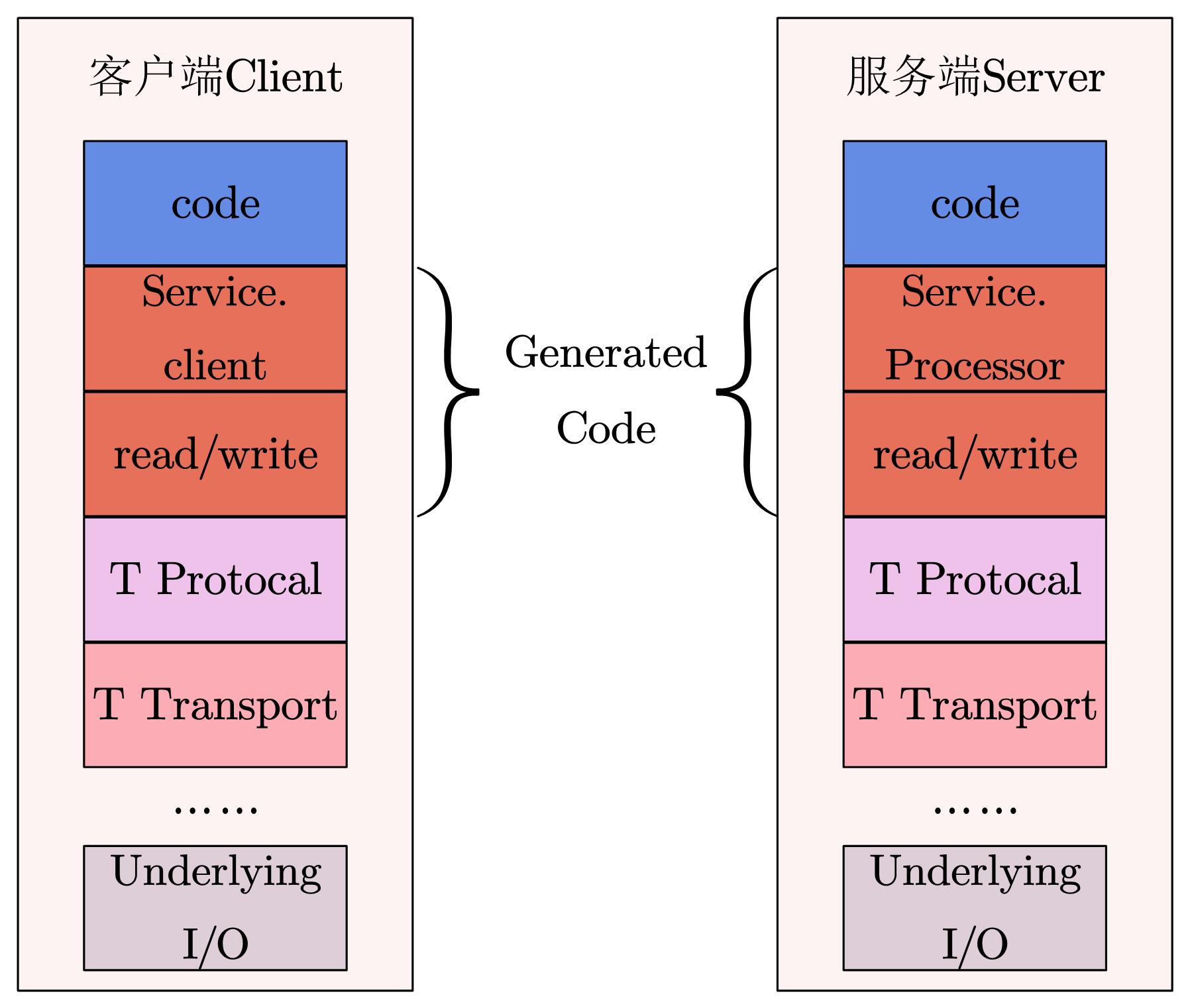
其中传输层和协议层是必须的。
Thrift允许用户指定传输通信协议类别,一般传输协议可分为两大类:文本text和二进制binary。
如果想节省带宽,提高传输效率,可采用二进制类型协议。有时会使用文本类型协议。
常用传输协议如下
TBinaryProtocol:普通二进制编码TCompactProtocol:比TBinaryProtocol更高效紧凑的二进制编码TJSONProtocol:基于JSON的编码TSimpleJSONProtocol:只提供JSON写协议,适用脚本语言解析
常用的传输层有
TSocket:阻塞式I/O传输TNonBlockingTransport:非阻塞式I/O传输,用于构建异步客户端TFrameTransport:非阻塞式I/O传输,按块进行传输,类似Java中的NIO模型
6.3 安装
安装可参考官网教程,在这以Ubuntu20.04为例
(1)下载依赖库
sudo apt-get install automake bison flex g++ git libboost-all-dev libevent-dev libssl-dev libtool make pkg-config
(2)下载安装文件并解压
wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/thrift/0.16.0/thrift-0.16.0.tar.gz
tar -xvzf thrift-0.16.0.tar.gz
(3)安装
cd thrift-0.16.0
sudo ./configure
sudo make
sudo make install
6.4 IDL
Thrift采用IDL(Interface Definition Language)定义通用服务接口,然后可借助Thrift提供的编译器将服务接口编译成指定语言编写的代码,从而实现跨语言功能。
6.4.1 基本类型
| IDL类型 | 描述 | 相应Java类型 |
|---|---|---|
i8 |
有符号8位整数 | byte |
i16 |
有符号16位整数 | short |
i32 |
有符号32位整数 | int |
i64 |
有符号64位整数 | long |
double |
64位浮点数 | double |
bool |
布尔值 | boolean |
string |
UTF-8字符串 | String |
常量用const修饰,例如const i32 id = 1
6.4.2 struct类型
语法格式
struct <struct_name> {
<id>: [field_property] <field_type> <field_name> [= <default_value>] [;|,]
}
使用说明
- 每个成员必须声明编号,而且不能重复,顺序与传输编码息息相关
- 字段性质有三种
optional:不填充则不序列化required:必须填充也必须序列化- 不指定:填充则会序列化
- 字段类型必须指明
- 字段声明语句之间可以用
;或,,或直接省略。分隔符可以混用,但不建议。 - 字段可以指定默认值
- 同一个文件可以定义多个
struct,也可通过include导入其它文件的struct struct不能继承,但可以嵌套,不过不能嵌套自己
例
struct User{
1: i32 id;
2: string name
}
6.4.3 容器类型
| IDL类型 | 描述 | 相应Java类型 |
|---|---|---|
list<T> |
有序列表,允许重复 | List |
set<T> |
无序列表,不允许重复 | Set |
map<K, V> |
key-value结构数据,key不允许重复 |
Map |
在使用容器类时需要指定泛型,否则无法编译。元素类型可以是service外的任何类型。
例
struct Test{
1: list<i32> intList;
2: map<i32, User> users
}
映射类型赋值时,键值用冒号:隔开
map<i32, string> users = {1: "xxx", 2: "yyy"}
可像c++用typedef给结构体取别名
typedef map<i32, string> xxx
6.4.4 枚举类型
枚举类型不能嵌套,且内部定义的常量必须是32位正整数
enum Status {
OK = 200;
NOT_FOUNT = 404
}
6.4.5 异常
异常exception定义类似struct,只是关键字不同。在编译时,异常默认继承编译语言的基础异常类
exception MyException {
1: i32 code;
2: string msg
}
6.4.6 服务定义类型
服务定义类型Service类似面向对象语言的接口
service MyService {
i32 convert(1:string param);
string toString(1:i32 param);
void print(1:string param)
}
6.4.7 命名空间
命名空间Namespace类似C++中的namespace或java中的package,它用于组织IDL的代码结构,隔离其它代码;也可用于解决类型名称冲突的问题。
例如
namespace java com.acwing.test
会转化为
package com.acwing.test
6.4.8 注释
单行注释和多行注释风格类似C++/Java
/**
* Multi-line Comment
*/
// Single-line Comment
6.4.9 导入
类似C++,IDL允许使用include导入其它thrift文件,文件名用双引号包裹,末尾无分号或逗号。
include "xxx.thrift"
6.4.10 编译
编译命令
thrift -gen cpp user.thrift # 可把cpp换成java、py
6.5 Thrift简单例子
6.5.1 定义IDL
(1)编写user.thrift文件
namespace java com.acwing
struct User {
1:i32 id
2:string name
}
service UserService {
User getbyID(1:i32 id)
bool isExist(1:string name)
}
(2)使用编译器编译user.thrift
thrift -gen java user.thrift
编译后,生成的代码文件将存储到当前目录下gen-java文件夹里
6.5.2 实现IDL
开发者只需关注以下四个核心内部接口/类,其中UserService是上面定义的service
Iface:服务端通过实现UserService接口,向客户端提供具体的同步业务逻辑AsyncIface:服务端通过实现UserService.Iface接口,向客户端提供具体的异步业务逻辑Client:客户端通过UserService.Client的实例对象,以同步的方式访问服务端提供的方法AsyncClient:客户端通过UserService.Client的实例对象,以异步的方式访问服务端提供的方法
在使用前,java需要配置依赖org.apache.thrift,python需要安装对应的包,下边将以Java为例说明不同模型下的IDL实现方式。Java可在pom.xml文件加入依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.thrift</groupId>
<artifactId>libthrift</artifactId>
<version>0.16.0</version>
</dependency>
如果提示java 不支持发行版本5,则在菜单File→settings找到Build, Execution, Deployment→Compiler→Java Compiler,把Project bytecode version设置为9,下边的Per-module bytecode version的Target bytecode version也设置为9。
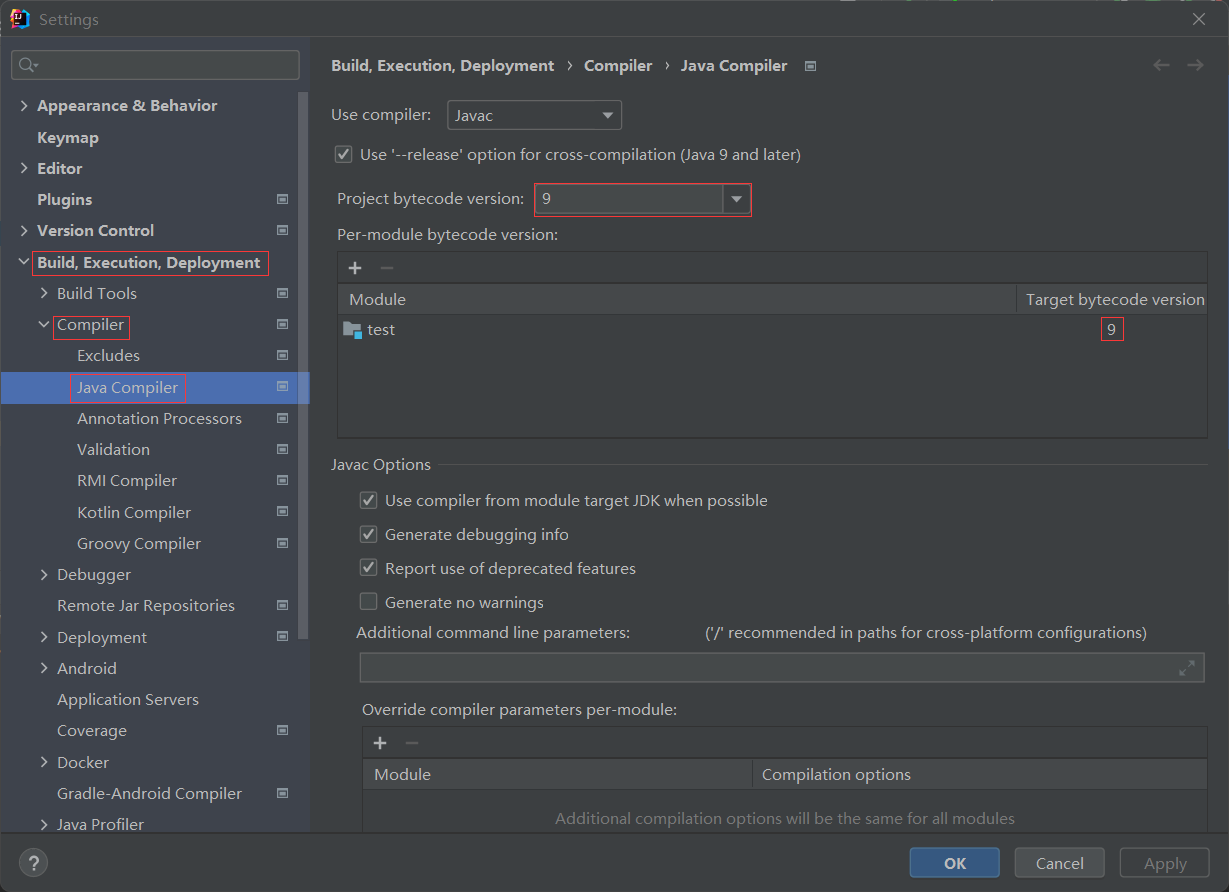
如果提示Failed to load class "org.slf4j.impl.StaticLoggerBinder",则再加入一个依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-nop</artifactId>
<version>1.7.2</version>
</dependency>
(1)单线程同步阻塞
① 将生成的User.java和UserService.java拷贝到src/main/java/src/com/acwing下
