第一讲 变量、输入输出、表达式与顺序语句
0. scanf 和 cin 的区别
注意:scanf 是不会自动过滤掉空格 和回车的 \n 的。
1. 单精度 $float$,双精度 $double$ 在 scanf 和 printf 中的使用规则
-
$double$ 对应
%lf,$float$ 对应%f。 -
printf中,%f通杀单精度和双精度;在scanf中,%f和%lf才有区别。为什么呢? -
printf的%f标识符的确既可以输出浮点数又可以输出双精度数。根据 “缺省参数扩展”规则, 不论范围内有没有原形都会在在类似printf的可变长度参数列表中采用, 浮点型的变量或扩展为双精度型, 因此printf()只会看到双精度数。 -
scanf,它接受指针,这里没有类似的类型提升。(通过指针)向 $float$ 存储和向 $double$ 存储大不一样,因此,scanf区别%f和%lf。
2. 浮点数保留位数
浮点数保留位数时用 scanf和printf,保留五位可以写成 %.5lf。
3. 一个整数乘上一个浮点数,会把精度较低的数变成精度较高的那个数
$double$ 可以看成非常大,$10^{300}$ 左右;$int$ 大概 $10^9$;
所以结果会把 $int$ 变量自动转换成 $double$ 变量。
4. 数学库cmath
开方时用 sqrt() 函数。
注意平方不能用 ^,必须写两遍。
5. 时间转换中 % 的使用
- 小时:
n / 3600 - 分钟:
n % 3600求剩余分钟数,然后再/ 60 - 秒:
n % 60求剩余秒数
- 求持续时间时,可以统一成分钟,用
duration = end - start,再计算小时和分钟。第二讲较难题 AcWing 668. 游戏时间2
6. 注意:有些语言中(4/3)无法得到1.3333…,建议在公式中使用(4/3.0)。
7. abs 函数
求两数的最大值,公式:$\max (a, b) = \frac{(a + b + abs(a - b))}{2}$
第二讲 判断语句
8. 判断条件
-
判断一个数是否是另一个的整数倍:
a % b == 0 || b % a == 0 -
判断 a, b, c 是否能构成三角形:
a + b > c && b + c > a && a + c > b
9. 交税
AcWing 672. 税 (y总解法比较好)
10. 手动比较三个数并进行排序
有三个整数 $a, b, c$
- $if (a > b)$,交换 $a$, $b$
- $if (a > c)$,交换 $a$, $c$
- $if (b > c)$,交换 $b$, $c$
从而得到 $a <= b <= c$
如何交换两个数?
if (a > b) {
int t = a;
a = b;
b = t;
// 从而得到 a < b
}
AcWing 663. 简单排序
类似题目:AcWing 666. 三角形类型
第三讲 循环语句
11. 循环输入
如果要输入的数很多的话,可以用循环来输入:
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
double x;
cin >> x;
}
12. swap函数用法
当不确定 $x$,$y$ 的顺序,又需要将小的先出现,可以写成这样:
if (x > y) swap(x, y);
AcWing 714. 连续奇数的和 1
AcWing 719. 连续奇数的和 2
13. 找出最大值
在 100 个数中找出最大值,代码模板:
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
{
int value;
cin >> value;
if (value > maximum)
maximum = value;
}
14. 对于不确定循环次数但有退出循环条件的可以用 while (true)
int x;
while (true)
{
cin >> x;
if (!x) break; //退出循环的条件 当x为0时
}
while 的两种处理方式:
while (cin >> m >> n, m > 0 && n > 0)中间用逗号,隔开while (true),然后里面写退出条件if (m <= 0 || n <= 0) break;
15. 输出矩阵(最后一列为PUM)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0, k = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m - 1; j++)
{
cout << k << ' ';
k++;
}
cout << "PUM" << endl;
k++;
}
return 0;
}
16. %的转义、整数转浮点数加(double)
printf("Percentage of coneys: %.2lf %%\n", (double)c * 100 / s);
17. Fibonacci递推
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int a = 0, b = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << a << ' ';
