Go语言 Web框架Gin
返回各种值
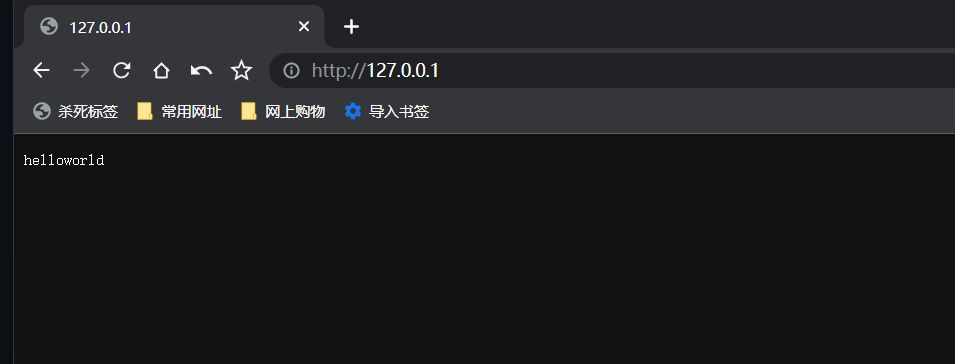
返回字符串
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "helloworld")
})
router.Run(":8080")
}
返回json
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
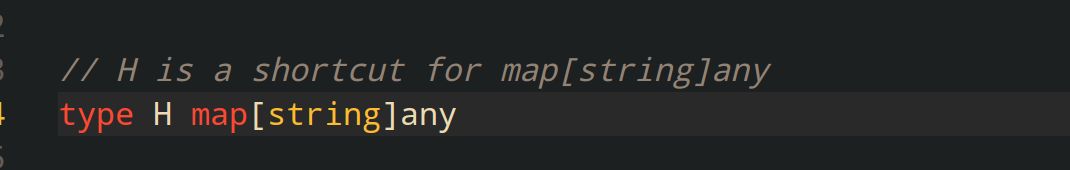
type Student struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Age int `json:"age"`
Number string `json: "number"`
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
var student Student = Student{
Name: "meowrain",
Age: 20,
Number: "10086",
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, student)
})
router.Run(":8080")
}
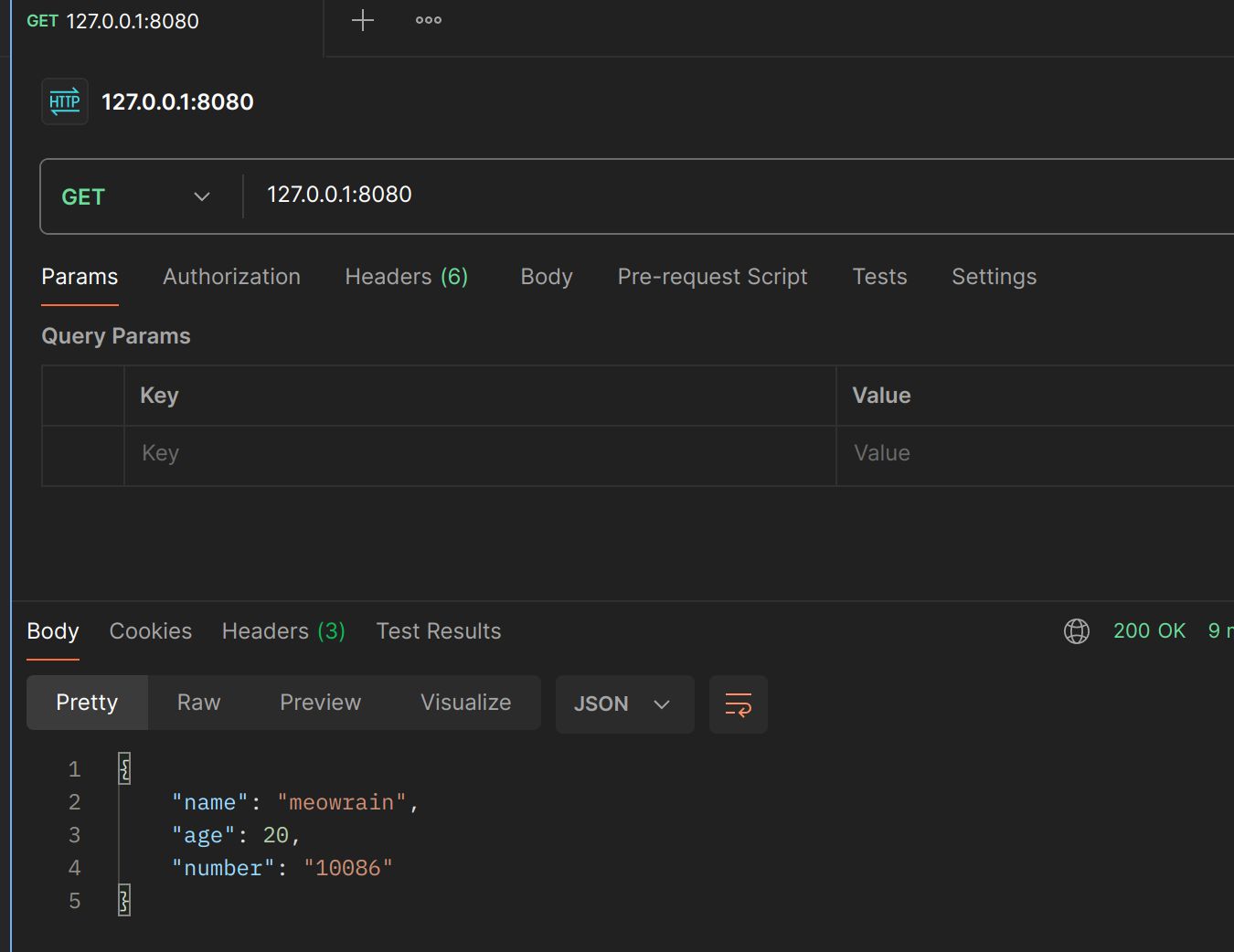
返回map
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
userMap := map[string]any{
"username": "meowrain",
"age": 20,
"number": 10086,
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, userMap)
})
router.Run(":8080")
}
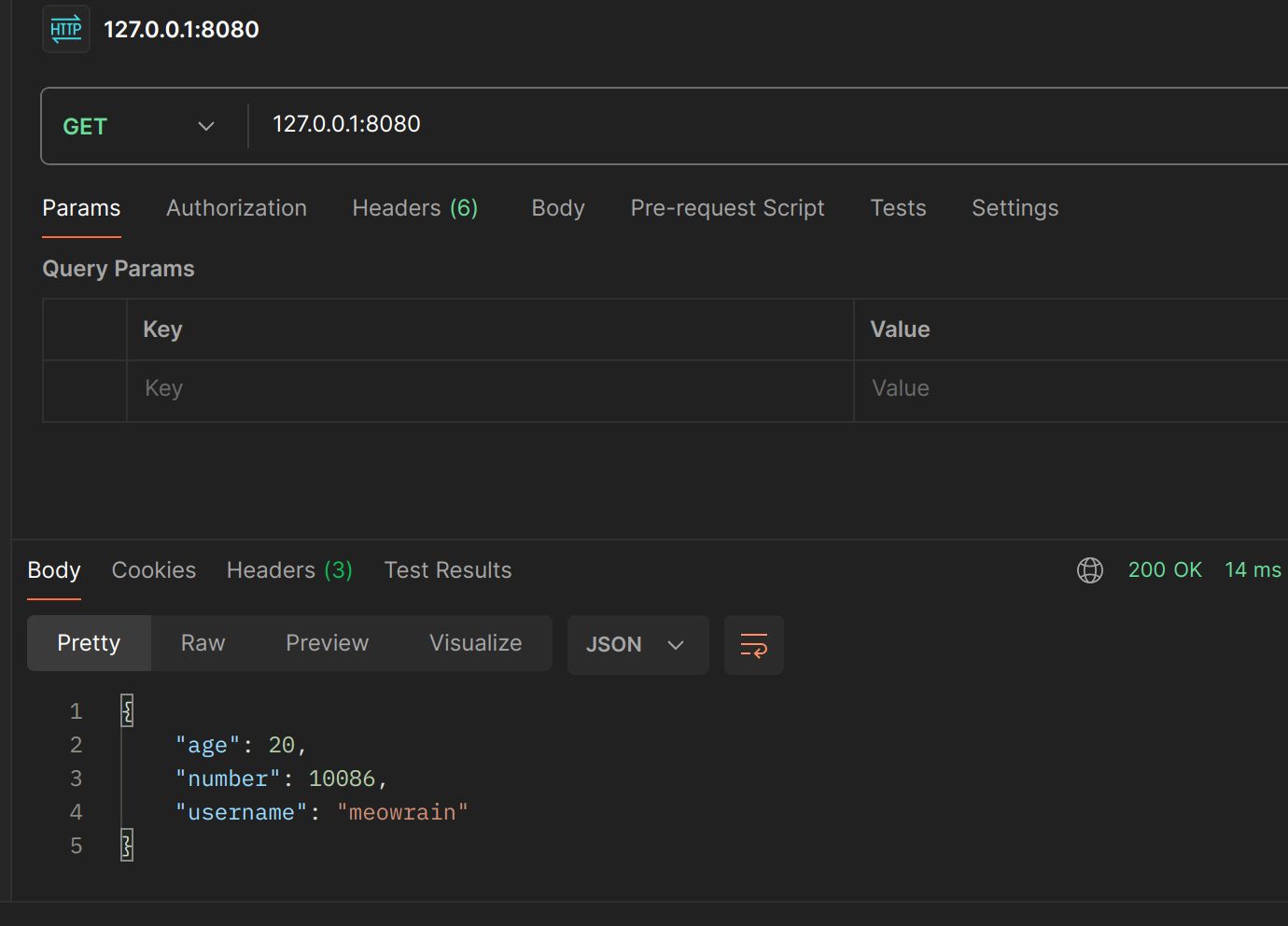
返回原始json
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"username": "meowrain",
"age": 20,
"number": 10086,
})
})
router.Run(":8080")
}
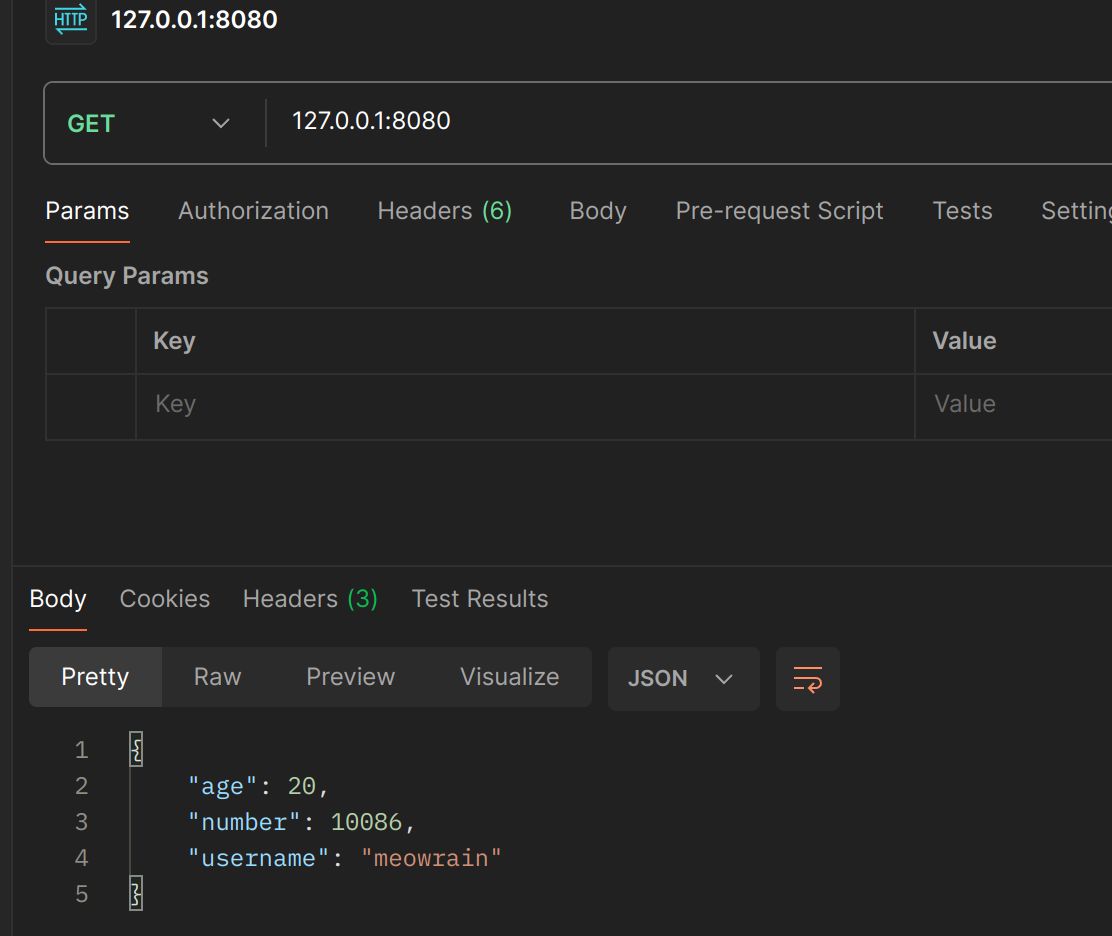
返回html并传递参数
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func _html(c *gin.Context) {
type UserInfo struct {
Username string `json:"username"`
Age int `json:"age"`
Password string `json:"-"`
}
user := UserInfo{
Username: "meowrain",
Age: 20,
Password: "12345678",
}
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{"obj": user})
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.LoadHTMLGlob("template/*")
router.GET("/", _html)
router.Run(":8080")
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>User Information</h1>
<p>Username: {{.obj.Username}}</p>
<p>Age: {{.obj.Age}}</p>
</body>
</html>
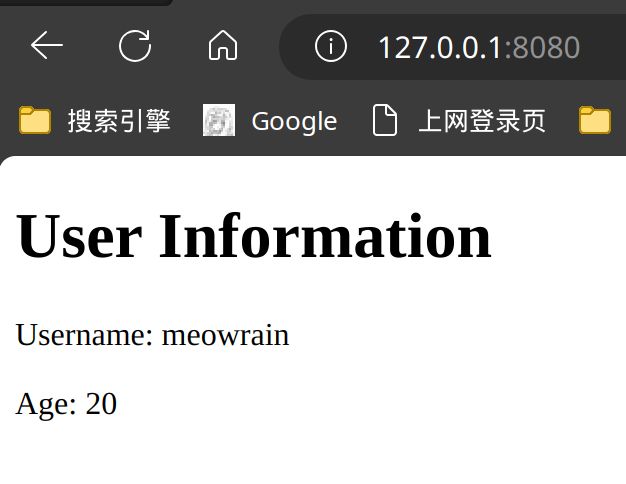
静态文件配置
router.Static和router.StaticFS都是用于处理静态文件的 Gin 框架路由处理方法,但它们有一些区别。
router.Static:- 使用
router.Static时,Gin 会简单地将请求的 URL 路径与提供的本地文件系统路径进行映射。通常,这适用于将 URL 路径直接映射到一个静态文件或目录。 -
示例:
router.Static("/static", "./static")将/static映射到当前工作目录下的./static文件夹。 -
router.StaticFS: router.StaticFS则允许你使用http.FileSystem对象,这可以提供更多的灵活性。你可以使用http.Dir创建http.FileSystem,并将其传递给router.StaticFS。- 这允许你更灵活地处理静态文件,例如从不同的源(内存、数据库等)加载静态文件,而不仅限于本地文件系统。
- 示例:
router.StaticFS("/static", http.Dir("/path/to/static/files"))使用本地文件系统路径创建一个http.FileSystem对象,然后将/static映射到这个文件系统。
总体而言,router.Static更简单,适用于基本的静态文件服务,而router.StaticFS提供了更多的灵活性,允许你自定义静态文件的加载方式。选择使用哪一个取决于你的具体需求。
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func _html(c *gin.Context) {
type UserInfo struct {
Username string `json:"username"`
Age int `json:"age"`
Password string `json:"-"`
}
user := UserInfo{
Username: "meowrain",
Age: 20,
Password: "12345678",
}
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{"obj": user})
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.LoadHTMLGlob("template/*")
router.Static("/static/", "./static")
router.GET("/", _html)
router.Run(":8080")
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>User Information</h1>
<p>Username: {{.obj.Username}}</p>
<p>Age: {{.obj.Age}}</p>
<img src="/static/c68a16221f5bdf5486749d0993052981178827471.jpg" />
</body>
</html>
重定向
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func _html(c *gin.Context) {
type UserInfo struct {
Username string `json:"username"`
Age int `json:"age"`
Password string `json:"-"`
}
user := UserInfo{
Username: "meowrain",
Age: 20,
Password: "12345678",
}
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{"obj": user})
}
func _redirect(c *gin.Context) {