② 在src/main/java/src/com/acwing下创建UserServiceImpl.java,实现UserService.Iface接口定义的方法,补充业务逻辑。
package src.com.acwing;
import org.apache.thrift.TException;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService.Iface {
public User getbyID(int id) throws TException {
User user = new User();
return user;
}
public boolean isExist(String name) throws TException {
return false;
}
}
③ 在 src/main/java/src/com/acwing下创建SimpleService.java,编写服务端代码
package src.com.acwing;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServer;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TSimpleServer;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TServerSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TServerTransport;
public class SimpleService {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
TServerTransport serverTransport = new TServerSocket(8848);
// 获取processor
UserService.Processor processor = new UserService.Processor(new UserServiceImpl());
// 指定协议为普通的二进制传输协议
TBinaryProtocol.Factory protocolFactory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
// 获取数据
TSimpleServer.Args targs = new TSimpleServer.Args(serverTransport);
// 处理数据
targs.processor(processor); // 业务逻辑
targs.protocolFactory(protocolFactory); // 按传输协议转化成二进制数据
// 单线程服务模型,一般用于测试
TServer server = new TSimpleServer(targs);
System.out.println("Starting the simple server...");
server.serve(); // 启动服务
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
若运行服务端程序,则服务端在8848端口监听客户端连接请求。
③ 在 src/main/java/src/com/acwing下创建SimpleClient.java,编写客户端代码
package src.com.acwing;
import org.apache.thrift.TException;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransport;
public class SimpleClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TTransport transport = null;
try {
// BIO
transport = new TSocket("localhost", 8848);
TProtocol protocol = new TBinaryProtocol(transport);
UserService.Client client = new UserService.Client(protocol);
transport.open();
// 调用RPC
User result = client.getbyID(250);
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
} catch (TException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (transport != null)
transport.close();
}
}
}
运行客户端程序,客户端将通过网络向服务端发送服务请求,并在控制台输出结果。
(2)Python跨语言调用测试
① 把user.thrift编译成Python文件,将生成的代码和文件放入Python项目中
thrift -gen py user.thrift
② 在Python项目所在环境安装thrift
pip install thrift
③ 创建Python客户端程序
from thrift.transport import TSocket, TTransport
from thrift.protocol import TBinaryProtocol
from com.acwing import UserService
# 创建socket
transport = TSocket.TSocket("localhost", 8848)
transport.setTimeout(1000)
# 增加缓存区,提高socket速度
transport = TTransport.TBufferedTransport(transport)
# 创建协议
protocol = TBinaryProtocol.TBinaryProtocol(transport)
# 创建客户端
client = UserService.Client(protocol)
# 启动客户端
transport.open()
result = Client.getbyID(250)
print(result)
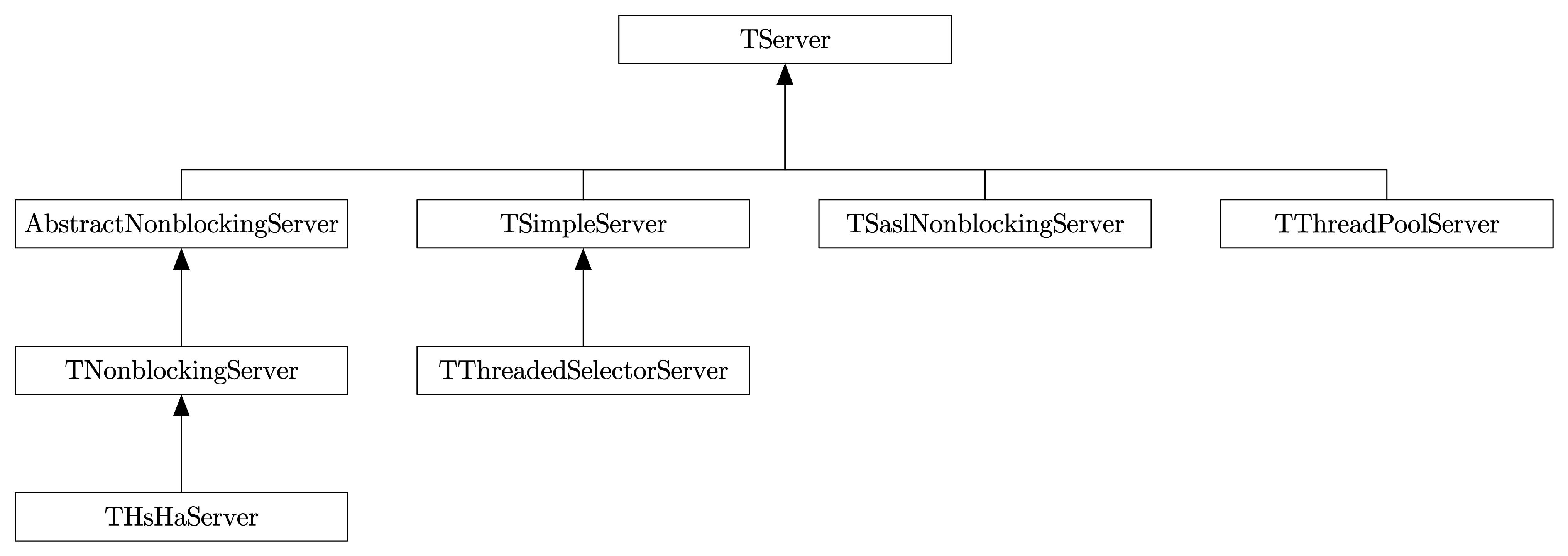
6.6 网络服务模型
Thrift提供三种网络服务模型
- 单线程模型
- 多线程模型
- 事件驱动模型
也可按是否阻塞分为
- 阻塞服务模型
TSimpleServerTThreadPoolServer
- 非阻塞服务模型
TNonblockingServerTHsHaServerTThreadedSelectorServer
6.6.1 TServer
TServer定义了静态内部类Args,它继承自抽象类AbstractServerArgs。
AbstractServerArgs采用建造者模式,向TServer提供各种工厂
| 工厂属性 | 工厂类型 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
ProcessorFactory |
TProcessorFactory |
处理层工厂类,用于创建TProcessor对象 |
InputTransportFactory |
TTransportFactory |
传输层输入工厂类,用于创建TTransport对象 |
OutputTransportFactory |
TTransportFactory |
传输层输出工厂类,用于创建TTransport对象 |
InputPrococolFactory |
TProtocolFactory |
协议层输入工厂类,用于创建TProtocol对象 |
OutputPrococolFactory |
TProtocolFactory |
协议层输出工厂类,用于创建TProtocol对象 |
TServer常用方法
serve():启动服务stop():关闭服务isServing():检查服务是否在运行
6.6.2 TSimpleServer
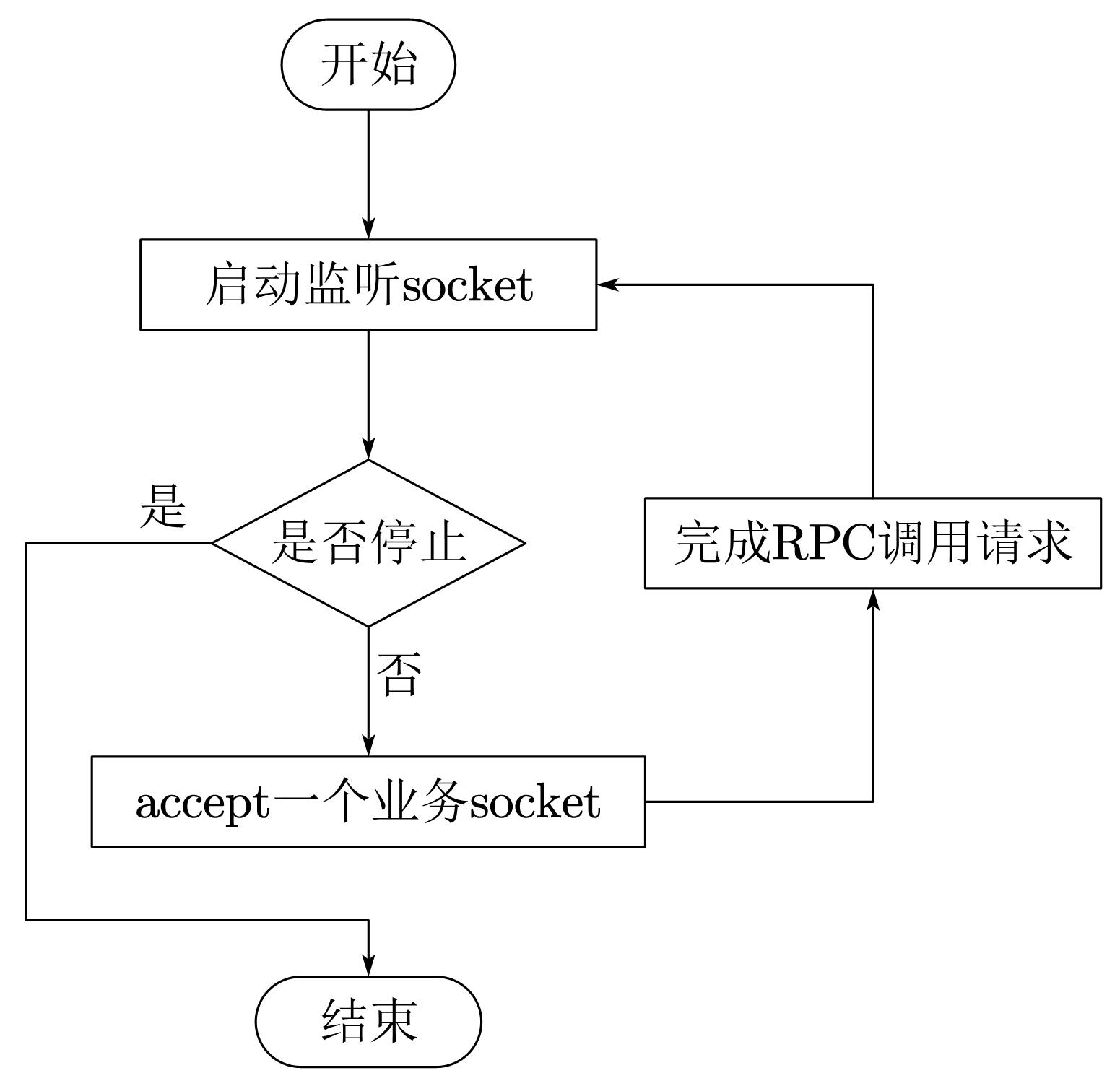
(1)原理
TSimpleServer的工作模型是最简单的阻塞I/O模型,一次只能接收一个socket,也只能处理一个socket,效率低,常用于演示,而不用于开发。
(2)服务端代码