int c = a + b;
a = b;
b = c;
}
return 0;
}
18. 约数的优化
C++ 的运算能力
- C++ 一秒钟内大概最多可以计算 $1$ 亿 ($10^8$) 次,每次循环 100 次,所以总共要计算 $1$ 亿 $\times 100$,超出运算能力了。
- 如果开方优化后,$10^8$ 开方为 $10^4$ 次,每次循环 100 次,所以最多运算 $10^6$ 次,即 $100$ 万次。
如果 $d$ 能整数 $x$ d | x,那么 $\frac{x}{d} $ 也能整除 $x$ x/d | x。
例:对于 $12$ 来说,$2$ 是 $12$ 的约数,$6$ 也是 $12$ 的约数;
又 $3$ 是 $12$ 的约数,$4$ 也是 $12$ 的约数;
所以我们只要枚举较小的那个约数即可。
$d \le \frac{x}{d}$
$d^{2} \le x$
$d \le \sqrt{x}$
// 求约数的和
for (int i = 1; i * i < x; i++)
{
if (x % i == 0)
{
s += i;
if (x / i != i && x / i != x) s += x / i; // 比如36只有一个平方根6
}
}
19. 判断是否是质数,和上一题同样的原理
// 判断是否是质数
bool is_prime = true;
for (int i = 2; i * i <= x; i++)
if (x % i == 0)
{
is_prime = false;
break;
}
if (is_prime) printf("%d is prime\n", x);
else printf("%d is not prime\n", x);
20. 曼哈顿距离画出菱形
曼哈顿距离:横坐标的差的绝对值 和纵坐标的差的绝对值的和。
$(x1, y1)、 (x2, y2)$
曼哈顿距离 = $|x1 - x2| + |y1 - y2|$
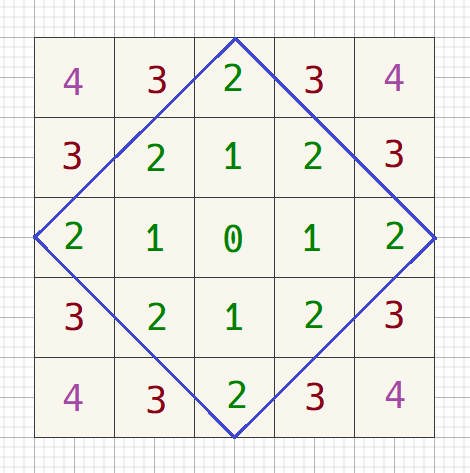
if (abs(i - cx) + abs(j - cy) <= n / 2) cout << '*';
else cout << ' ';
第四讲 数组
21. 数组输入输出操作
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) scanf("%d", &x[i]);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) printf("X[%d] = %d\n", i, x[i]);
22. 二维数组求右上、左上、左下、右下部分
22.1 二维数组求右上半部分
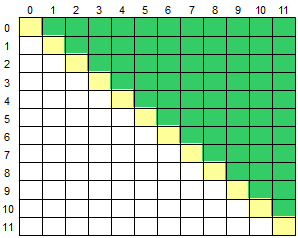
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j < 12; j++)
22.2 二维数组求左上半部分
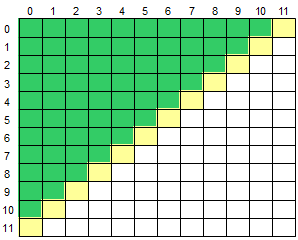
for (int i = 0; i < 12; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= 10 - i; j++)
22.3 二维数组求左下半部分
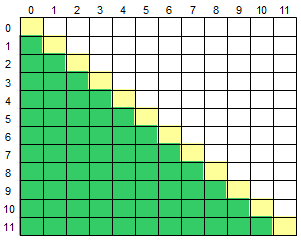
for (int i = 1; i < 12; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
22.4 二维数组求右下半部分
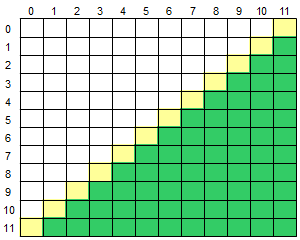
for (int i = 1; i < 12; i++)
for (int j = 12 - i; j < 12; j++)
23. 二维数组的上、下、左、右区域
23.1 二维数组的上方区域
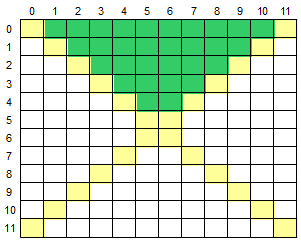
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j < 11 - i; j++)
24. 翻转数组
int a[20], b[20];
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) cin >> a[i];
// for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) b[i] = a[19 - i];
for (int i = 0, j = 19 - i; i < 20, j >= 0; i++, j--) b[j] = a[i]; //这步用双指针
25. 数据溢出
long long 的 $printf$ 输出是 %lld
AcWing 741. 斐波那契数列
26. 求数组中的最小数和它的位置