c.Redirect(301, "https://www.baidu.com")
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.LoadHTMLGlob("template/*")
router.Static("/static/", "./static")
router.GET("/", _html)
router.GET("/baidu", _redirect)
router.Run(":8080")
}
301和302的区别
HTTP状态码中的301和302分别表示重定向(Redirect)。它们之间的主要区别在于重定向的性质和原因:
- 301 Moved Permanently(永久重定向):
- 当服务器返回状态码301时,它告诉客户端请求的资源已经被永久移动到新的位置。
- 客户端收到301响应后,应该更新书签、链接等,将这个新的位置作为将来所有对该资源的请求的目标。
-
搜索引擎在遇到301时,通常会更新索引,将原始URL替换为新的URL。
-
302 Found(临时重定向):
- 当服务器返回状态码302时,它表示请求的资源暂时被移动到了另一个位置。
- 客户端收到302响应后,可以在不更新书签和链接的情况下继续使用原始URL。
- 搜索引擎在遇到302时,通常会保留原始URL在索引中,并不会立即更新为新的URL。
总体来说,使用301通常是在确定资源永久移动的情况下,而302通常用于暂时性的重定向,即资源可能在将来回到原始位置。选择使用哪种状态码取决于你希望客户端和搜索引擎如何处理被重定向的资源。
路由
默认路由
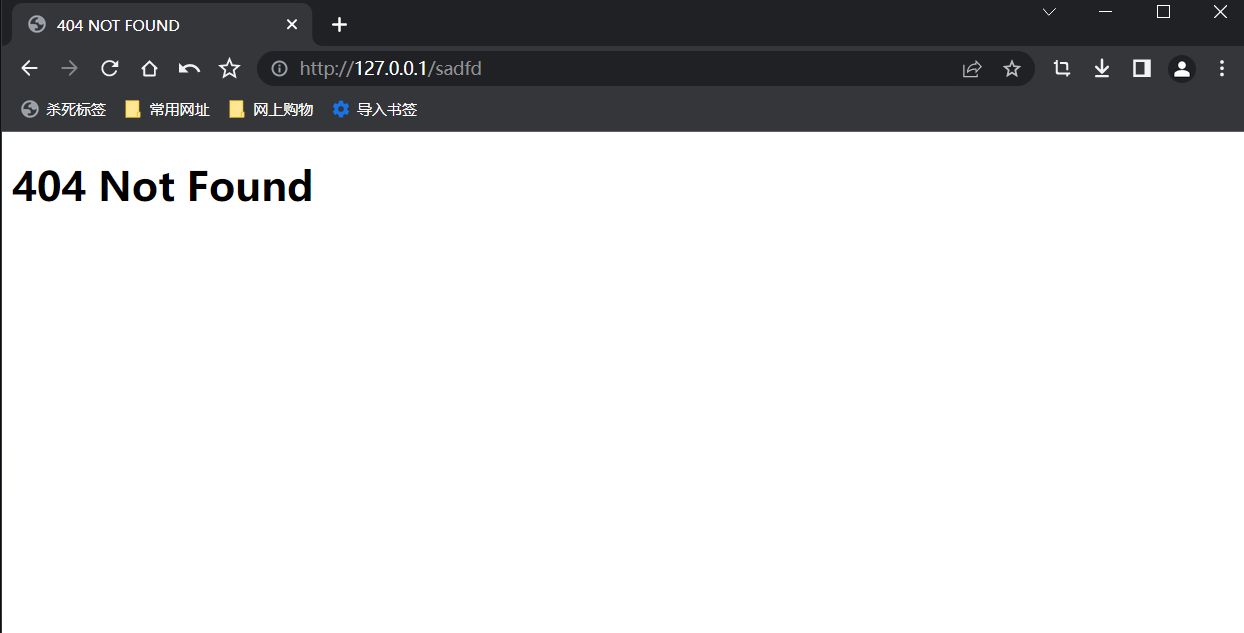
当访问路径不被匹配的时候返回默认路由内容
目录结构
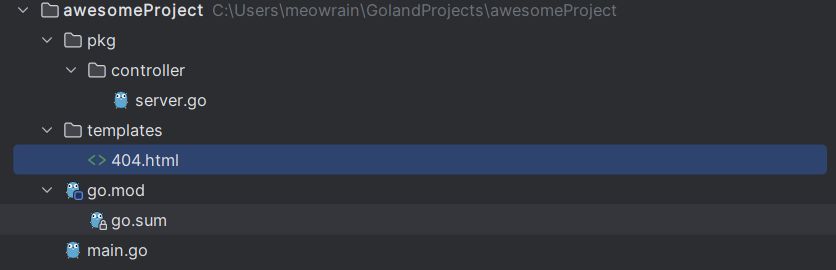
//main.go
package main
import (
"awesomeProject/pkg/controller"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.LoadHTMLGlob("templates/*")
router.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.String(200, "helloworld")
})
router.NoRoute(controller.Default_route)
router.Run(":80")
}
//server.go
package controller
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func Default_route(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusNotFound, "404.html", nil)
}
<!--404.html-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>404 NOT FOUND</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>404 Not Found</h1>
</body>
</html>
效果
路由组
参考:https://www.liwenzhou.com/posts/Go/gin/#c-0-7-2
我们可以将拥有共同URL前缀的路由划分为一个路由组。习惯性一对{}包裹同组的路由,这只是为了看着清晰,你用不用{}包裹功能上没什么区别。
//main.go
package main
import (
"awesomeProject/pkg/controller"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
userGroup := router.Group("/user")
{
userGroup.GET("/all", controller.GetUserList)
userGroup.GET("/detail", controller.GetUserDetail)
}
router.LoadHTMLGlob("templates/*")
router.NoRoute(controller.Default_route)
router.Run(":80")
}
//controller/userController.go
package controller
import (
. "awesomeProject/pkg/entity"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
"strconv"
)
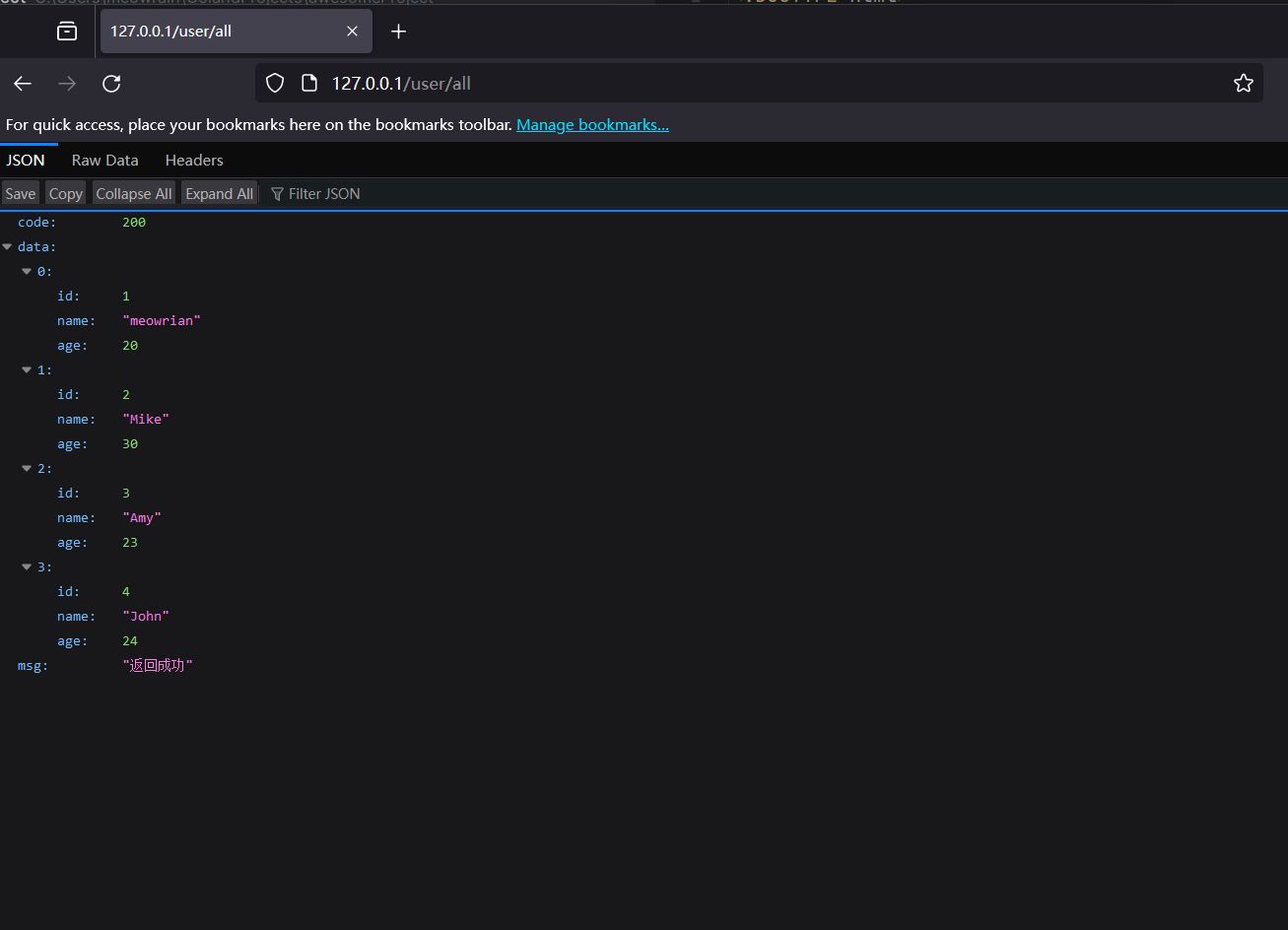
func GetUserList(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, Response{
Code: http.StatusOK,
Data: UserList,
Msg: "返回成功",
})
}
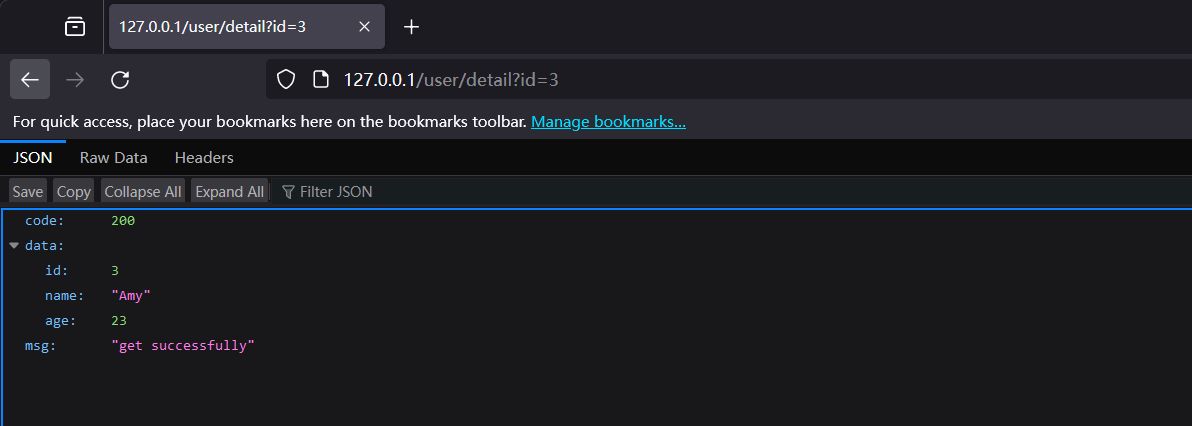
func GetUserDetail(c *gin.Context) {
id := c.Query("id")
for _, res := range UserList {
if strconv.Itoa(res.ID) == id {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, Response{
Code: http.StatusOK,
Data: res,
Msg: "get successfully",
})
}
}
}
//user.go
package entity
type User struct {
ID int `json:"id"`
Name string `json:"name"`
Age int `json:"age"`
}
type Response struct {
Code int `json:"code"`
Data any `json:"data"`
Msg string `json:"msg"`
}
var UserList []User = []User{
{
ID: 1,
Name: "meowrian",
Age: 20,
},
{
ID: 2,
Name: "Mike",
Age: 30,
},
{
ID: 3,
Name: "Amy",
Age: 23,
},
{
ID: 4,
Name: "John",
Age: 24,
},
}
//server.go
package controller
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http"
)
func Default_route(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusNotFound, "404.html", nil)
}
路由组也是支持嵌套的
参数
查询参数
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
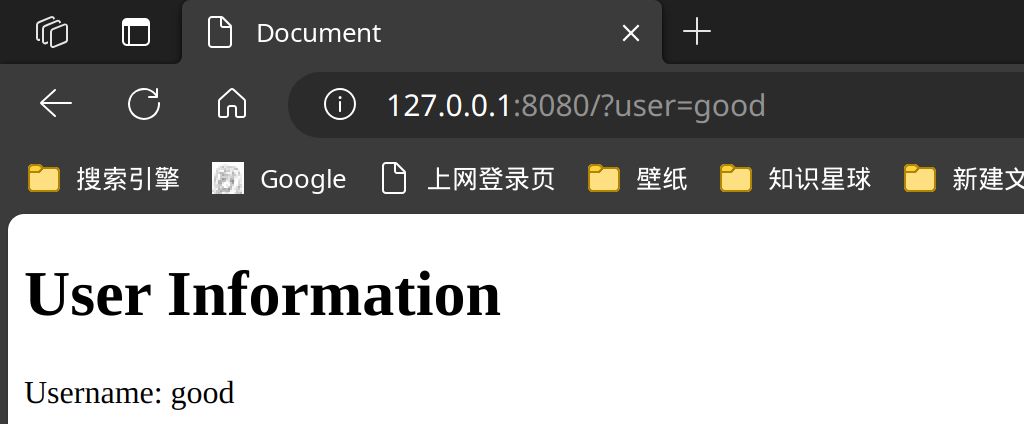
func _query(c *gin.Context) {
user := c.Query("user")
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"user": user,
})
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.LoadHTMLGlob("template/*")
router.Static("/static", "./static")