package src.com.acwing;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServer;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TSimpleServer;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TServerSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TServerTransport;
public class SimpleService {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
TServerTransport serverTransport = new TServerSocket(8848);
// 获取processor
UserService.Processor processor = new UserService.Processor(new UserServiceImpl());
TBinaryProtocol.Factory protocolFactory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
//单线程服务模型,一般用于测试
TSimpleServer.Args targs = new TSimpleServer.Args(serverTransport);
targs.processor(processor);
targs.protocolFactory(protocolFactory);
TServer server = new TSimpleServer(targs);
System.out.println("Starting the simple server. . . ");
server.serve();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
(3)客户端代码
package src.com.acwing;
import org.apache.thrift.TException;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransport;
public class SimpleClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TTransport transport = null;
try {
// BIO
transport = new TSocket("localhost", 8848);
TProtocol protocol = new TBinaryProtocol(transport);
UserService.Client client = new UserService.Client(protocol);
// 建立连接
transport.open();
// 调用RPC
User result = client.getbyID(250);
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
} catch (TException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (transport != null)
transport.close();
}
}
}
6.6.3 TThreadPoolServer
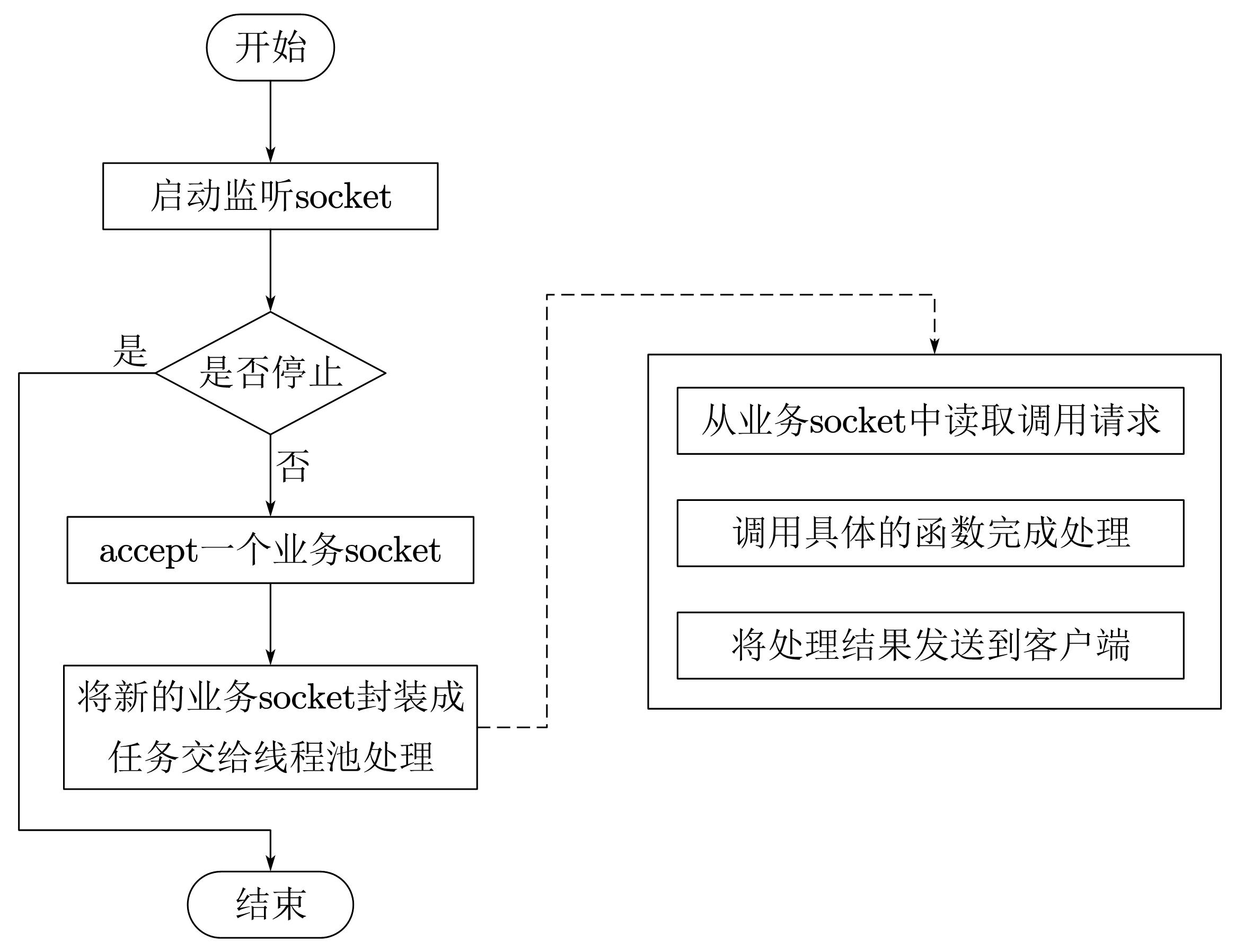
(1)原理
TThreadPoolServer采用阻塞socket方式工作,主线程负责阻塞式监听是否有新socket到来,具体的业务处理交由一个线程池来处理。
(2)服务端代码
package src.com.acwing;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TBinaryProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServer;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TThreadPoolServer;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TServerSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TServerTransport;
public class SimpleService {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
TServerTransport serverTransport = new TServerSocket(8848);
UserService.Processor processor = new UserService.Processor(new UserServiceImpl());
TBinaryProtocol.Factory protocolFactory = new TBinaryProtocol.Factory();
// 换成TThreadPoolServer对象(与TSimpleServer单线程模型的不同之处)
TThreadPoolServer.Args targs = new TThreadPoolServer.Args(serverTransport);
targs.processor(processor);
targs.protocolFactory(protocolFactory);
TServer server = new TThreadPoolServer(targs);
System.out.println("Starting the simple server. . . ");
server.serve();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
(3)客户端代码
与TSimpleServer一致
(4)优缺点
优点
TThreadPoolServer拆分了监听线程Accept Thread和处理客户端连接的工作线程Worker Thread,数据读取和业务处理都交给线程池处理,这使得在并发量较大时,新连接也能被及时接受。- 线程池模式比较适合服务端能预知最多有多少个客户端并发的情况,这时每个请求都能被业务线程池及时处理,性能也非常高
缺点
- 线程池模式的处理能力受限于线程池的工作能力,当并发请求数大于线程池中的线程数时,新请求也只能排队等待
- 线程池默认允许创建的最大线程数量为
Integer.MAX_VALUE,如果处理不好内存分配问题,服务端可能会创建出大量线程,导致内存溢出
6.6.4 TNonblockingServer
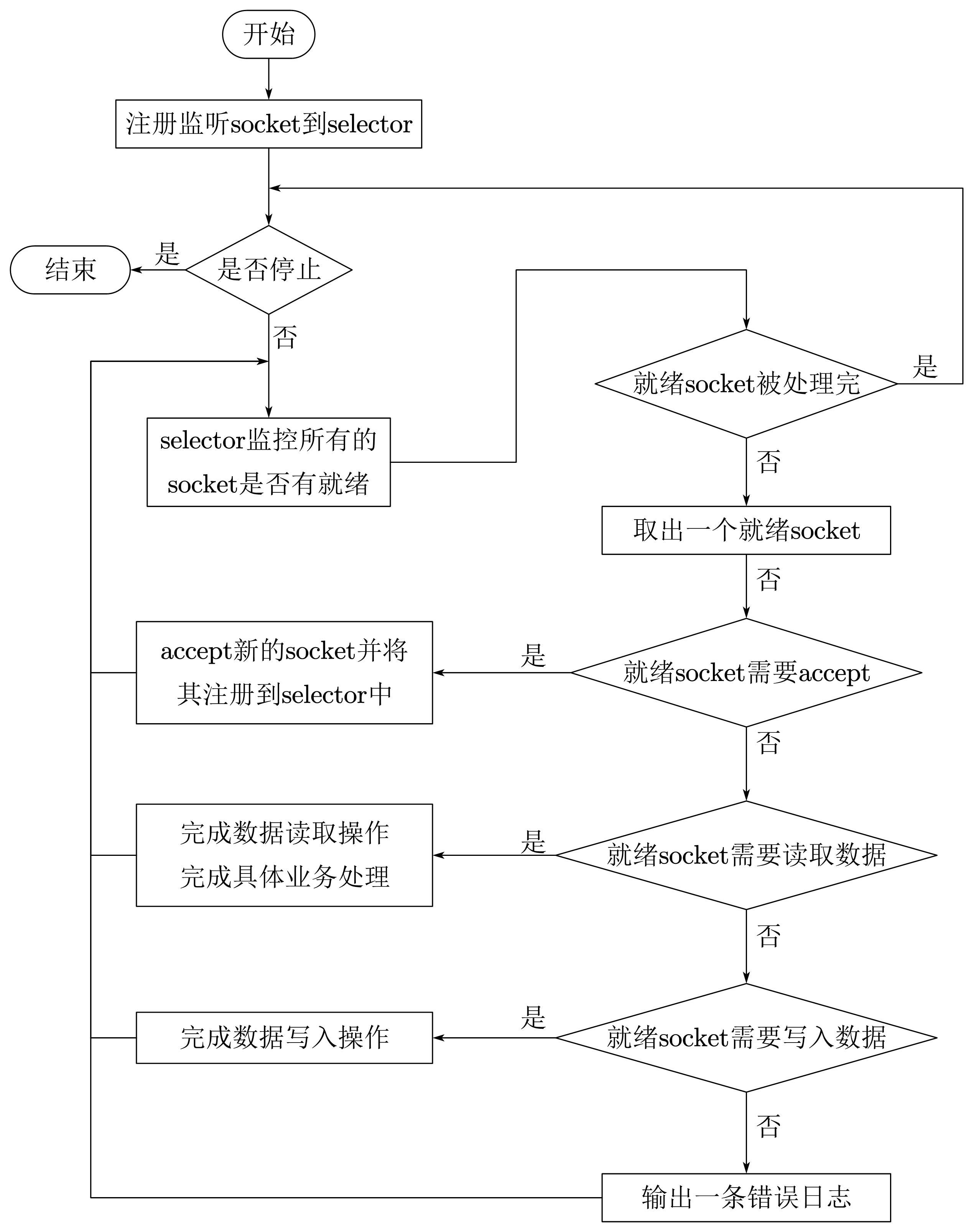
(1)原理
TNonblockingServer模式也是单线程工作,但是采用非阻塞I/O模式,利用I/O多路复用模型处理socket就绪事件。对于有数据到来的socket进行数据读取操作,对于有数据发送的socket则进行数据发送操作,对于监听socket则产生一个新业务socket并将其注册到selector上。TNonblockingServer要求底层的传输通道必须使用TFramedTransport。
(2)服务端代码
package src.com.acwing;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TCompactProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TNonblockingServer;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServer;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TNonblockingServerSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.layered.TFramedTransport;
public class SimpleService {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 更换套接字为TNonblockingServerSocket类型
TNonblockingServerSocket serverTransport = new TNonblockingServerSocket(8848);
UserService.Processor processor = new UserService.Processor(new UserServiceImpl());