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (nums[i] < nums[p])
p = i;
27. 难题:平方矩阵(困难)Hard
27.1 AcWing 753. 平方矩阵 I

while (cin >> n, n)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
int up = i, down = n - i + 1, left = j, right = n - j + 1;
cout << min(min(up, down), min(left, right)) << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
27.2 AcWing 754. 平方矩阵 II
先确定左上右下的对角线,然后再按下图规律填充矩阵:
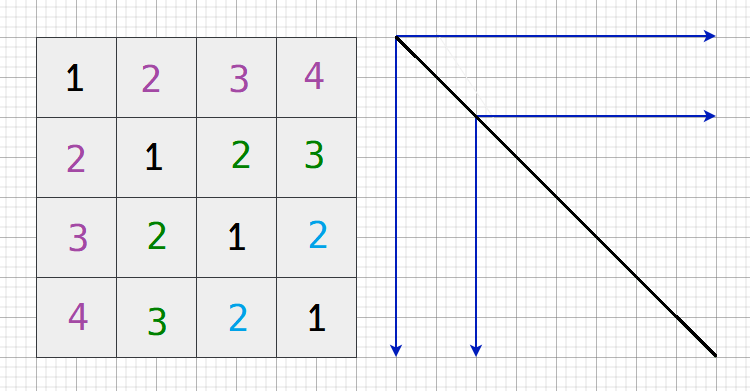
while(cin >> n, n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
q[i][i] = 1;
for (int j = i + 1, k = 2; j < n; j++, k++)
{
q[i][j] = k;
q[j][i] = k;
}
}
}
28. 螺旋矩阵/蛇形矩阵(重要!)
0 → ( 0, 1)
1 ↓ ( 1, 0)
2 ← ( 0,-1)
3 ↑ (-1, 0)
需要改变方向:(1) 撞墙出界时 (2) 重复时
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int res[N][N];
int main()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int dx[] = {0, 1, 0, -1}, dy[] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
int x = 0, y = 0, d = 0;
for (int k = 1; k <= n * m; k++)
{
res[x][y] = k;
int a = x + dx[d], b = y + dy[d];
if (a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >= m || res[a][b])
{
d = (d + 1) % 4;
a = x + dx[d], b = y + dy[d]; //更新a,b
}
x = a, y = b; //更新x,y
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) cout << res[i][j] << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
第五讲 字符串
0x1. 字符和整数的转化
常用ASCII值
-
特殊值:
A - Z是 $65$ ~ $92$,a - z是 $97$ ~ $122$,0 - 9是 $48$ ~ $57$。 -
强制转换:
cpp char c = 'a'; cout << (int)c << endl; // 同理 (char)97 将97转换成a
/* 输入一行字符,统计出其中数字字符的个数,以及字母字符的个数。*/
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char c;
int nums = 0, chars = 0;
while (cin >> c)
{
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') nums++;
else if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z' || c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') chars++;
}
printf("nums: %d\nchars: %d\n", nums, chars);
return 0;
}
ASCII码:
32 space
49 1
32+48=81
81 'Q'
0x2. 字符数组
-
字符串就是字符数组加上结束符
'\0' -
可以使用 字符串 来初始化 字符数组,但此时要注意,每个字符串结尾会暗含一个
'\0'字符,因此字符数组的长度至少要比字符串的长度多 $1$
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a1[] = {'C', '+', '+'}; //不是字符串,列表初始化,没有空字符
char a2[] = {'C', '+', '+', '\0'}; //列表初始化,含有显式的空字符,是字符串
char a3[] = "C++"; //自动添加表示字符串结尾的空字符
char a4[6] = "Daniel"; //错误,没有空间可存放空字符!