router.GET("/", _query)
router.Run(":8080")
}
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin")
func _query(c *gin.Context) {
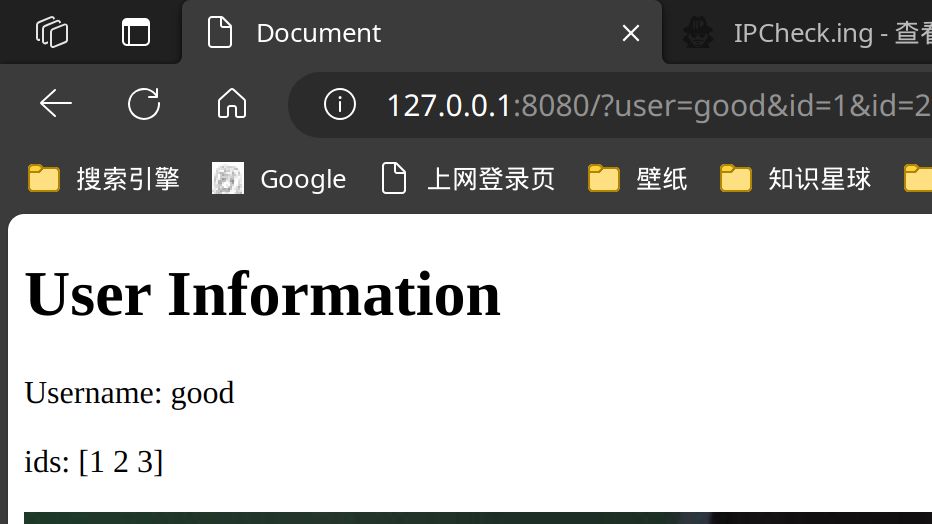
user, ok := c.GetQuery("user")
ids := c.QueryArray("id") //拿到多个相同的查询参数
maps := c.QueryMap("id")
fmt.Println(maps)
if ok {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"user": user,
"id": ids,
})
} else {
c.String(http.StatusOK, "No query!")
}
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.LoadHTMLGlob("template/*")
router.Static("static", "./static")
router.GET("/", _query)
router.Run(":8080")
}
请求为: http://127.0.0.1:8080/?user=good&id=1&id=2&id=3&id[good]=meowrain
动态参数
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "net/http")
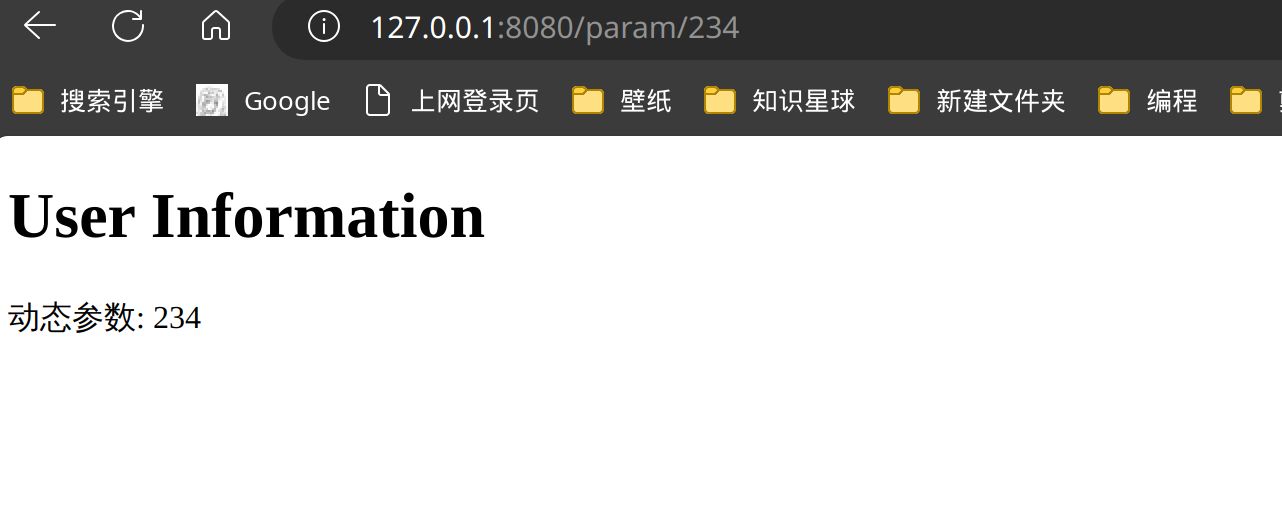
func _param(c *gin.Context) {
param := c.Param("user_id")
fmt.Println(param)
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"param": param,
})
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.LoadHTMLGlob("template/*")
router.Static("static", "./static")
router.GET("/param/:user_id", _param)
router.Run(":8080")
}
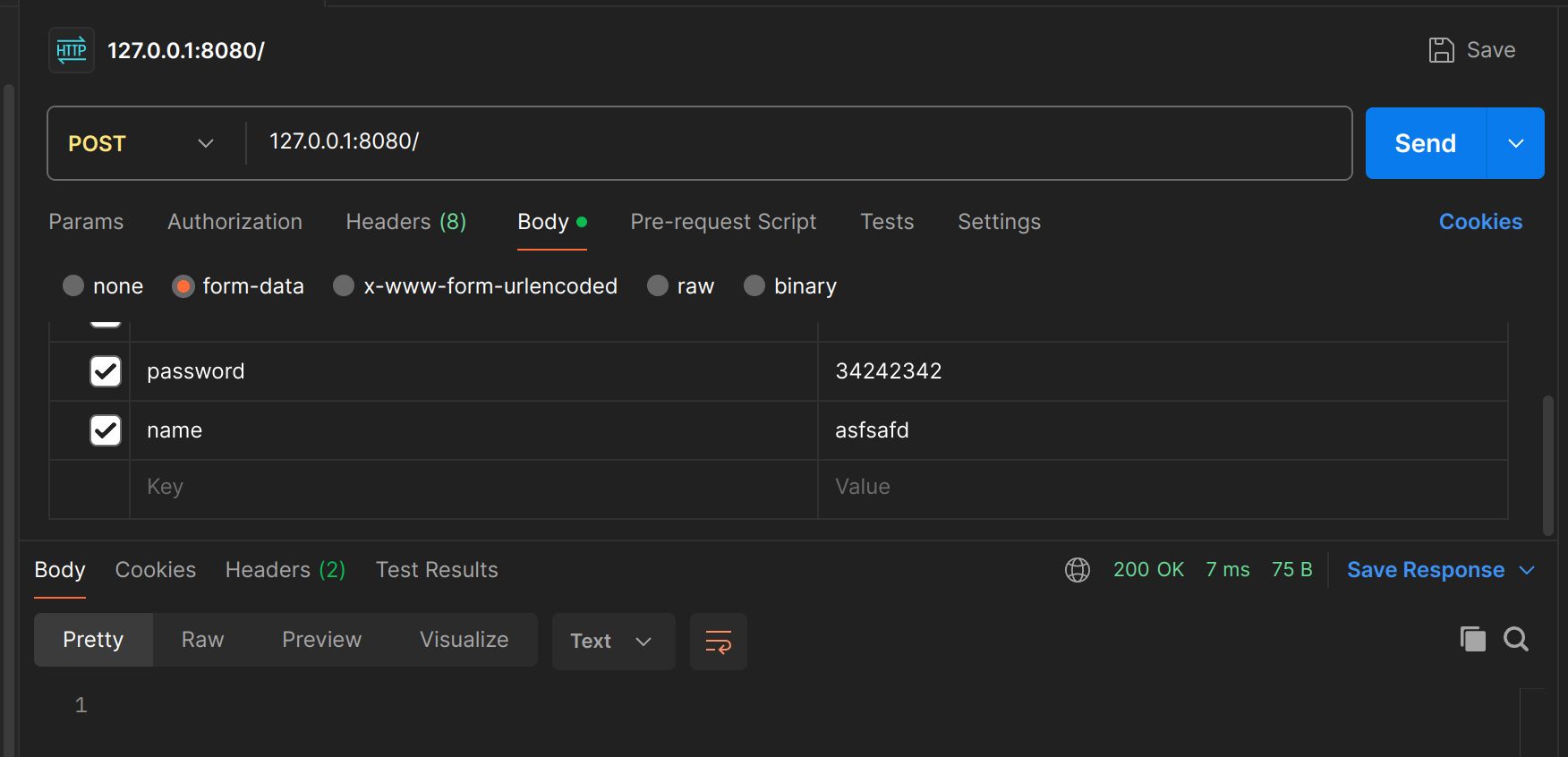
表单参数PostForm
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http")
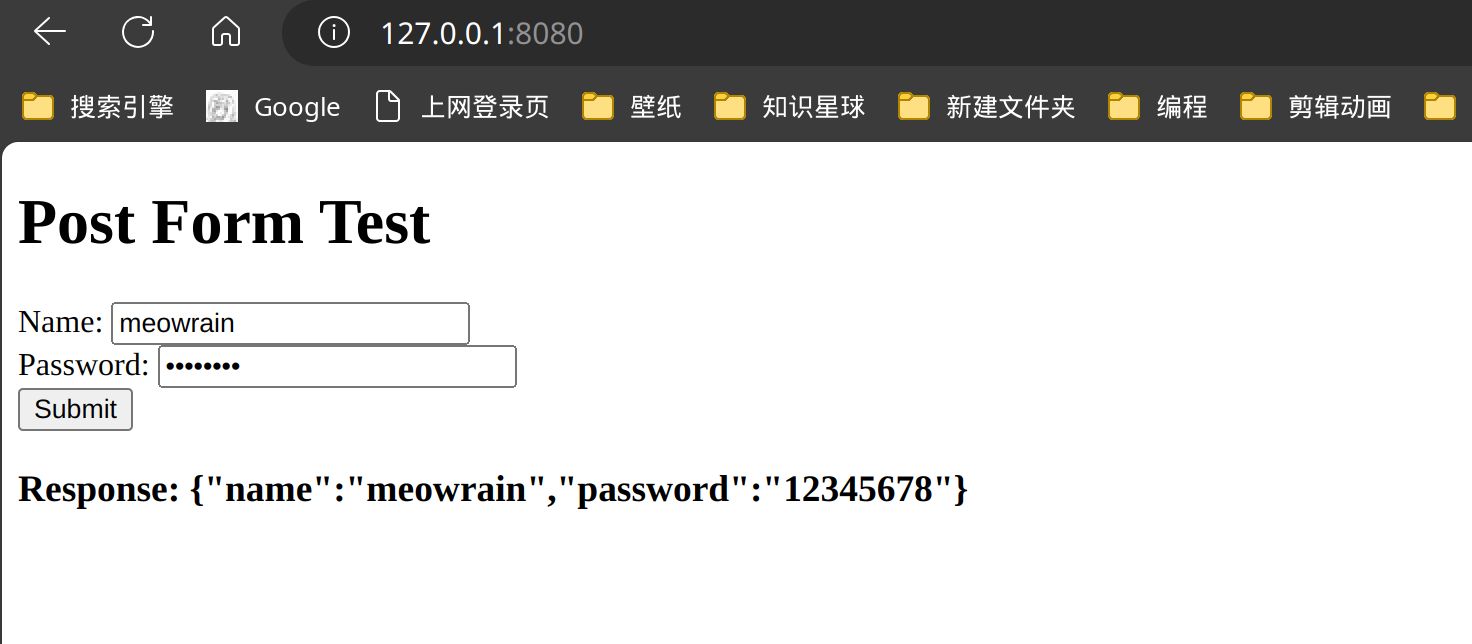
func postForm(c *gin.Context) {
name := c.PostForm("name")
password := c.PostForm("password")
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"name": name,
"password": password,
})
}
func index(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{})
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.LoadHTMLGlob("template/*")
router.Static("static", "./static")
router.GET("/", index)
router.POST("/post", postForm)
router.Run(":8080")
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Post Form Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Post Form Test</h1>
<form id="myForm" action="/post" method="post">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name" required>
<br> <label for="password">Password: </label>
<input type="password" id="password" name="password" required>
<br> <button type="button" onclick="postData()">Submit</button>
</form>
<h3 id="response">Response: </h3>
<script>
function postData() {
var form = document.getElementById("myForm");
var formData = new FormData(form);
var resp = document.getElementById("response");
fetch('http://127.0.0.1:8080/post', {
method: 'POST',
body: formData
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
console.log('Success:', data);
resp.innerText = "Response: " + JSON.stringify(data)
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error('Error:', error);
resp.innerText = "Response Error: " + JSON.stringify(error)
});
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
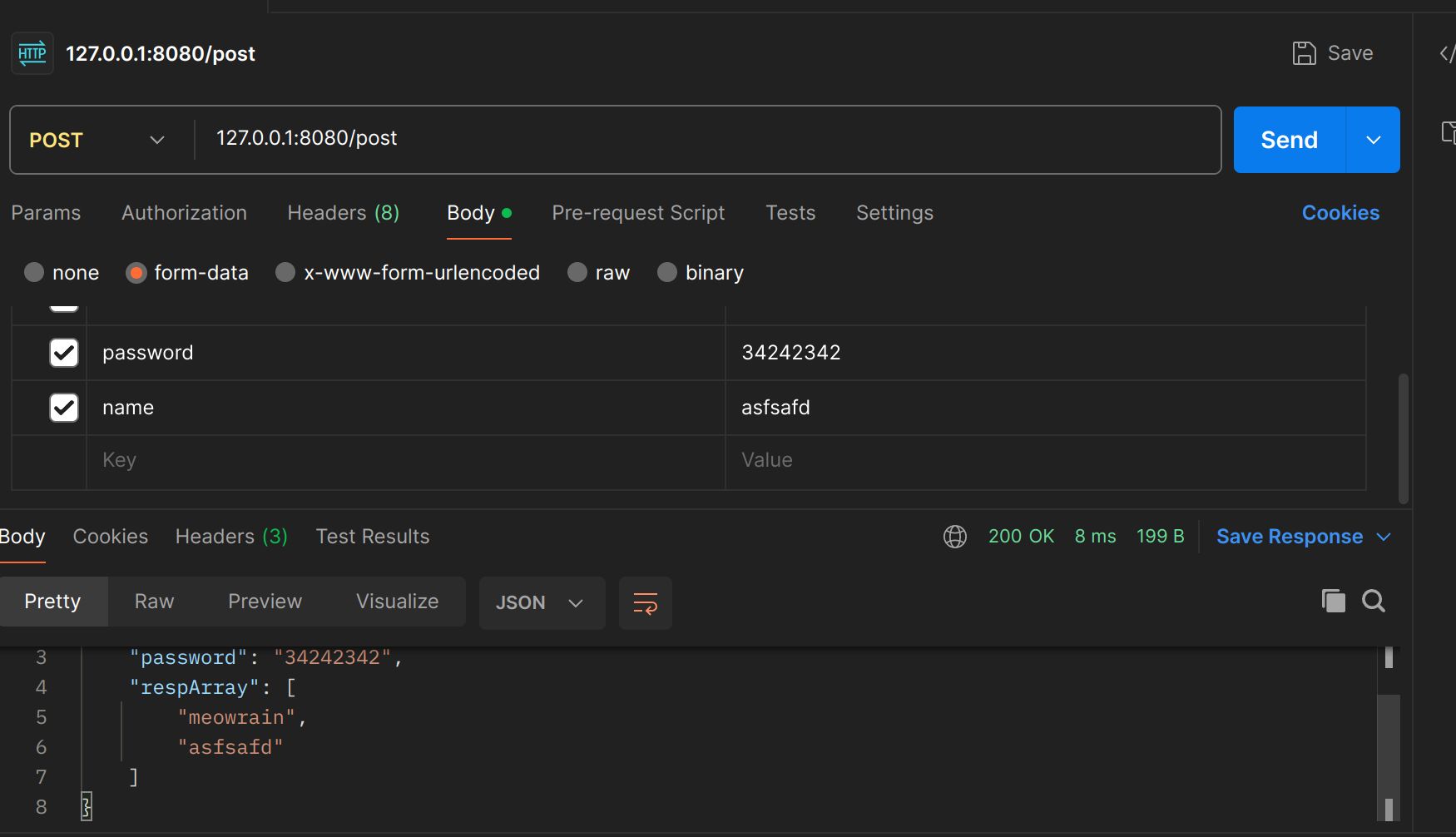
postFormArray函数
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http")
func postForm(c *gin.Context) {
name := c.PostForm("name")
password := c.PostForm("password")
respArr := c.PostFormArray("name")
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"name": name,
"password": password,
"respArray": respArr,
})
}
func index(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{})
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.LoadHTMLGlob("template/*")
router.Static("static", "./static")
router.GET("/", index)
router.POST("/post", postForm)
router.Run(":8080")
}
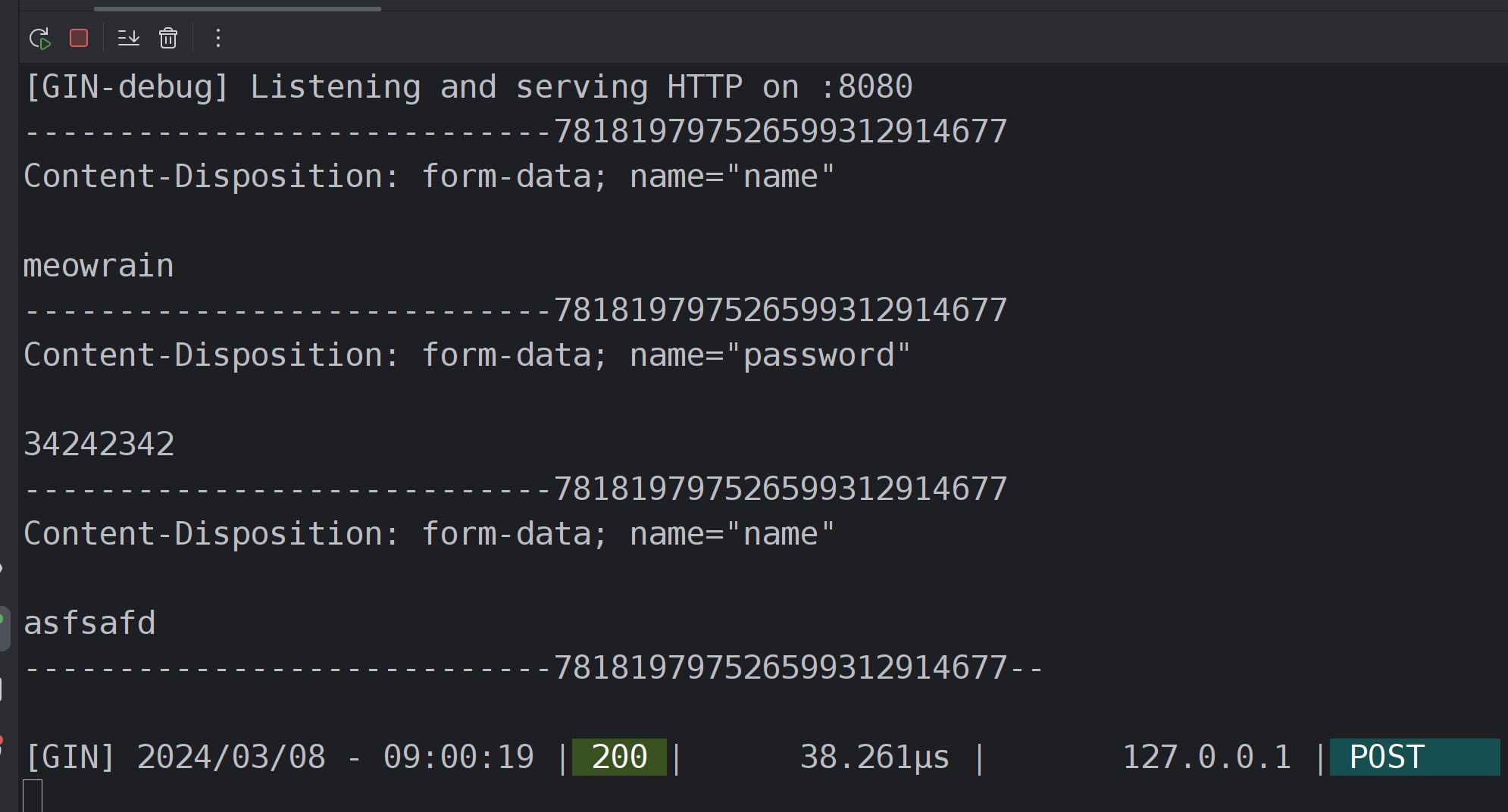
原始参数
/*
原始参数
*/
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin")
func _raw(c *gin.Context) {