// 更换协议为TCompactProtocol类型
TCompactProtocol.Factory protocolFactory = new TCompactProtocol.Factory();
// 指定TFramedTransport类型Factory
TFramedTransport.Factory tTransport = new TFramedTransport.Factory();
// 更换成TNonblockingServer对象
TNonblockingServer.Args targs = new TNonblockingServer.Args(serverTransport);
targs.processor(processor);
targs.protocolFactory(protocolFactory);
targs.transportFactory(tTransport);
TServer server = new TNonblockingServer(targs);
System.out.println("Starting non-blocking server. . . ");
server.serve();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
(3)客户端代码
package src.com.acwing;
import org.apache.thrift.TException;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TCompactProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransport;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.layered.TFramedTransport;
public class SimpleClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TTransport transport = null;
try {
// 使用非阻塞I/O模型
transport = new TFramedTransport(new TSocket("localhost", 8848));
// 更换为TCompactProtocol协议
TProtocol protocol = new TCompactProtocol(transport);
UserService.Client client = new UserService.Client(protocol);
// 建立连接
transport.open();
// 调用RPC
User result = client.getbyID(250);
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
} catch (TException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (transport != null)
transport.close();
}
}
}
(4)优缺点
优点
相比TSimpleServer,TNonblockingServer的效率提升主要体现在I/O多路复用上。TNonblockingServer采用非阻塞l/0,对accept/read/write等I/O事件进行监控和处理,同时监控多个socket的状态变化。
缺点
TNonblockingServer在业务处理上还是采用单线程顺序来完成。在业务处理比较复杂、耗时的时候,例如某些接
函数需要读取数据库执行时间较长,会导致整个服务被阻塞住,此时该模式效率也不高,因为多个调用请求任务依然是顺序一个接一个执行
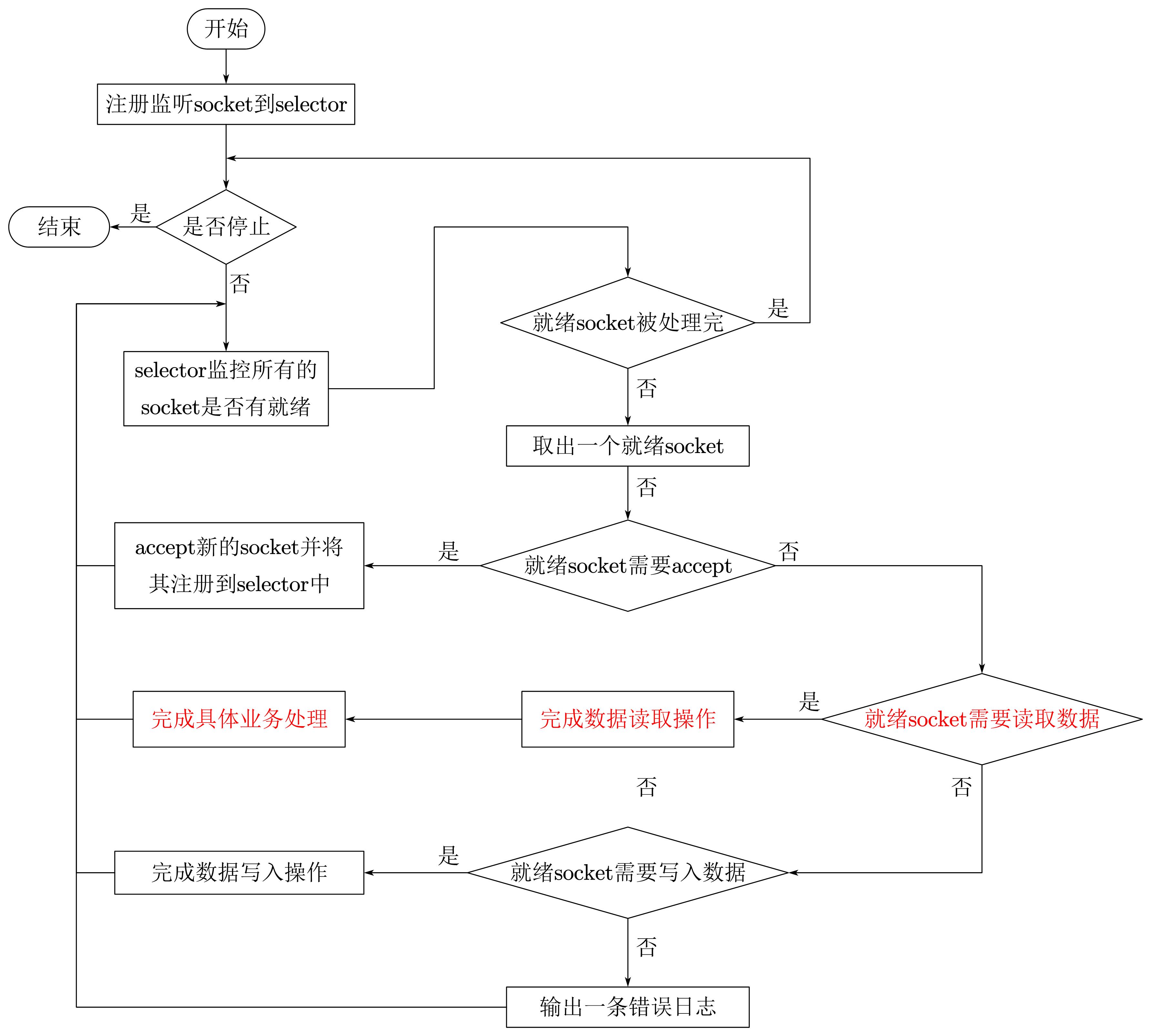
6.6.5 THsHaServer
(1)原理
THsHaServer针对TNonblockingServer的缺陷,引入了线程池提高了任务处理的并发能力。它继承于TNonblockingServer,与TNonblockingServer一样,要求底层的传输通道必须使用TFramedTransport。
(2)服务端代码
package src.com.acwing;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TCompactProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.server.THsHaServer;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServer;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TNonblockingServerSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.layered.TFramedTransport;
public class SimpleService {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
TNonblockingServerSocket serverTransport = new TNonblockingServerSocket(8848);
UserService.Processor processor = new UserService.Processor(new UserServiceImpl());
TCompactProtocol.Factory protocolFactory = new TCompactProtocol.Factory();
TFramedTransport.Factory tTransport = new TFramedTransport.Factory();
// 更换成THsHaServer对象
THsHaServer.Args targs = new THsHaServer.Args(serverTransport);
targs.processor(processor);
targs.protocolFactory(protocolFactory);
targs.transportFactory(tTransport);
TServer server = new THsHaServer(targs);
System.out.println("Starting HsHa server. . . ");
server.serve();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
(3)客户端代码
与TNonblockingServer一致。
(4)优缺点
优点
THsHaServer与TNonblockingServer模式相比,THsHaServer在完成数据读取之后,将业务处理过程交由一个线程池来完成,主线程直接返回进行下一次循环操作,效率大大提升。
缺点
主线程仍然需要完成所有socket的监听接收、数据读取和数据写入操作。当并发请求数较大时,且发送数据量较多时
监听socket上新连接请求不能被及时接受。
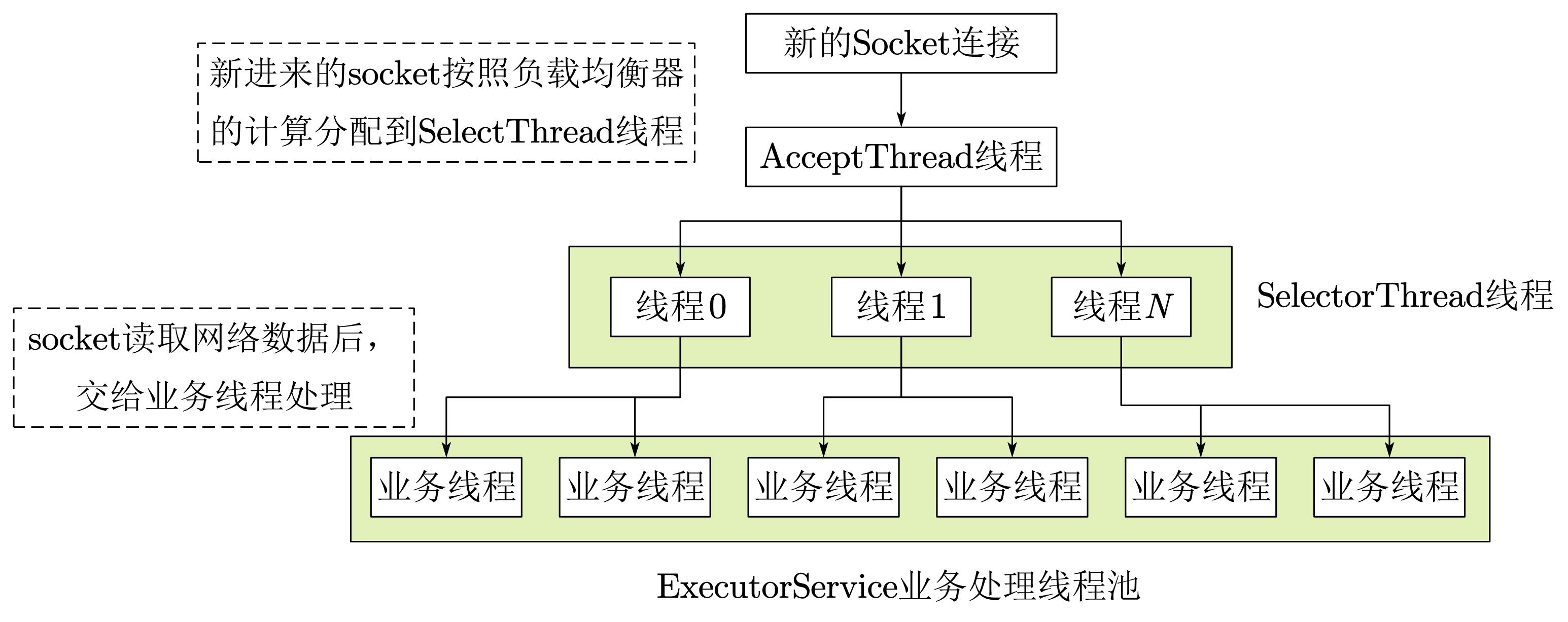
6.6.6 TThreadSelectorServer
(1)原理
TThreadedSelectorServer是对THsHaServer的一种扩充,它将selector中的读写I/O事件(read/write)从主线程中分离出来,同时引入worker工作线程池。
TThreadedselectorServer模式是目前Thrift提供的最高级的线程服务模型,它内部有如果几个部分构成:
- 一个
AcceptThread专门用于处理监听socket上的新连接。 - 若干个
SelectorThread专门用于处理业务socket的网络I/O读写操作,所有网络数据的读写均是有这些线程来完成。 - 一个负载均衡器
SelectorThreadLoadBalancer对象,主要用于AcceptThread线程接收到一个新socket连接请求时
决定将这个新连接请求分配给哪个SelectorThread线程。 - 一个
ExecutorService类型的工作线程池,在SelectorThread线程中,监听到有业务socket中有调用请求过来,则将请求数据读取之后,交给ExecutorService线程池中的线程完成此次调用的具体执行。主要用于处理每个RPC请求的handler回调处理。