return 0;
}
2.1 读入字符数组
注意:scanf 和 cin 都是读到 空格 或 回车 为止
输入
- 读入字符数组时,
scanf("%s", s);无须加取址符号&,因为变量s本身就是个地址。 - 输入也可以用
cin >> s; - 如果想读到从下标
1开始的话,写成scanf("%s", s + 1)
输出
- 可以用
cout << s; - 也可以写成
printf("%s\n", s); - 如果想从下标
1或2开始,则写成cout << s + 1;(从下标1开始输出) 或printf("%s\n", s + 1);
// 字符数组 vs 字符
char str[31]; //字符数组
scanf("%s", str); //不要加取址符&
char c; //字符
scanf("\n%c", &c); //过滤掉回车
2.2. 读入一整行
(1) 字符数组 用 fgets 或 cin.getline 输入;输出也可以用 puts
- 这里的
stdin是把标准读入当成文件来读入。 - 输出除了用
printf也可以用puts,等价于printf("%s\n", s);它会自动补上换行符 fgets输入会自动加上回车,所以用puts(输出自带回车) 的话会多一个回车
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char s[100];
fgets(s, 100, stdin); //stdin 把终端当文件读入
cin.getline(s, 100);
cout << s << endl;
printf("%s", s);
puts(s); //等价于 printf("%s\n", s); 包括换行符
return 0;
}
(2) 字符串 用 getline(cin, s); 输入
- 如果是整行
string类型的字符串,则用getline()来输入
string s;
getline(cin , s);
- 如果是单个
string类型,用cin读入,不能用scanf读入
字符串用cin读会去掉多余空格
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
while (cin >> s) cout << s << ' ';
return 0;
}
/*
输入样例:
Hello world.This is c language.
输出样例:
Hello world.This is c language.
*/
2.3 字符数组的常用操作
-
下面几个函数需要引入头文件:
#include <cstring> -
(1)
strlen(str),求字符串的长度,只计算字符串的元素,\0不计入其中 - (2)
strcmp(a, b),比较两个字符串的大小,$a < b$ 返回 $-1$,$a == b$ 返回 $0$,$a > b$ 返回 $1$。这里的比较方式是字典序! - (3)
strcpy(a, b),将字符串 $b$ 复制给从 $a$ 开始的字符数组。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char s1[100] = "hello world!", s2[100];
cout << strlen(s1) << endl;
strcpy(s2, s1); // 把后者复制给前者
cout << strcmp(s1, s2) << endl;
return 0;
}
-
(4) 遍历字符数组中的字符
注意:如果没先存
len而写成i < strlen(a),那么就两重循环了。
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a[100] = "hello world";
for (int i = 0, len = strlen(a); i < len; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
经典题:给定一个只包含小写字母的字符串,请你找到第一个仅出现一次的字符。如果没有,输出“no”。
/*开一个数组,存储 a 到 z 的出现次数
'a' 'b' 'c' 'd' ... 'z'
0 1 2 3 ... 25
*/
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int cnt[26];
char str[100010];
int main()
{
cin >> str;
int len = strlen(str);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) cnt[str[i] - 'a'] ++;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
if (cnt[str[i] - 'a'] == 1)
{
cout << str[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
puts("no");
return 0;
}
因为字符数组最后是 \0,所以循环条件写成如下即可
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++)
经典题:密码翻译,输入一个只包含小写字母的字符串,将其中的每个字母替换成它的后继字母,如果原字母是’z’,则替换成’a’。
for (char &c : s)
if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') c = (c - 'a' + 1) % 26 + 'a';
else if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') c = (c - 'A' + 1) % 26 + 'A';
难题:字符串模拟题
stoi(str);//将字符串转换成数字atoi(str.c_str());//将字符数组转换成数字
class Solution {
public:
int strToInt(string str) {
int k = 0;
//去掉空格
while (k < str.size() && str[k] == ' ') k++;
bool is_neg = false;
long long res = 0;
//判断正负
if (str[k] == '-') k++, is_neg = true;
else if (str[k] == '+') k++;
//字符变数字
while (k < str.size() && str[k] >= '0' && str[k] <= '9')
{
res = res * 10 + str[k] - '0';
k++;
}
// 处理特例
if (is_neg) res *= -1;
if (res > INT_MAX) res = INT_MAX;
if (res < INT_MIN) res = INT_MIN;
return res;
// return stoi(str); //将字符串转换成数字
// return atoi(str.c_str()); //将字符数组转换成数字
}
};
0x3. 标准库类型 string
- 可变长的字符序列,可以动态分配,比字符数组更加好用。需要引入头文件:
#include <string> - 可将两个字符串拼接在一起