buf, err := c.GetRawData()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("error:", err)
return
}
fmt.Println(string(buf))
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.POST("/", _raw)
router.Run(":8080")
}
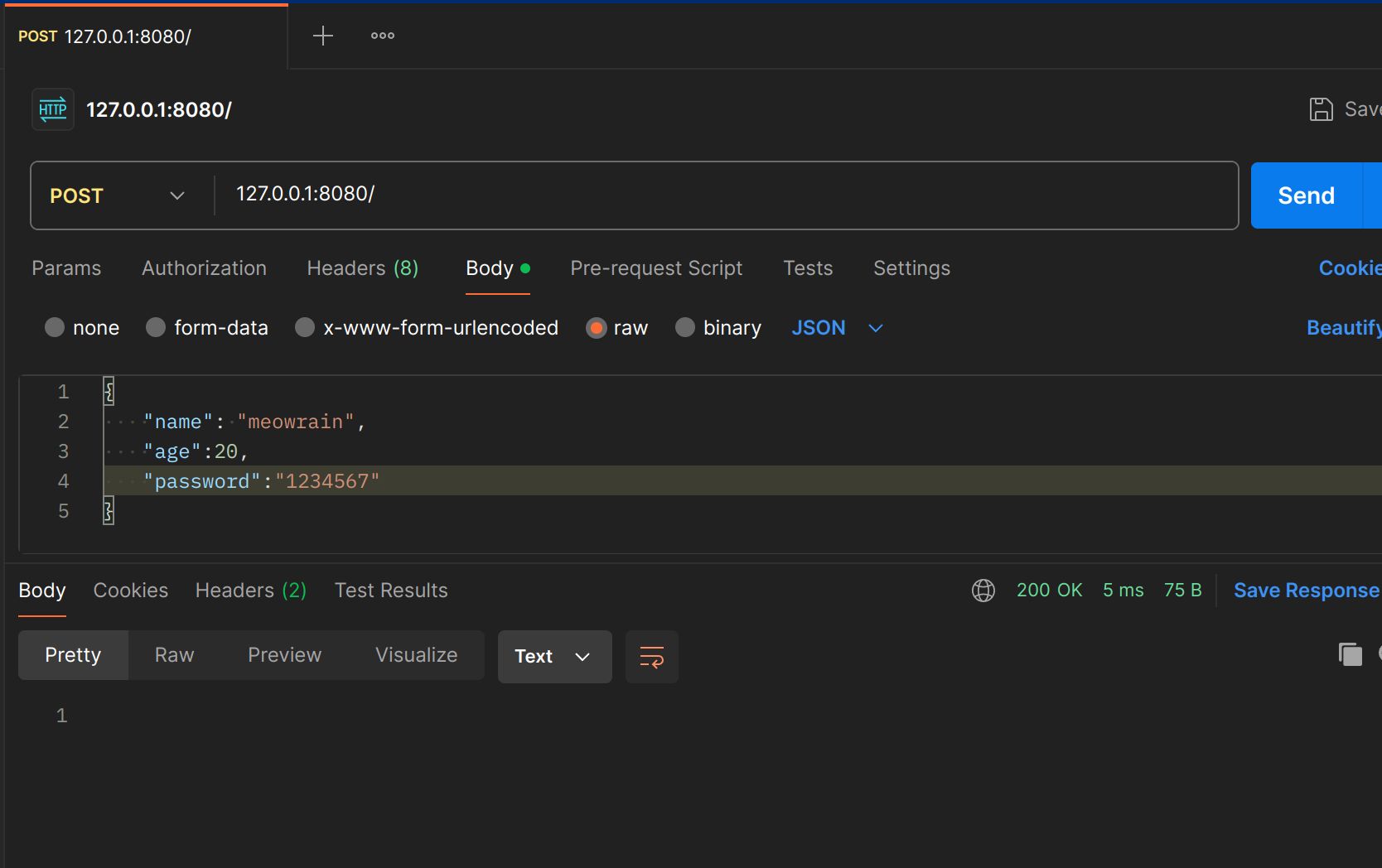
解析json数据
/*
原始参数
*/
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt" "github.com/gin-gonic/gin")
func bindJSON(c *gin.Context, obj any) error {
body, err := c.GetRawData()
contentType := c.GetHeader("Content-Type")
fmt.Println("ContentType:", contentType)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("error:", err)
return err
}
switch contentType {
case "application/json":
err := json.Unmarshal(body, obj)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err.Error())
return err
}
}
return nil
}
func raw(c *gin.Context) {
type User struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Age int `json:"age"`
Password string `json:"-"`
}
var user User
err := bindJSON(c, &user)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error binding JSON:", err)
return
}
fmt.Println(user)
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.POST("/", raw)
router.Run(":8080")
}
四大请求方式

简单实现以下CRUD
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http" "strconv")
type Article struct {
Id int `json:"id"`
Title string `json:"title"`
Content string `json:"content"`
Author string `json:"author"`
}
type Response struct {
Code int `json:"code"`
Data any `json:"data"`
Msg string `json:"msg"`
}
var articleList []Article = []Article{
{
1,
"Go语言从入门到精通",
"Learn better",
"Mike Jason",
},
{
2,
"Java从入门到精通",
"Java is good",
"Jack Smith",
},
{
3,
"Javascript从入门到精通",
"Javascript is a nice programming language!",
"Amy Gorden",
},
{
4,
"Python从入门到精通",
"Python is a simple language!",
"Jack Buffer",
},
}
/*简单增删改查*/
func _getList(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, Response{Code: 200, Data: articleList, Msg: "获取成功"})
}
func _getDetail(c *gin.Context) {
id := c.Param("id")
flag := false
for _, res := range articleList {
if strconv.Itoa(res.Id) == id {
flag = true
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, Response{
Code: 200,
Data: res,
Msg: "获取成功!",
})
}
}
if flag == false {
c.JSON(404, Response{
Code: 404,
Data: "Not Found the data",
Msg: "获取失败,因为数据不存在",
})
}
}
func _create(c *gin.Context) {
id, _ := strconv.ParseInt(c.PostForm("id"), 10, 0)
title := c.PostForm("title")
content := c.PostForm("content")
author := c.PostForm("author")
var article Article = Article{
Id: int(id),
Title: title,
Content: content,
Author: author,
}
articleList = append(articleList, article)
c.JSON(200, Response{Code: 200, Data: article, Msg: "添加成功!"})
}
func _delete(c *gin.Context) {
id := c.Param("id")
index := -1
for i, res := range articleList {
if strconv.Itoa(res.Id) == id {
index = i
break
}
}
if index != -1 {
articleList = append(articleList[:index], articleList[index+1:]...)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, Response{Code: 200, Data: nil, Msg: "删除成功"})
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusNotFound, Response{Code: 404, Data: "Not Found the data", Msg: "删除失败,数据不存在"})
}
}
func _update(c *gin.Context) {
id, _ := strconv.Atoi(c.Param("id"))
title := c.PostForm("title")
content := c.PostForm("content")
author := c.PostForm("author")
found := false
for i, res := range articleList {
if res.Id == id {
found = true
articleList[i] = Article{
id,
title,
content,
author,
}
break
}
}
if found {
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, Response{