(2)服务器代码
package src.com.acwing;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TCompactProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TServer;
import org.apache.thrift.server.TThreadedSelectorServer;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TNonblockingServerSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.layered.TFramedTransport;
public class ThreadedSelectorServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
TNonblockingServerSocket serverTransport = new TNonblockingServerSocket(8848);
UserService.Processor processor = new UserService.Processor(new UserServiceImpl());
TCompactProtocol.Factory protocolFactory = new TCompactProtocol.Factory();
TFramedTransport.Factory tTransport = new TFramedTransport.Factory();
// 更换成THsHaServer对象
TThreadedSelectorServer.Args targs = new TThreadedSelectorServer.Args(serverTransport);
targs.processor(processor);
targs.protocolFactory(protocolFactory);
targs.transportFactory(tTransport);
TServer server = new TThreadedSelectorServer(targs);
System.out.println("Starting ThreadedSelector server. . . ");
server.serve();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
(3)客户端代码
package src.com.acwing;
import org.apache.thrift.TException;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TCompactProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.protocol.TProtocol;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TSocket;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.TTransport;
import org.apache.thrift.transport.layered.TFramedTransport;
public class ThreadedSelectorClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
handle();
}).start();
}
}
public static void handle() {
TTransport transport = null;
try {
transport = new TFramedTransport(new TSocket("localhost", 8848));
TProtocol protocol = new TCompactProtocol(transport);
UserService.Client client = new UserService.Client(protocol);
transport.open();
// 调用RPC
User result = client.getbyID(250);
System.out.println("Result: " + result);
} catch (TException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (transport != null)
transport.close();
}
}
}
6.7 AcWing匹配系统实战
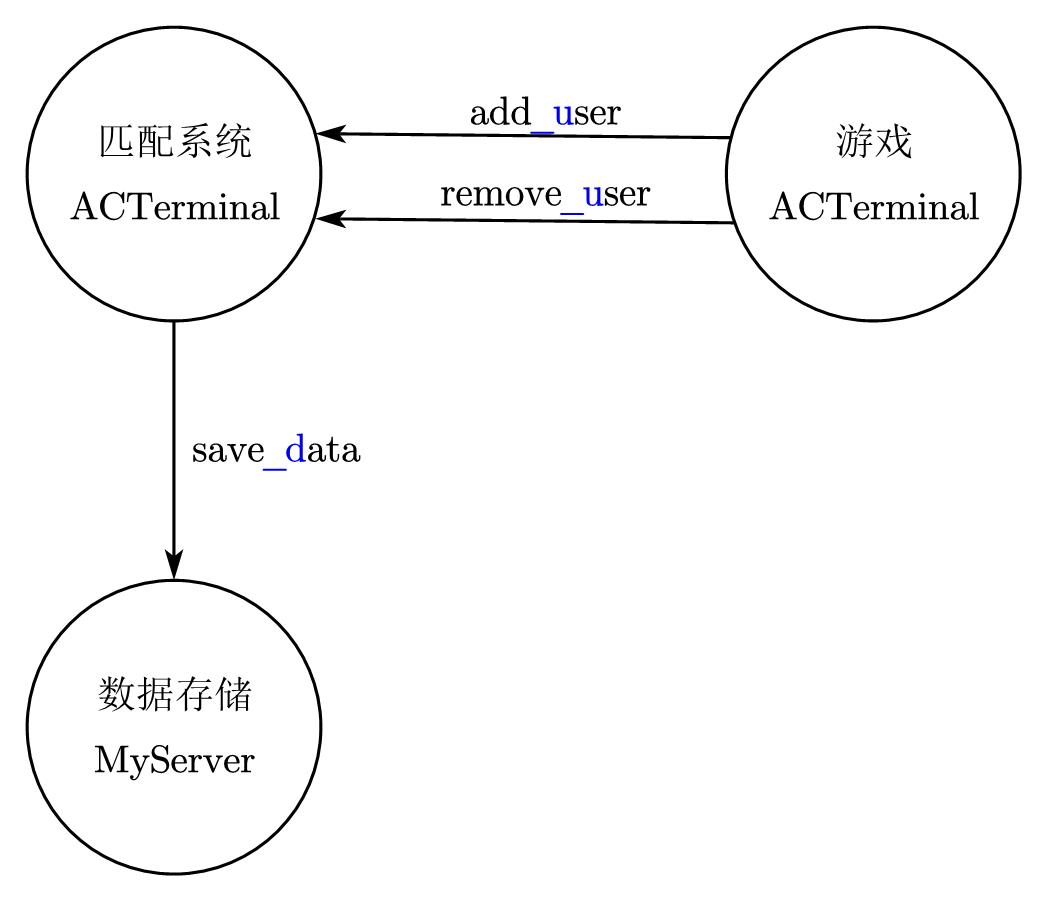
6.7.1 创建服务端和服务端
(1)创建服务端
用thrift生成服务端cpp代码
thrift -gen cpp thrift/match.thrift
把gen-cpp里的文件复制到match_system/src/match_server里,然后把Match_server.skeleton.cpp重命名为main.cpp,并放到上一级目录match_system/src
mkdir match_system/src/match_server
mv gen-cpp/* match_system/src/match_server
cd match_system/src/match_server
mv Match_server.skeleton.cpp main.cpp
用vim修改main.cpp
① 修改头文件引用#include "Match.h"→#include "match_server/Match.h",让其正确引用
② 在MatchHandler里给方法add_user()和remove_user()添加返回值return 0
③ 引入头文件#include <iostream>,在main方法的server.serve()上一行添加输出语句std::cout << "Start Match Server" << std::endl
编译main.cpp以及match_server目录下的所有cpp文件
g++ -c main.cpp match_server/*.cpp
链接,需要引入thrift的动态库-lthrift
g++ *.o -o main -lthrift
尝试运行
./main
(2)创建客户端
用thrift生成服务端python代码
thrift -gen py thrift/match.thrift
删除gen-py目录里的Match_remote文件,然后把gen-py里的文件复制到game/src/match_client里
rm gen-py/Match_remote
mkdir ame/src/match_client
mv gen-py/* game/src/match_client
在官网找到使用Python编写的客户端模板并修改
- 删除前4行代码
- 用
Match替代Calculator - 用
match_client.match替代tutorial,修改成实际路径 - 删掉教学代码——
transport.open()与transport.close()之间的代码,替换成自己的业务代码 - 加入调试部分代码
__main__
from match_client.match import Match
from match_client.match.ttypes import User
from thrift import Thrift
from thrift.transport import TSocket
from thrift.transport import TTransport
from thrift.protocol import TBinaryProtocol
def main():
# Make socket
transport = TSocket.TSocket('localhost', 9090)
# Buffering is critical. Raw sockets are very slow
transport = TTransport.TBufferedTransport(transport)
# Wrap in a protocol
protocol = TBinaryProtocol.TBinaryProtocol(transport)
# Create a client to use the protocol encoder
client = Match.Client(protocol)