3.1 定义和初始化
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1; //默认的空字符串
string s2 = s1; // s2是s1的副本
string s3 = "hiya"; //s3是该字符串字面值的副本
string s4(10, 'c'); //s4的内容是 cccccccccc
return 0;
}
3.2 string 上的操作
- 不能用
scanf("%s", &s1)来读入string,这是错的;只能用cin来读入 -
不能用
printf直接输出string,需要写成:cpp printf(“%s”, s.c_str()); //或 puts(s1.c_str());c_str()返回的是字符数组的首地址 -
使用
getline读取一整行 -
string的empty和size操作。size()是 $O(1)$ 复杂度,strlen()是 $O(n)$ 的复杂度。
3.3 字面值和 string 对象相加
- 做加法运算时,字面值和字符都会被转化成
string对象,因此直接相加就是将这些字面值串联起来
string s1 = "hello", s2 = "world";// 在s1和s2中都没有标点符号
string s3 = s1 + "," + s2 + '!';
- 当把
string对象和字符字面值及字符串字面值混在一条语句中使用时,必须确保每个加法运算符的两侧的运算对象至少有一个是string
string s4 = s1 + ",";// 正确:把一个string对象和有一个字面值相加
string s5 = "hello" + ","; // 错误:两个运算对象都不是string
string s6 = s1 + "," + "world"; // 正确,每个加法运算都有一个运算符是string
string s7 = "hello" + "," + s2; // 错误:不能把字面值直接相加,运算是从左到右进行的
29. 技巧:比较时,把字符串变量存为数字
设猎人为 0
狗熊为 1
枪 为 2
1 赢 0
2 赢 1
0 赢 2
x y
if(x == y) Tie
if (x = (y + 1) % 3) Player1 赢
else Player2 赢
30.substr(pos, count) 的用法
substr(pos, count)函数:
pos - 要包含的首个字符的位置
count - 子串的长度
返回含子串 [pos, pos+count) 的 string
举例:左旋转字符串:
输入:”abcdefg” , n=2
输出:”cdefgab”
class Solution {
public:
string leftRotateString(string str, int n) {
return str.substr(n) + str.substr(0, n);
}
};
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string a, b;
while (cin >> a >> b)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < a.size(); i++)
if (a[i] > a[p]) p = i;
/* substr(pos, count)函数
pos - 要包含的首个字符的位置
count - 子串的长度
返回含子串 [pos, pos+count) 的 string
*/
cout << a.substr(0, p + 1) + b + a.substr(p + 1) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
31. fgets() 与 cin.getline() 的区别
- 用
fgets()输入字符数组时,还要记得去掉末尾回车 - 用
cin.getline()输入字符数组时,不用做这步操作
用 fgets() 输入字符数组:
// 用 fgets() 输入字符数组
char a[100], b[100];
// 去掉末尾回车
fgets(a, 100, stdin);
fgets(b, 100, stdin);
int x = strlen(a), y = strlen(b);
if (a[x-1] == '\n') a[x - 1] = 0;
if (b[y-1] == '\n') b[y - 1] = 0;
用 cin.getline() 输入字符数组:
// 用 cin.getline() 输入字符数组
char a[100], b[100];
cin.getline(a, 100);
cin.getline(b, 100);
fgets输入会自动带上回车,如果再用puts输出(自动带上回车),就有两个回车了,多出一个回车
#include <cstdio>
void print(char str[])
{
// puts(str); 由于 fgets会在最后加上回车,所以这里再用puts就多出一个回车,换printf
printf("%s", str); //而且也不要写成 "%s\n"
}
int main()
{
char str[110];
fgets(str, 110, stdin);
print(str);
return 0;
}
32. 将大写字母变成小写字母 1) ASCII 码 2) tolower函数
'A' + 32 == 'a',字符'A'的 ASCII 码是 $65$,'a'的 ASCII 码是 $97$,它们之间相差 $32$,所以s[i] += 32;c = tolower(c)
string a, b;
getline(cin, a), getline(cin, b);
for (char& c : a) c = tolower(c);
for (char& c : b) c = tolower(c);
33. stringstream 的用法
sstream 头文件定义了三个类型来支持内存 IO,这些类型可以向 string 写入数据,从 string 读取数据,就像 string 是一个 IO流一样。
istringstream从 string 读取数据ostringstream向 string 写入数据- 头文件
stringstream用于读写给定 string 的字符串流,既可从 string 读数据也可向 string 写数据
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s, a, b;
getline(cin, s);
cin >> a >> b;
stringstream ssin(s); //ssin 类似 cin
string str;
while (ssin >> str)
if (str == a) cout << b << ' ';
else cout << str << ' ';
return 0;
}
34. 双指针算法
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
int j = i;
while (j < s.size() && s[j] == s[i]) j++;
i = j - 1;
}
35. string 句子有句号先去掉句号
while (cin >> str)
{
if (str.back() == '.') str.pop_back();
...