Code: 200,
Data: nil,
Msg: "更新成功",
})
return
} else {
c.JSON(http.StatusNotFound, Response{
Code: 404,
Data: "Not found the data",
Msg: "更新失败,因为数据不存在",
})
}
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.GET("/articles", _getList)
router.GET("/articles/:id", _getDetail)
router.POST("/articles", _create)
router.PUT("/articles/:id", _update)
router.DELETE("/articles/:id", _delete)
router.Run(":8080")
}
文件上传
上传单个文件
package main
import (
"awesomeProject/pkg/controller"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.LoadHTMLGlob("templates/*")
router.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(200, "upload.html", nil)
})
router.POST("/upload",controller.Upload_file)
router.NoRoute(controller.Default_route)
router.Run(":80")
}
package controller
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func Default_route(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusNotFound, "404.html", nil)
}
//文件上传
func Upload_file(c *gin.Context) {
file, err := c.FormFile("f1")
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{
"message": err.Error(),
})
return
}
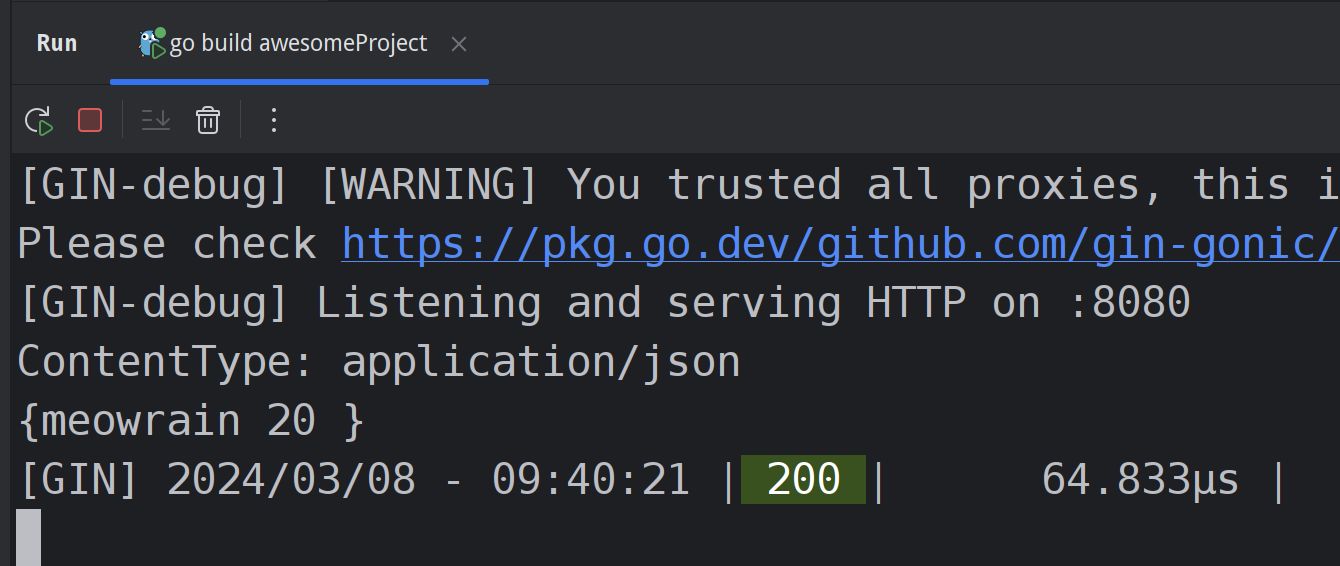
log.Println(file.Filename)
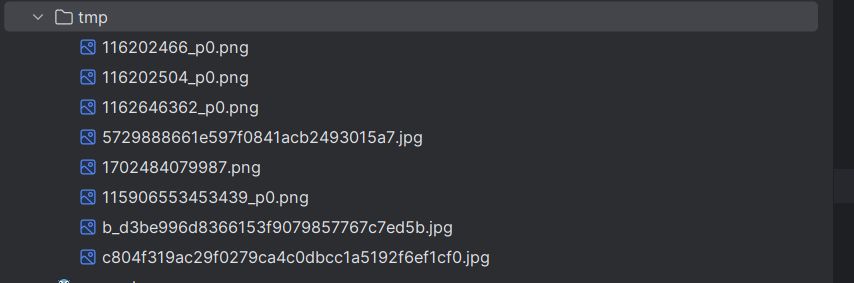
dst := fmt.Sprintf("./tmp/%s", file.Filename)
c.SaveUploadedFile(file, dst)
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": fmt.Sprintf("'%s' uploaded", file.Filename),
})
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<title>上传文件示例</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f2f2f2;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100vh;
margin: 0;
}
form {
background-color: #fff;
padding: 30px;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
text-align: center;
}
input[type="file"] {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
input[type="submit"] {
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: white;
padding: 10px 20px;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
}
input[type="submit"]:hover {
background-color: #45a049;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form id="uploadForm">
<input type="file" id="fileInput" name="f1">
<input type="button" value="上传" onclick="uploadFile()">
</form>
<script>
function uploadFile() {
let fileInput = document.getElementById('fileInput');
let file = fileInput.files[0];
if (file) {
let formData = new FormData();
formData.append('f1', file);
fetch('/upload', {
method: 'POST',
body: formData
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(result => {
console.log(result);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error:', error);
});
} else {
console.error('No file selected.');
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
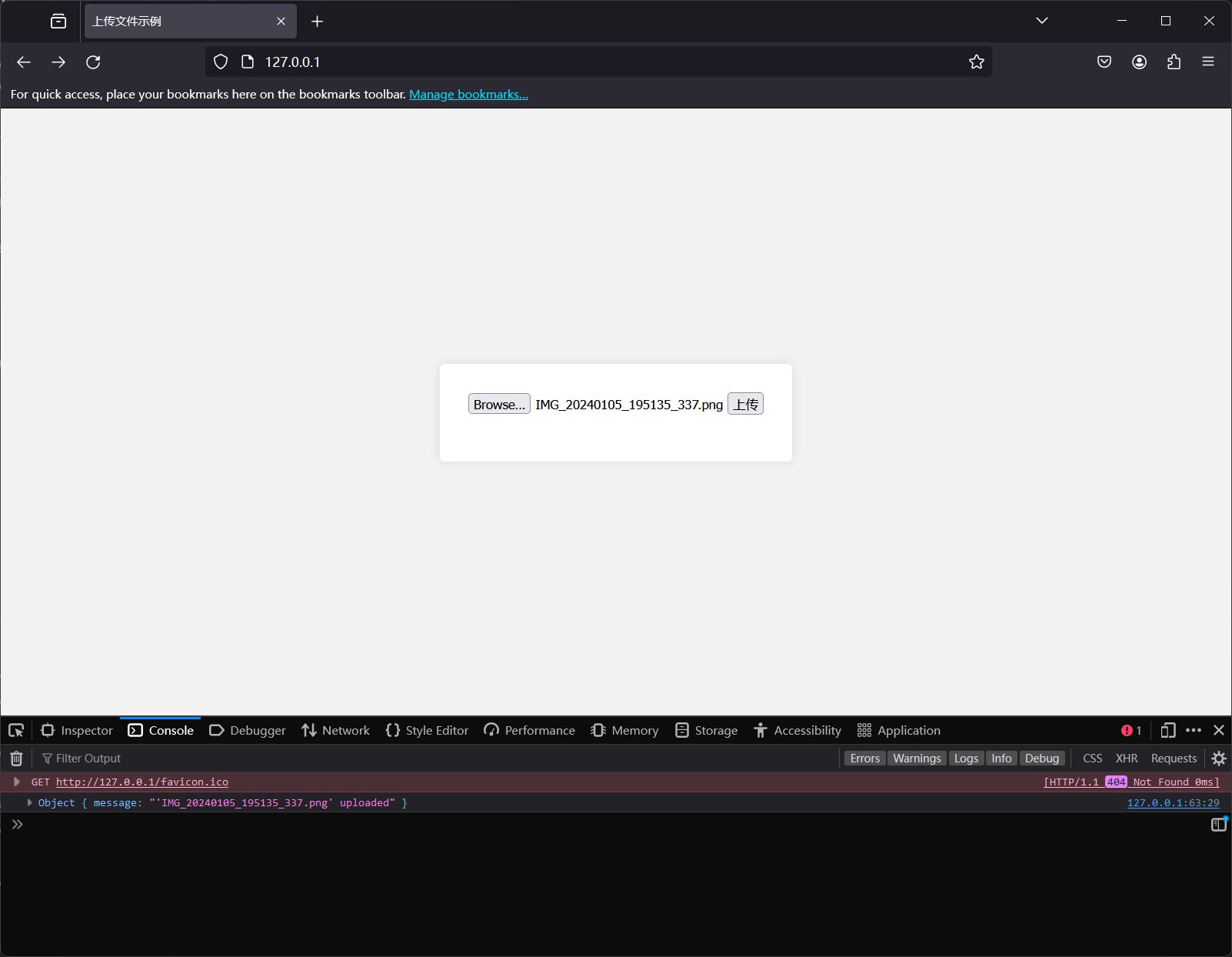

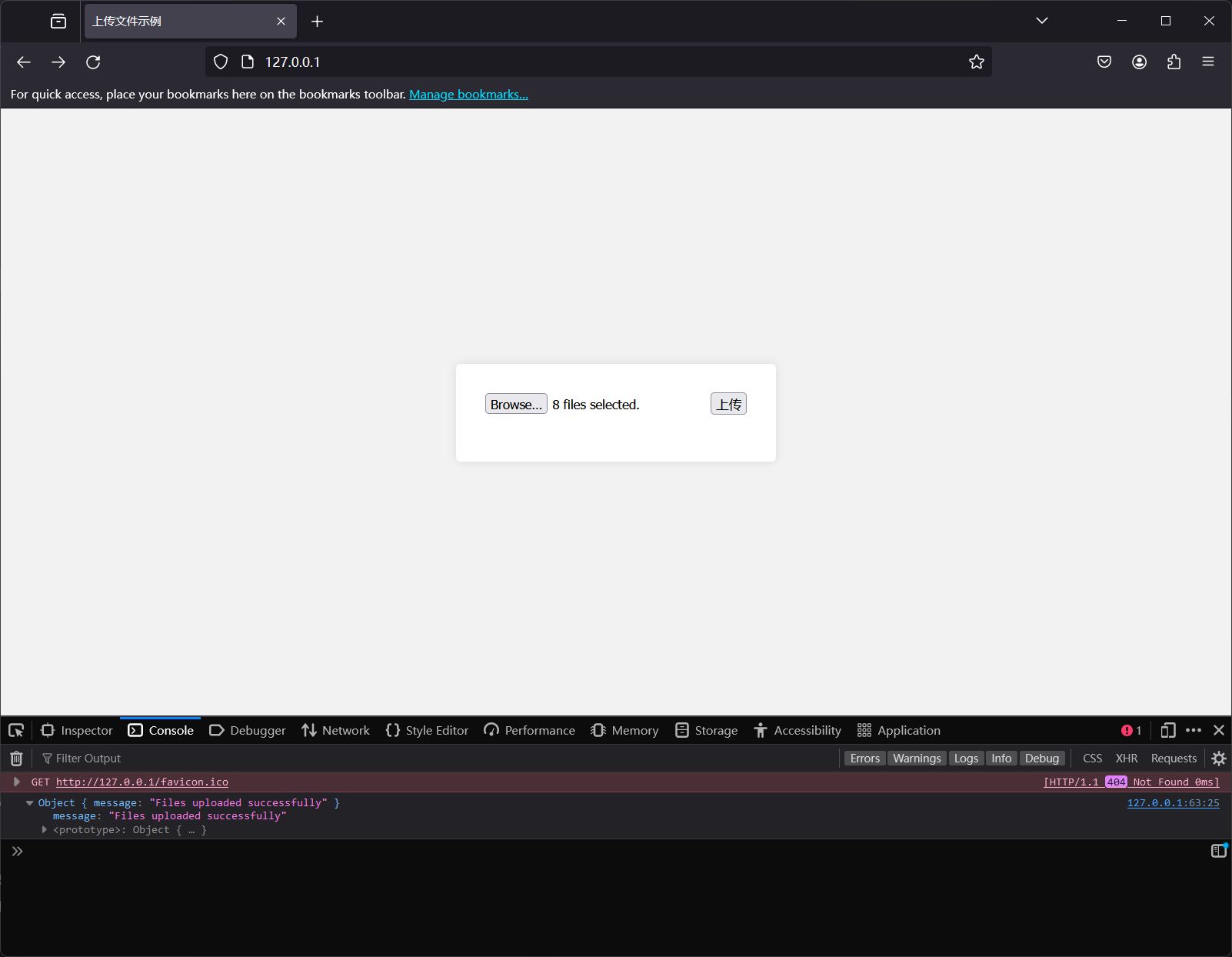
上传多个文件
package main
import (
"awesomeProject/pkg/controller"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.LoadHTMLGlob("templates/*")
router.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(200, "upload.html", nil)
})
router.POST("/upload", controller.UploadFiles)
router.NoRoute(controller.Default_route)
router.Run(":80")
}
package controller
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func Default_route(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusNotFound, "404.html", nil)
}
func UploadFiles(c *gin.Context) {
err := c.Request.ParseMultipartForm(100 << 20) // 100 MB limit
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{
"message": err.Error(),
})
return
}