# Connect!
transport.open()
user = User(1, 'yxc', 1500)
client.add_user(user, "")
# Close!
transport.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
把文件保存到game/src下
新开一个终端,开启服务端./main,在另一个服务端执行客户端
python3 client.py
如果服务端出现add_user,说明客户端创建成功。
6.7.2 实现客户端业务逻辑
from match_client.match import Match
from match_client.match.ttypes import User
from thrift import Thrift
from thrift.transport import TSocket
from thrift.transport import TTransport
from thrift.protocol import TBinaryProtocol
from sys import stdin
def operate(op, user_id, username, score):
# Make socket
transport = TSocket.TSocket('localhost', 9090)
# Buffering is critical. Raw sockets are very slow
transport = TTransport.TBufferedTransport(transport)
# Wrap in a protocol
protocol = TBinaryProtocol.TBinaryProtocol(transport)
# Create a client to use the protocol encoder
client = Match.Client(protocol)
# Connect!
transport.open()
user = User(user_id, username, score)
if op == "add":
client.add_user(user, "")
elif op == "remove":
client.remove_user(user, "")
# Close!
transport.close()
def main():
for line in stdin:
op, user_id, username, score = line.split(' ')
operate(op, int(user_id), username, int(score))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
此时运行客户端后,可在控制台读入数据op user_id username score,例如add 233 yxc 1000
6.7.3 实现服务端业务逻辑
响应客户端请求和处理客户端请求可以拆分成两个独立过程,可使用多线程提高其效率。假设使用两个线程完成服务端响应和处理过程:一个线程负责响应客户端请求,接收客户端指令;另一个线程负责处理指令,完成匹配。
在本案例中,请求主要指客户端指令:添加用户add_user()和删除用户remove_user(),因此可用一个结构体Task描述该指令,其中type用于区分指令类型。
struct Task {
User user;
string type; // "add"或"remove"
};
响应客户端请求的线程可看做生产者,它创建若干个Task对象;处理客户端请求的线程可看做消费者,按照一定的规则删除Task对象,因此可用生产者消费者模型实现该过程。生产者消费者模型需要通信媒介,常用的一种实现方式是消费队列。
在代码实现中,消费队列是生产者进程和消费者进程的共享变量,多个线程同时修改它可能会导致结果出错,因此需要引入锁机制。当某个线程拿到消费队列的锁mutex后,消费队列只能由该线程使用,当另一个线程想使用时,会发现消费队列已上锁并进入阻塞状态,直到锁mutex被释放。
消费者线程可看做是一个while(True) {...}的程序,它在main方法中创建。当没有task可消费时,会不停占用CPU资源,消耗系统资源,影响生产者线程接收数据。为了解决这个问题,可以使用条件变量condition_variable。条件变量可以让线程主动进入阻塞状态,直到被另一个线程的notify相关方法唤醒。因此当消费者线程发现消费队列为空时,主动进入阻塞状态,直到生产者进程接收客户端指令,修改消费者队列后再唤醒消费者线程消费task。因此消费队列可按如下方式设计。
// 使用互斥锁的消费队列
struct MessageQueue {
queue<Task> q; // 消费队列
mutex m; // 互斥锁
condition_variable cv; // 条件变量,用于阻塞所在线程
}message_queue;
为了实现上述描述的生产者消费者模型,需要引入以下库文件。
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
消费队列保存的是一个个待处理的任务task,而不是用户列表,因此需要创建一个类Pool,记录当前匹配池的情况以及定义匹配池的操作。匹配池Pool的操作主要包括:添加用户、删除用户、匹配、保存匹配结果。其代码设计如下所示:
class Pool {
// 匹配池
public:
void save_result(int a, int b) {
printf("Match Result: %d %d\n", a, b);
}
void match() {
while (users.size() > 1) {
// 选择队头两名用户匹配
auto a = users[0], b = users[1];
users.erase(users.begin());
users.erase(users.begin());
save_result(a.id, b.id);
}
}
void add(User user) {
users.push_back(user);
}
void remove(User user) {
// 根据id逐个查找用户,找到后删除
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++) // 用uint32_t变量防止size()出现warnning
if (users[i].id == user.id) {
users.erase(users.begin() + i);
break;
}
}
private:
vector<User> users; // 用户列表
}pool;
每次匹配选取用户列表里最靠前的两名用户来匹配,保存匹配记录后,移除这两名用户。
综上所述,可得到如下完整的服务端代码:
#include "match_server/Match.h"
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/server/TSimpleServer.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TServerSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::server;
using namespace ::match_service;
using namespace std;
// 消费者线程消费的最小单位
struct Task {
User user;
string type; // "add"或"remove"
};
// 使用互斥锁的消费队列
struct MessageQueue {
queue<Task> q; // 消费队列
mutex m; // 互斥锁
condition_variable cv; // 条件变量,用于阻塞所在线程
}message_queue;
class Pool {
// 匹配池
public:
void save_result(int a, int b) {
printf("Match Result: %d %d\n", a, b);
}
void match() {
while (users.size() > 1) {
// 选择队头两名用户匹配
auto a = users[0], b = users[1];
users.erase(users.begin());
users.erase(users.begin());
save_result(a.id, b.id);
}
}
void add(User user) {
users.push_back(user);
}
void remove(User user) {
// 根据id逐个查找用户,找到后删除
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++) // 用uint32_t变量防止size()出现warnning
if (users[i].id == user.id) {
users.erase(users.begin() + i);
break;
}
}
private:
vector<User> users; // 用户列表
}pool;
class MatchHandler : virtual public MatchIf {
public:
MatchHandler() {
// Your initialization goes here
}
/**
* user: 添加的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 在匹配池中添加一个名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t add_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("add_user\n");
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m); // 加锁,防止同时修改消费队列出现异常
message_queue.q.push({user, "add"});
message_queue.cv.notify_all(); // 唤醒消费者线程(在这只有消费者这一个)
return 0;
}
/**
* user: 删除的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 从匹配池中删除一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t remove_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("remove_user\n");
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m); // 加锁,防止同时修改消费队列出现异常
message_queue.q.push({user, "remove"});
message_queue.cv.notify_all(); // 唤醒消费者线程
return 0;
}
};
void consume_task() {
while (true) {
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
if (message_queue.q.empty()) {
message_queue.cv.wait(lck); // 进入阻塞状态,直到被其它线程的nofity方法唤醒
} else {
auto task = message_queue.q.front(); // 取出一个任务消费
message_queue.q.pop();
lck.unlock(); // 处理完共享变量后及时解锁
if (task.type == "add") pool.add(task.user);
else if (task.type == "remove") pool.remove(task.user);
pool.match();
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int port = 9090;
::std::shared_ptr<MatchHandler> handler(new MatchHandler());
::std::shared_ptr<TProcessor> processor(new MatchProcessor(handler));
::std::shared_ptr<TServerTransport> serverTransport(new TServerSocket(port));
::std::shared_ptr<TTransportFactory> transportFactory(new TBufferedTransportFactory());
::std::shared_ptr<TProtocolFactory> protocolFactory(new TBinaryProtocolFactory());
TSimpleServer server(processor, serverTransport, transportFactory, protocolFactory);
std::cout << "Start Match Server" << std::endl;
std::thread matching_thread(consume_task); // 创建消费者线程
server.serve();
return 0;
}
由于服务端使用了线程库,因此在链接时,需要加参数-pthread链接线程相关库文件。
g++ *.o -o main -lthrift -pthread
6.7.4 实现数据存储
用thrift生成Save客户端cpp代码
thrift -gen cpp thrift/save.thrift
删掉服务端代码,然后把gen-cpp里的文件复制到match_system/src/save_client里
rm gen-cpp/Save_server.skeleton.cpp
mkdir match_system/src/save_client
mv gen-cpp/* match_system/src/save_client
rm gen-cpp
参考官网的C++客户端模板,修改match_system/src的main.cpp
① 加入模板中需要,但main.cpp没有的头文件
#include <thrift/transport/TTransportUtils.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TSocket.h>
② 引入生成的Save.h
#include "save_client/Save.h"
③ 添加save.thrift定义的命名空间,保证代码正确引用Save.h的内容
using namespace ::save_service;
④ 把模板main方法里的内容拷贝到match_system/src/main.cpp的Pool类的void save_result(int a, int b)方法的printf(...)后边,并用gg=G格式化代码,然后按如下修改
- 把粘贴代码里
new TSocket("localhost", 9090)的localhost改成第4讲配置的myserver的IP - 把
CalculatorClient换成SaveClient - 删除
try语句块里的transport->open();与transport->close();之间的教学语句,然后加入语句client.save_data("myserver_username", "密码md5前八位", a, b);,注意myserver_username指第4章配置的myserver的用户名,可通过homework 4 getinfo查看,例如acs_1234- 为了防止密码泄露风险,校验采用密码md5码的前八位,可通过命令
echo your_password | md5sum | cut -c 1-8获得,其中your_password是你的明文密码
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> socket(new TSocket("xx.xx.xx.xx", 9090)); // xx.xx.xx.xx为自己myserver的IP
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> transport(new TBufferedTransport(socket));
std::shared_ptr<TProtocol> protocol(new TBinaryProtocol(transport));
SaveClient client(protocol);
try {
transport->open();
client.save_data("acs_1234", "abcdefgh", a, b); // 替换换成自己myserver的用户名和密码mk5前八位
transport->close();
} catch (TException& tx) {
cout << "ERROR: " << tx.what() << endl;
}
修改后main.cpp代码如下
#include "match_server/Match.h"
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/server/TSimpleServer.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TServerSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TTransportUtils.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TSocket.h>
#include "save_client/Save.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::server;
using namespace ::match_service;
using namespace ::save_service;
using namespace std;
struct Task {
User user;
string type;
};
struct MessageQueue {
queue<Task> q;
mutex m;
condition_variable cv;
}message_queue;
class Pool {
public:
void save_result(int a, int b) {
printf("Match Result: %d %d\n", a, b);
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> socket(new TSocket("123.57.47.211", 9090));
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> transport(new TBufferedTransport(socket));
std::shared_ptr<TProtocol> protocol(new TBinaryProtocol(transport));
SaveClient client(protocol);
try {
transport->open();