form := c.Request.MultipartForm
if form == nil || form.File == nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadRequest, gin.H{
"message": "No files provided in the request",
})
return
}
files := form.File["f1"]
for _, file := range files {
dst := fmt.Sprintf("./tmp/%s", file.Filename)
if err := c.SaveUploadedFile(file, dst); err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusInternalServerError, gin.H{
"message": fmt.Sprintf("Failed to save file %s: %s", file.Filename, err.Error()),
})
return
}
log.Println(file.Filename)
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, gin.H{
"message": "Files uploaded successfully",
})
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<title>上传文件示例</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
background-color: #f2f2f2;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
height: 100vh;
margin: 0;
}
form {
background-color: #fff;
padding: 30px;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
text-align: center;
}
input[type="file"] {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
input[type="submit"] {
background-color: #4CAF50;
color: white;
padding: 10px 20px;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
}
input[type="submit"]:hover {
background-color: #45a049;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form id="uploadForm">
<input type="file" id="fileInput" name="f1" multiple>
<input type="button" value="上传" onclick="uploadFile()">
</form>
<script>
function uploadFile() {
let fileInput = document.getElementById('fileInput');
let formData = new FormData();
for (const file of fileInput.files) {
formData.append('f1', file);
}
fetch('/upload', {
method: 'POST',
body: formData
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(result => {
console.log(result);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error:', error);
});
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
判断上传文件的类型
在Gin框架中,可以使用binding模块提供的FormFile函数来获取上传的文件,然后检查文件的MIME类型。具体步骤如下:
- 在处理函数中使用
c.FormFile获取上传的文件:
file, err := c.FormFile("file")
if err != nil {
c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "获取文件失败")
return
}
- 打开文件并读取文件头部的几个字节,以识别文件的MIME类型:
f, err := file.Open()
if err != nil {
c.String(http.StatusInternalServerError, "打开文件失败")
return
}
defer f.Close()
buffer := make([]byte, 512)
_, err = f.Read(buffer)
if err != nil {
c.String(http.StatusInternalServerError, "读取文件失败")
return
}
- 使用
http.DetectContentType函数检测文件的MIME类型:
contentType := http.DetectContentType(buffer)
- 判断文件类型是否允许:
allowedTypes := []string{"image/jpeg", "image/png", "application/pdf"}
allowed := false
for _, t := range allowedTypes {
if t == contentType {
allowed = true
break
}
}
if !allowed {
c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "不支持的文件类型")
return
}
完整的示例代码如下:
func uploadFile(c *gin.Context) {
file, err := c.FormFile("file")
if err != nil {
c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "获取文件失败")
return
}
f, err := file.Open()
if err != nil {
c.String(http.StatusInternalServerError, "打开文件失败")
return
}
defer f.Close()
buffer := make([]byte, 512)
_, err = f.Read(buffer)
if err != nil {
c.String(http.StatusInternalServerError, "读取文件失败")
return
}
contentType := http.DetectContentType(buffer)
allowedTypes := []string{"image/jpeg", "image/png", "application/pdf"}
allowed := false
for _, t := range allowedTypes {
if t == contentType {
allowed = true
break
}
}
if !allowed {
c.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "不支持的文件类型")
return
}
// 处理文件...
}
在上面的示例中,我们定义了一个允许的MIME类型列表allowedTypes,包括image/jpeg、image/png和application/pdf。如果上传的文件类型不在允许列表中,就会返回错误响应。你可以根据需求修改允许的文件类型列表。
请求头相关
获取所有请求头
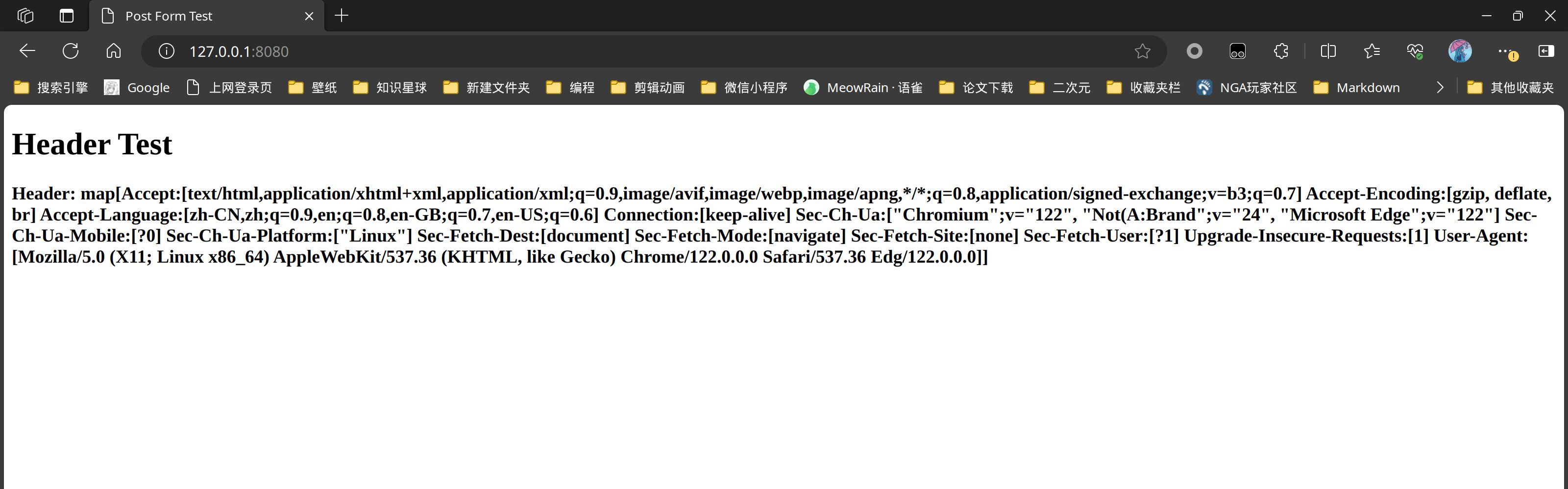
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "net/http")
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.LoadHTMLGlob("template/*")
router.Static("static", "./static")
router.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.HTML(http.StatusOK, "index.html", gin.H{
"header": c.Request.Header,
})
fmt.Println(c.Request.Header)
})
router.Run(":8080")
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Post Form Test</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Header Test</h1>
<h3>Header: {{.header}}</h3>
</body>
</html>
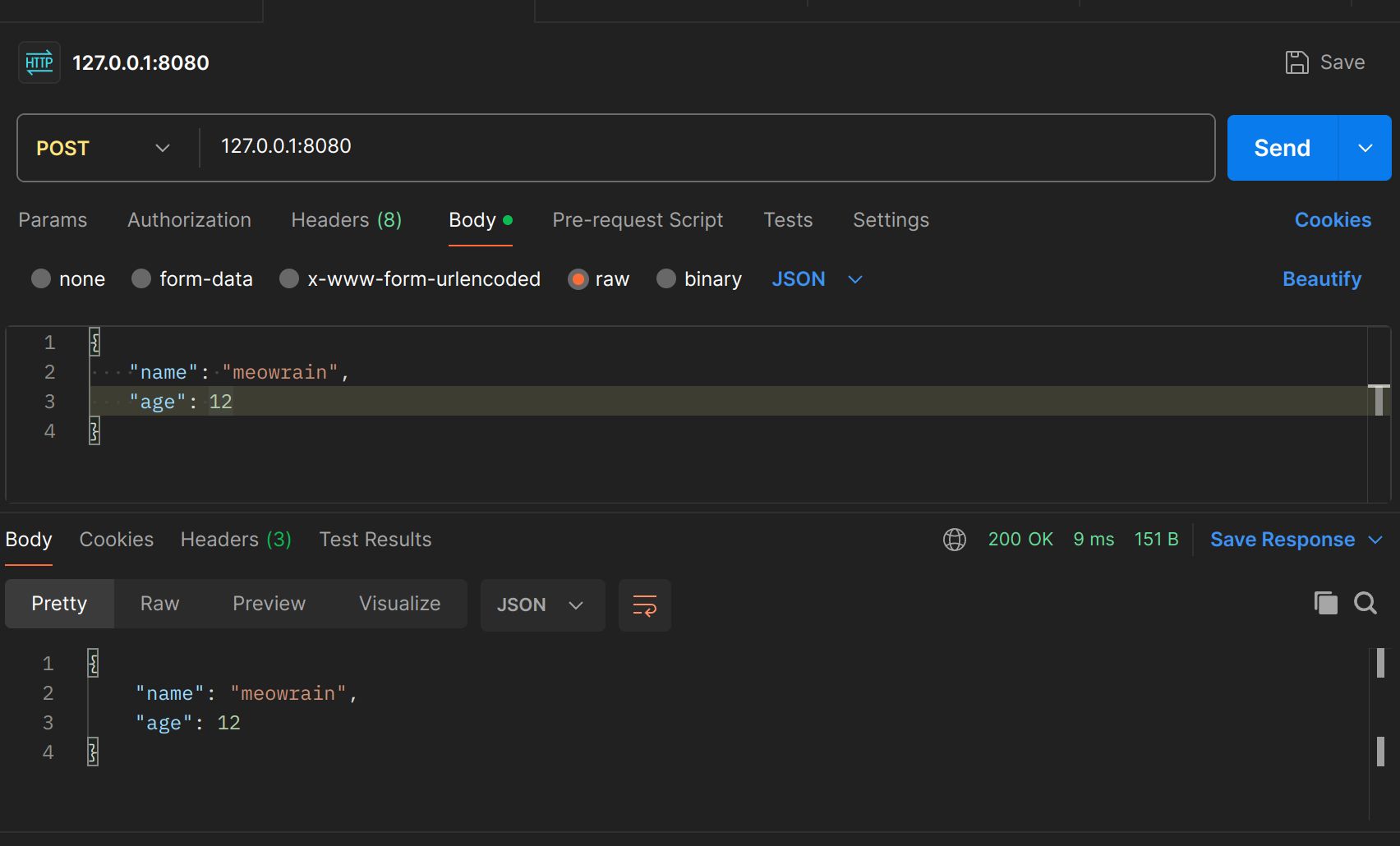
绑定参数bind
绑定post发送的json数据转换为Student结构体的成员变量值,然后再把这个结构体转换为json对象
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "net/http")
type Student struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Age int `json:"age"`
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.POST("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
var stu Student
err := c.BindJSON(&stu)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("error: ", err)
c.JSON(http.StatusBadGateway, err)
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, stu)
})
router.Run(":8080")
}
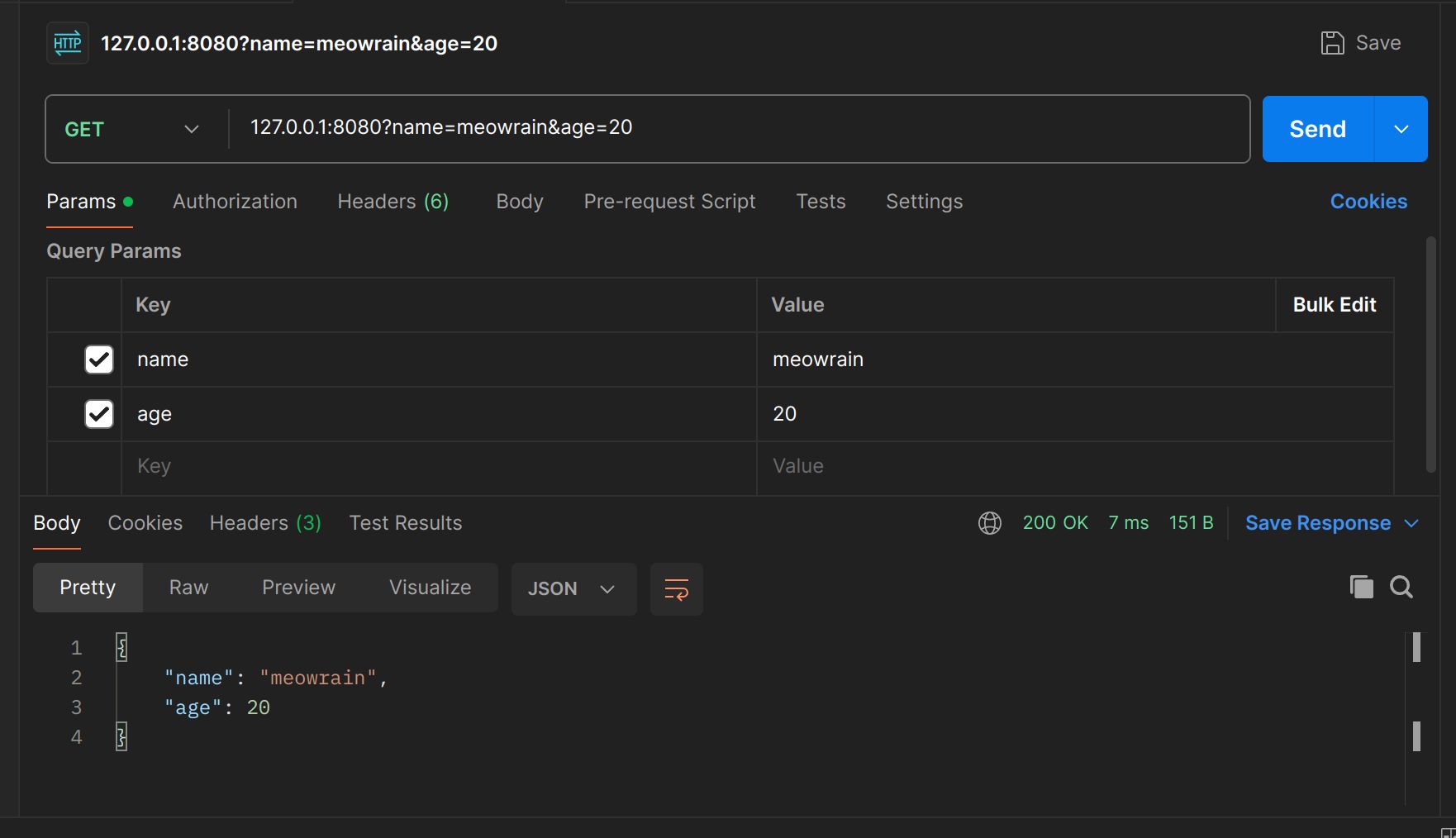
绑定查询参数
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "net/http")
type Student struct {
Name string `json:"name" form:"name"`
Age int `json:"age" form:"age"`
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.GET("/", func(c *gin.Context) {
var stu Student
err := c.BindQuery(&stu)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("error: ", err)
c.JSON(http.StatusBadGateway, err)
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, stu)
})
router.Run(":8080")
}
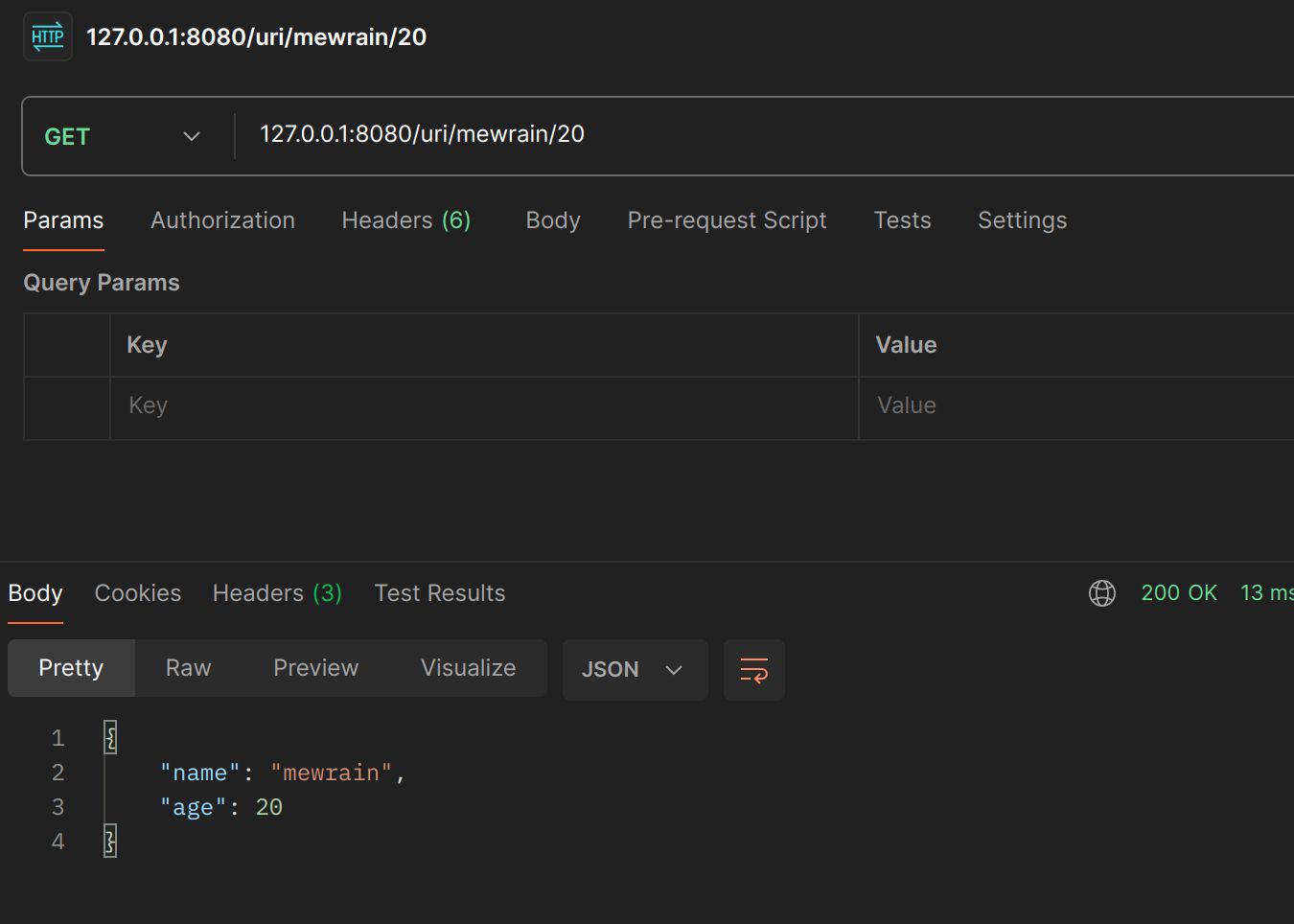
bind URI
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin" "net/http")
type Student struct {
Name string `json:"name" form:"name" uri:"name"`