client.save_data("acs_3929", "6df6b19d", a, b);
transport->close();
} catch (TException& tx) {
cout << "ERROR: " << tx.what() << endl;
}
}
void match() {
while (users.size() > 1) {
auto a = users[0], b = users[1];
users.erase(users.begin());
users.erase(users.begin());
save_result(a.id, b.id);
}
}
void add(User user) {
users.push_back(user);
}
void remove(User user) {
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++)
if (users[i].id == user.id) {
users.erase(users.begin() + i);
break;
}
}
private:
vector<User> users;
}pool;
class MatchHandler : virtual public MatchIf {
public:
MatchHandler() {
// Your initialization goes here
}
/**
* user: 添加的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 在匹配池中添加一个名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t add_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("add_user\n");
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "add"});
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
/**
* user: 删除的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 从匹配池中删除一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t remove_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("remove_user\n");
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "remove"});
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
};
void consume_task() {
while (true) {
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
if (message_queue.q.empty()) {
message_queue.cv.wait(lck);
} else {
auto task = message_queue.q.front();
message_queue.q.pop();
lck.unlock();
if (task.type == "add") pool.add(task.user);
else if (task.type == "remove") pool.remove(task.user);
pool.match();
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
int port = 9090;
::std::shared_ptr<MatchHandler> handler(new MatchHandler());
::std::shared_ptr<TProcessor> processor(new MatchProcessor(handler));
::std::shared_ptr<TServerTransport> serverTransport(new TServerSocket(port));
::std::shared_ptr<TTransportFactory> transportFactory(new TBufferedTransportFactory());
::std::shared_ptr<TProtocolFactory> protocolFactory(new TBinaryProtocolFactory());
TSimpleServer server(processor, serverTransport, transportFactory, protocolFactory);
std::cout << "Start Match Server" << std::endl;
std::thread matching_thread(consume_task);
server.serve();
return 0;
}
⑤ 编译及链接代码
g++ -c main.cpp save_client/*.cpp
g++ *.o -o main -lthrift -pthread
⑥ 检验
首先把game/src/client.py的operate方法的localhost改成127.0.0.1
然后在tmux开启两个bash,分别在match_system/src执行./main和game/src执行python3 client.py
在客户端输入若干指令,观察服务端的匹配情况。
最后登录保存数据的服务器ssh myserver,查看~/homework/lesson_6/result.txt是否存在,是否有匹配信息。
6.7.5 编写匹配逻辑
修改match_system/src/main.cpp
(1)改成每1秒匹配一次
① 去掉消费者进程方法consume_task的阻塞代码,让它解锁后直接匹配,然后休眠1s
void consume_task() {
while (true) {
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
if (message_queue.q.empty()) {
// message_queue.cv.wait(lck);
lck.unlock();
pool.match();
sleep(1);
} else {
auto task = message_queue.q.front();
message_queue.q.pop();
lck.unlock();
if (task.type == "add") pool.add(task.user);
else if (task.type == "remove") pool.remove(task.user);
pool.match();
}
}
}
② 引入sleep()需要的头文件
#include <unistd.h>
(2)编写匹配逻辑
首先按分值升序排序,依次检查相邻用户的分值差的绝对值是否小于50,如果满足立即匹配这两名用户。
修改Pool类中match()方法的匹配逻辑
void match() {
while(users.size() > 1) {
sort(users.begin(), users.end(), [&](User& a, User& b){
return a.score < b.score;
});
bool success = false;
for (uint32_t i = 1; i < users.size(); i++) {
auto a = users[i - 1], b = users[i];
if (b.score - a.score <= 50) {
users.erase(users.begin() + i - 1, users.begin() + i + 1);
save_result(a.id, b.id);
success = false;
break;
}
}
if (success) break; // 匹配成功后立即停止,防止进入死循环
}
}
(3)验证匹配逻辑
编译main.cpp,运行服务端和客户端,在客户端测试以下代码。
add 1 1 1000
add 2 2 2000
add 3 3 999
如果匹配系统给1和3匹配,则说明逻辑基本正确。
6.7.6 改用多线程并发
参考官网C++服务端模板,修改match_system/src/main.cpp
(1)添加缺少的头文件
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadManager.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadFactory.h>
#include <thrift/server/TThreadedServer.h>
#include <thrift/TToString.h>
(2)替换掉main()方法里的服务器构建过程
TThreadedServer server(
std::make_shared<CalculatorProcessorFactory>(std::make_shared<CalculatorCloneFactory>()),
std::make_shared<TServerSocket>(9090), //port
std::make_shared<TBufferedTransportFactory>(),
std::make_shared<TBinaryProtocolFactory>()
);
(3)复制工厂代码到main方法上边,注释掉输出信息
/*
CalculatorIfFactory is code generated.
CalculatorCloneFactory is useful for getting access to the server side of the
transport. It is also useful for making per-connection state. Without this
CloneFactory, all connections will end up sharing the same handler instance.
*/
class CalculatorCloneFactory : virtual public CalculatorIfFactory {
public:
~CalculatorCloneFactory() override = default;
CalculatorIf* getHandler(const ::apache::thrift::TConnectionInfo& connInfo) override
{
std::shared_ptr<TSocket> sock = std::dynamic_pointer_cast<TSocket>(connInfo.transport);
// cout << "Incoming connection\n";
// cout << "\tSocketInfo: " << sock->getSocketInfo() << "\n";
// cout << "\tPeerHost: " << sock->getPeerHost() << "\n";
// cout << "\tPeerAddress: " << sock->getPeerAddress() << "\n";
// cout << "\tPeerPort: " << sock->getPeerPort() << "\n";
return new CalculatorHandler;
}
void releaseHandler( ::shared::SharedServiceIf* handler) override {
delete handler;
}
};
(3)将Calculator替换成Match
:1,$s/Calculator/Match/g
(4)修改参数releaseHandler
void releaseHandler( MatchIf* handler) override {
delete handler;
}
最终代码如下
#include "match_server/Match.h"
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/server/TSimpleServer.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TServerSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TTransportUtils.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TSocket.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadManager.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadFactory.h>
#include <thrift/server/TThreadedServer.h>
#include <thrift/TToString.h>
#include "save_client/Save.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::server;
using namespace ::match_service;
using namespace ::save_service;
using namespace std;
struct Task
{
User user;
string type;
};
struct MessageQueue
{
queue<Task> q;
mutex m;
condition_variable cv;
} message_queue;
class Pool
{
public:
void save_result(int a, int b)
{
printf("Match Result: %d %d\n", a, b);
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> socket(new TSocket("123.57.47.211", 9090));
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> transport(new TBufferedTransport(socket));
std::shared_ptr<TProtocol> protocol(new TBinaryProtocol(transport));
SaveClient client(protocol);
try
{
transport->open();
client.save_data("acs_3929", "6df6b19d", a, b);
transport->close();
}
catch (TException& tx)
{
cout << "ERROR: " << tx.what() << endl;
}
}
void match()
{
while(users.size() > 1)
{
sort(users.begin(), users.end(), [&](User& a, User& b)
{
return a.score < b.score;
});
bool flag = true;
for (uint32_t i = 1; i < users.size(); i++)
{
auto a = users[i - 1], b = users[i];
if (b.score - a.score <= 50)
{
users.erase(users.begin() + i - 1, users.begin() + i + 1);
save_result(a.id, b.id);
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if (flag) break; // 匹配成功后立即停止,防止进入死循环
}
}
void add(User user)
{
users.push_back(user);
}
void remove(User user)
{
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++)
if (users[i].id == user.id)
{
users.erase(users.begin() + i);
break;
}
}
private:
vector<User> users;
} pool;
class MatchHandler : virtual public MatchIf
{
public:
MatchHandler()
{
// Your initialization goes here
}
/**
* user: 添加的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 在匹配池中添加一个名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t add_user(const User& user, const std::string& info)
{
// Your implementation goes here
printf("add_user\n");
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "add"});
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
/**
* user: 删除的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 从匹配池中删除一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t remove_user(const User& user, const std::string& info)
{
// Your implementation goes here
printf("remove_user\n");
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "remove"});
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
};
void consume_task()
{
while (true)
{
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
if (message_queue.q.empty())
{
// message_queue.cv.wait(lck);
lck.unlock();
pool.match();
sleep(1);
}
else
{
auto task = message_queue.q.front();
message_queue.q.pop();
lck.unlock();
if (task.type == "add") pool.add(task.user);
else if (task.type == "remove") pool.remove(task.user);
pool.match();
}
}
}
/*
MatchIfFactory is code generated.