Age int `json:"age" form:"age" uri:"age"`
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.GET("/uri/:name/:age", func(c *gin.Context) {
var stu Student
err := c.ShouldBindUri(&stu)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("error: ", err)
c.JSON(http.StatusBadGateway, err)
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, stu)
})
router.Run(":8080")
}
常用验证器
// 不能为空,并且不能没有这个字段
required: 必填字段,如:binding:"required"
// 针对字符串的长度
min 最小长度,如:binding:"min=5"
max 最大长度,如:binding:"max=10"
len 长度,如:binding:"len=6"
// 针对数字的大小
eq 等于,如:binding:"eq=3"
ne 不等于,如:binding:"ne=12"
gt 大于,如:binding:"gt=10"
gte 大于等于,如:binding:"gte=10"
lt 小于,如:binding:"lt=10"
lte 小于等于,如:binding:"lte=10"
// 针对同级字段的
eqfield 等于其他字段的值,如:PassWord string `binding:"eqfield=Password"`
nefield 不等于其他字段的值
- 忽略字段,如:binding:"-"
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"net/http")
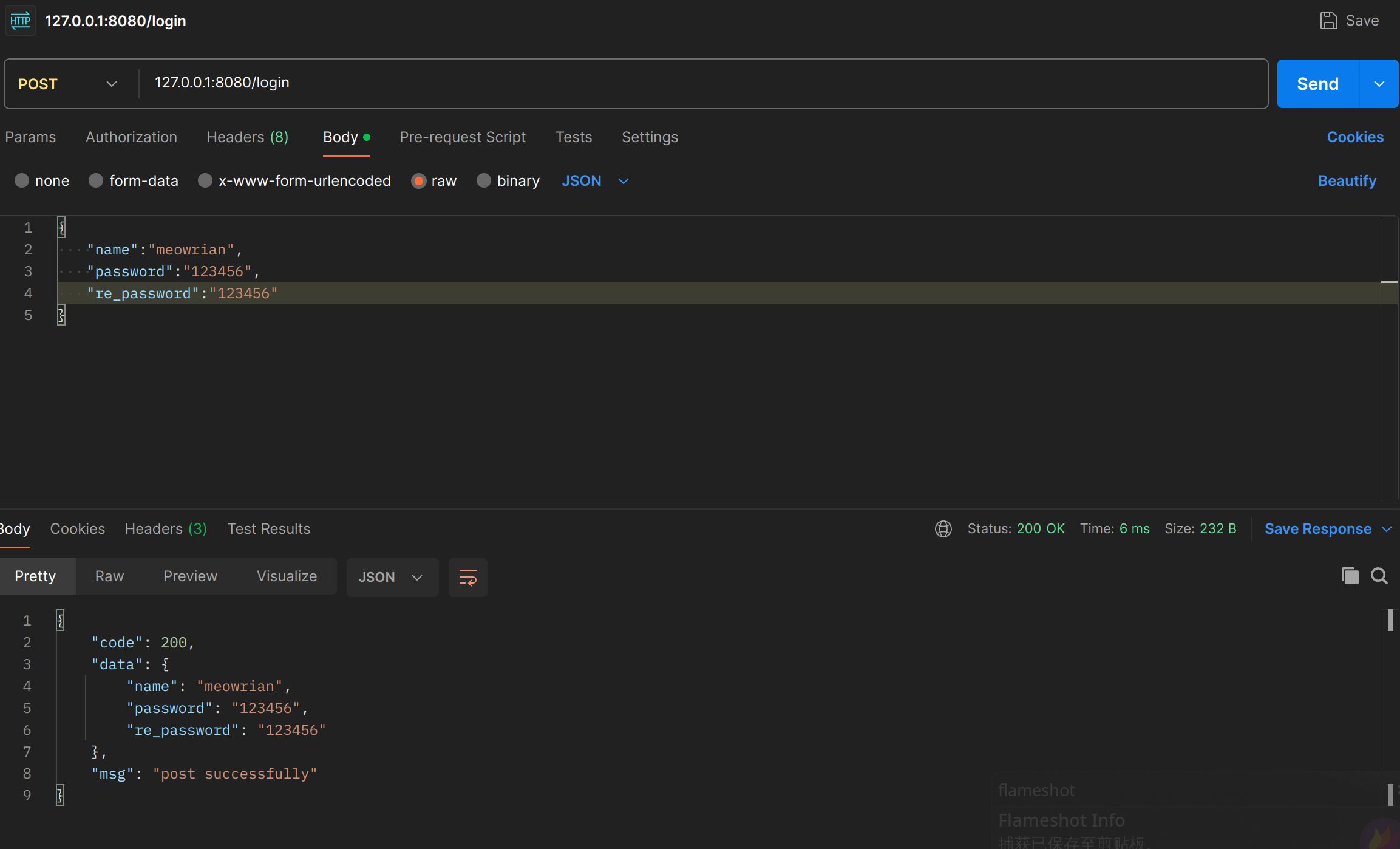
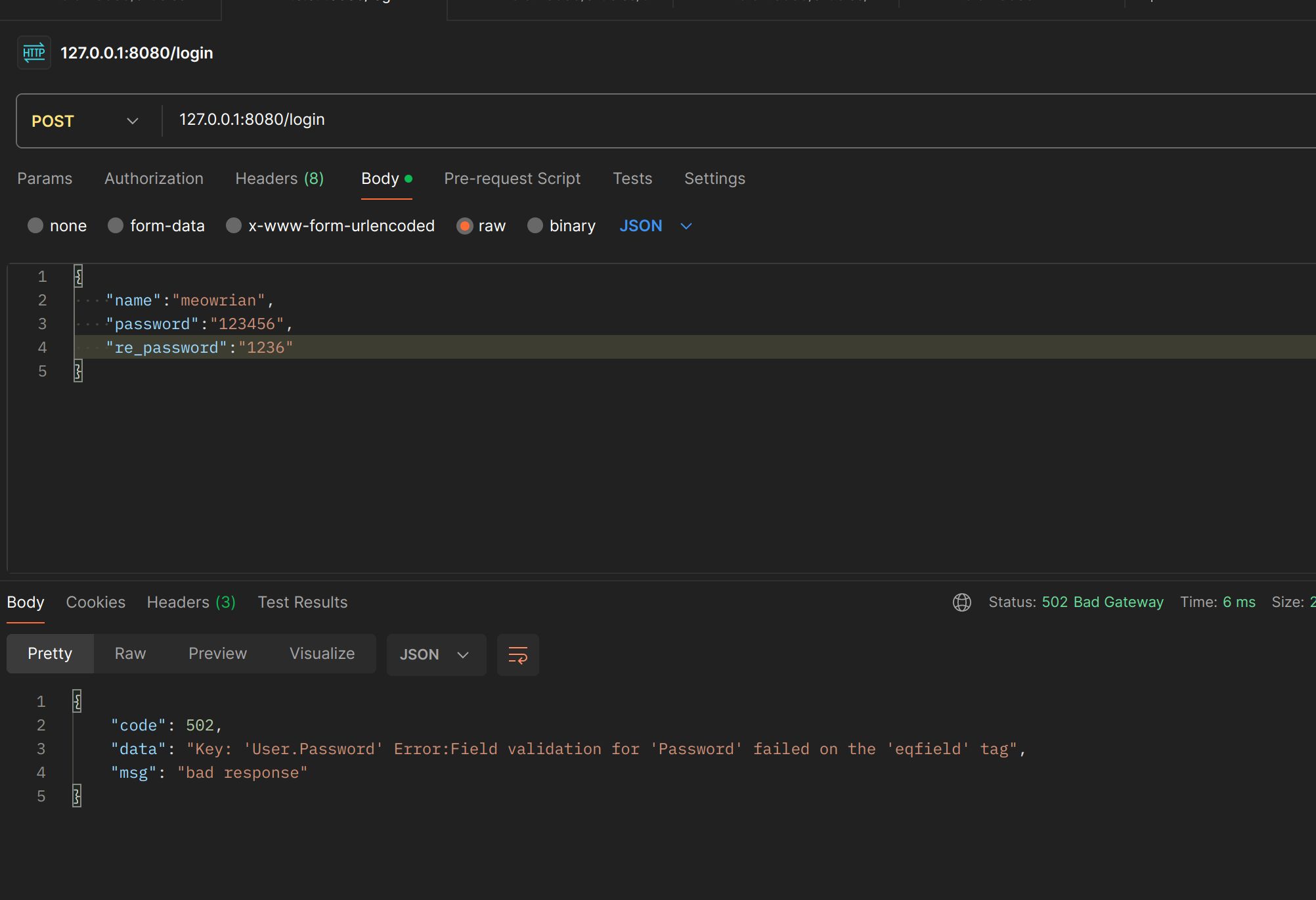
type User struct {
Name string `json:"name" binding:"required"`
Password string `json:"password" binding:"eqfield=Re_Password"`
Re_Password string `json:"re_password"`
}
type Response struct {
Code int `json:"code"`
Data any `json:"data"`
Msg string `json:"msg"`
}
func main() {
router := gin.Default()
router.POST("/login", func(c *gin.Context) {
var user User
err := c.ShouldBindJSON(&user)
if err != nil {
c.JSON(http.StatusBadGateway, Response{
Code: http.StatusBadGateway,
Data: err.Error(),
Msg: "bad response",
})
return
}
c.JSON(http.StatusOK, Response{
Code: http.StatusOK,
Data: user,
Msg: "post successfully",
})
})
router.Run(":8080")
}
密码相同
密码不同
我们看到报错对用户不是很友好,我们可以自定义验证的错误信息
TODO
gin内置验证器
// 枚举 只能是red 或green
oneof=red green
// 字符串
contains=fengfeng // 包含fengfeng的字符串
excludes // 不包含
startswith // 字符串前缀
endswith // 字符串后缀
// 数组
dive // dive后面的验证就是针对数组中的每一个元素
// 网络验证
ip
ipv4
ipv6
uri
url
// uri 在于I(Identifier)是统一资源标示符,可以唯一标识一个资源。
// url 在于Locater,是统一资源定位符,提供找到该资源的确切路径
// 日期验证 1月2号下午3点4分5秒在2006年
datetime=2006-01-02
Gin中间件
Gin中的中间件必须是一个gin.HandlerFunc类型。