MatchCloneFactory is useful for getting access to the server side of the
transport. It is also useful for making per-connection state. Without this
CloneFactory, all connections will end up sharing the same handler instance.
*/
class MatchCloneFactory : virtual public MatchIfFactory
{
public:
~MatchCloneFactory() override = default;
MatchIf* getHandler(const ::apache::thrift::TConnectionInfo& connInfo) override
{
std::shared_ptr<TSocket> sock = std::dynamic_pointer_cast<TSocket>(connInfo.transport);
// cout << "Incoming connection\n";
// cout << "\tSocketInfo: " << sock->getSocketInfo() << "\n";
// cout << "\tPeerHost: " << sock->getPeerHost() << "\n";
// cout << "\tPeerAddress: " << sock->getPeerAddress() << "\n";
// cout << "\tPeerPort: " << sock->getPeerPort() << "\n";
return new MatchHandler;
}
void releaseHandler( MatchIf* handler) override
{
delete handler;
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
TThreadedServer server(
std::make_shared<MatchProcessorFactory>(std::make_shared<MatchCloneFactory>()),
std::make_shared<TServerSocket>(9090), //port
std::make_shared<TBufferedTransportFactory>(),
std::make_shared<TBinaryProtocolFactory>()
);
std::cout << "Start Match Server" << std::endl;
std::thread matching_thread(consume_task);
server.serve();
return 0;
}
6.7.7 动态匹配
思想
如果匹配池有两个人不满足分值差不超过50,按之前的逻辑这两个人永远不会被匹配,但这样体验不好,因此引入动态匹配。每个人允许的分值差是动态变化的,它等于等待时间$\times 50$。如果两个人的分值差都在各自允许的分值差范围内,则匹配这两人。
例如甲的分值为1000分,乙为1500分。甲已经等待了11秒,其允许分值差为550分;乙等待了9秒,其运输分值差为450分。尽管二者分数差在甲当前的容忍范围内,但不在乙的容忍范围内,因此不匹配。再过1秒后,时间差也在乙的容忍范围内了,可以匹配了。
实现
(1)修改match_system/src/main.cpp的Pool类
① 引入等待时间成员变量vector<int> wt;
② 让add_user()和remove_user()支持wt的添加与删除
③ 修改match()方法并引入check_match()方法
得到的Pool类如下
class Pool {
public:
void save_result(int a, int b) {
printf("Match Result: %d %d\n", a, b);
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> socket(new TSocket("123.57.47.211", 9090));
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> transport(new TBufferedTransport(socket));
std::shared_ptr<TProtocol> protocol(new TBinaryProtocol(transport));
SaveClient client(protocol);
try {
transport->open();
client.save_data("acs_3929", "6df6b19d", a, b);
transport->close();
} catch (TException& tx) {
cout << "ERROR: " << tx.what() << endl;
}
}
bool check_match(uint32_t i, uint32_t j)
{
auto a = users[i], b = users[j];
int dt = abs(a.score - b.score);
int a_max_dif = wt[i] * 50;
int b_max_dif = wt[j] * 50;
return dt <= a_max_dif && dt <= b_max_dif;
}
void match()
{
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < wt.size(); i++)
wt[i]++; // 更新等待时间
while(users.size() > 1)
{
bool flag = true;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++)
{
for (uint32_t j = i + 1; j < users.size(); j++)
{
if (check_match(i, j))
{
auto a = users[i], b = users[j];
users.erase(users.begin() + j); // 使用erase删除时,要先删后边的
wt.erase(wt.begin() + j);
users.erase(users.begin() + i); // 再删前边的
wt.erase(wt.begin() + i);
save_result(a.id, b.id);
flag = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (flag) break; // 匹配成功后立即停止,防止进入死循环
}
}
void add(User user) {
users.push_back(user);
wt.push_back(0);
}
void remove(User user) {
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++)
if (users[i].id == user.id) {
users.erase(users.begin() + i);
wt.erase(wt.begin() + i);
break;
}
}
private:
vector<User> users;
vector<int> wt; // 等待时间
}pool;
(2)删除consume_task()里else里的pool.match(),保证先匹配,且等待时间正确。
最终服务端代码如下
#include "match_server/Match.h"
#include <thrift/protocol/TBinaryProtocol.h>
#include <thrift/server/TSimpleServer.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TServerSocket.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TBufferTransports.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TTransportUtils.h>
#include <thrift/transport/TSocket.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadManager.h>
#include <thrift/concurrency/ThreadFactory.h>
#include <thrift/server/TThreadedServer.h>
#include <thrift/TToString.h>
#include "save_client/Save.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <unistd.h>
using namespace ::apache::thrift;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::protocol;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::transport;
using namespace ::apache::thrift::server;
using namespace ::match_service;
using namespace ::save_service;
using namespace std;
struct Task {
User user;
string type;
};
struct MessageQueue {
queue<Task> q;
mutex m;
condition_variable cv;
}message_queue;
class Pool {
public:
void save_result(int a, int b) {
printf("Match Result: %d %d\n", a, b);
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> socket(new TSocket("123.57.47.211", 9090));
std::shared_ptr<TTransport> transport(new TBufferedTransport(socket));
std::shared_ptr<TProtocol> protocol(new TBinaryProtocol(transport));
SaveClient client(protocol);
try {
transport->open();
client.save_data("acs_3929", "6df6b19d", a, b);
transport->close();
} catch (TException& tx) {
cout << "ERROR: " << tx.what() << endl;
}
}
bool check_match(uint32_t i, uint32_t j)
{
auto a = users[i], b = users[j];
int dt = abs(a.score - b.score);
int a_max_dif = wt[i] * 50;
int b_max_dif = wt[j] * 50;
return dt <= a_max_dif && dt <= b_max_dif;
}
void match()
{
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < wt.size(); i++)
wt[i]++; // 更新等待时间
while(users.size() > 1)
{
bool flag = true;
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++)
{
for (uint32_t j = i + 1; j < users.size(); j++)
{
if (check_match(i, j))
{
auto a = users[i], b = users[j];
users.erase(users.begin() + j); // 使用erase删除时,要先删后边的
wt.erase(wt.begin() + j);
users.erase(users.begin() + i); // 再删前边的
wt.erase(wt.begin() + i);
save_result(a.id, b.id);
flag = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (flag) break; // 匹配成功后立即停止,防止进入死循环
}
}
void add(User user) {
users.push_back(user);
wt.push_back(0);
}
void remove(User user) {
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < users.size(); i++)
if (users[i].id == user.id) {
users.erase(users.begin() + i);
wt.erase(wt.begin() + i);
break;
}
}
private:
vector<User> users;
vector<int> wt; // 等待时间
}pool;
class MatchHandler : virtual public MatchIf {
public:
MatchHandler() {
// Your initialization goes here
}
/**
* user: 添加的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 在匹配池中添加一个名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t add_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("add_user\n");
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "add"});
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
/**
* user: 删除的用户信息
* info: 附加信息
* 从匹配池中删除一名用户
*
* @param user
* @param info
*/
int32_t remove_user(const User& user, const std::string& info) {
// Your implementation goes here
printf("remove_user\n");
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
message_queue.q.push({user, "remove"});
message_queue.cv.notify_all();
return 0;
}
};
void consume_task() {
while (true) {
unique_lock<mutex> lck(message_queue.m);
if (message_queue.q.empty()) {
// message_queue.cv.wait(lck);
lck.unlock();
pool.match();
sleep(1);
} else {
auto task = message_queue.q.front();
message_queue.q.pop();
lck.unlock();
if (task.type == "add") pool.add(task.user);
else if (task.type == "remove") pool.remove(task.user);
}
}
}
/*
MatchIfFactory is code generated.
MatchCloneFactory is useful for getting access to the server side of the
transport. It is also useful for making per-connection state. Without this
CloneFactory, all connections will end up sharing the same handler instance.
*/
class MatchCloneFactory : virtual public MatchIfFactory {
public:
~MatchCloneFactory() override = default;
MatchIf* getHandler(const ::apache::thrift::TConnectionInfo& connInfo) override
{
std::shared_ptr<TSocket> sock = std::dynamic_pointer_cast<TSocket>(connInfo.transport);
// cout << "Incoming connection\n";
// cout << "\tSocketInfo: " << sock->getSocketInfo() << "\n";
// cout << "\tPeerHost: " << sock->getPeerHost() << "\n";
// cout << "\tPeerAddress: " << sock->getPeerAddress() << "\n";
// cout << "\tPeerPort: " << sock->getPeerPort() << "\n";
return new MatchHandler;
}
void releaseHandler( MatchIf* handler) override {
delete handler;
}
};
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
TThreadedServer server(
std::make_shared<MatchProcessorFactory>(std::make_shared<MatchCloneFactory>()),
std::make_shared<TServerSocket>(9090), //port
std::make_shared<TBufferedTransportFactory>(),
std::make_shared<TBinaryProtocolFactory>()
);
std::cout << "Start Match Server" << std::endl;
std::thread matching_thread(consume_task);
server.serve();
return 0;
}
验证
使用下述作为客户端输入,观察是否延迟匹配。
add 1 1 1000
add 2 2 1500
在用homework 6 test前,先关闭客户端,然后启动服务端。


大佬,这是自己实现了这个了吗,还是跟着y总敲的啊
跟着y总敲的,同时也参考了别的资料
谢谢!!!