}
36. 字符串数组 - 倒排单词
字符串数组有别于字符数组,定义字符串数组 string str[100];
可以先用 while (cin >> str[n]) 读入,统计 n
倒排单词可以倒序排,输出 str[i] << ' '
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str[100];
int n = 0;
while (cin >> str[n]) n++;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << str[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
37. substr() 的用法
for ()
{
当前循环移位得到 a': a = a.substr(1) + a[0];
判断 b 是否是 a' 的子串
for (起点...)
for (枚举对应位置)
如果不一样,break
如果都一样,说明是子串
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
if (a.size() < b.size()) swap(a, b);
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++)
{
a = a.substr(1) + a[0];
for (int j = 0; j + b.size() <= a.size(); j++)
{
int k = 0;
for (; k < b.size(); k++)
if (a[j + k] != b[k]) break;
if (k == b.size())
{
puts("true");
return 0;
}
}
}
puts("false");
return 0;
}
类似技巧的难题:AcWing 778. 字符串最大跨距
38. 字符串的最大周期
- 这道题是让我们求几次方 $n$ 最大值,可以把字符串当成周期串来处理
- $len$ 是字符串总长,假定最大周期是 $n$,最小单位子串的长度为 $m = len/n$
- 可以采用倒序
n = len再n--,找到最大周期 $n$ 就可以break跳出 - 一个条件是
len % n == 0 - 设单位子串为
string r = str.substr(0, m); - 如果将单位子串循环 $n$ 遍后得到的字符串等于 $str$,说明 $n$ 是我们要求的最小周期
- 输出 $n$,并
break跳出即可
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
while (cin >> str, str != ".")
{
int len = str.size();
for (int n = len; n; n--)
if (len % n == 0)
{
int m = len / n;
string s = str.substr(0, m);
string r;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) r += s;
if (r == str)
{
cout << n << endl;
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
第六讲 函数
39. 递归求阶乘
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int fact(int n)
{
if (n == 1) return 1;
return n * fact(n - 1);
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
cout << fact(n) << endl;
return 0;
}
40. 递归Fibonacci数列
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int f(int n)
{
if (n <= 2) return 1;
return f(n - 1) + f(n - 2);
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
cout << f(n) << endl;
return 0;
}
41. 双指针翻转数组
void reverse(int a[], int size)
{
for (int i = 0, j = size - 1; i < j; i++, j--)
swap(a[i], a[j]);
}
双指针算法调整奇偶顺序
class Solution {
public:
void reOrderArray(vector<int> &array) {
int i = 0, j = array.size() - 1;
while (i < j)
{
while (i < j && array[i] % 2) i++; //如果是奇数,那么指针i向后
while (i < j && array[j] % 2 == 0) j--; //如果是偶数,指针j向前
if (i < j) swap(array[i], array[j]);
}
}
};
42. 数组去重
int get_unique_count(int a[], int n)
{
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
bool is_unique = true;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (a[i] == a[j])
{
is_unique = false;
break;
}
if (is_unique) cnt++;
}
return cnt;
}
43. 选择排序算法
// 选择排序算法
void sort(int a[], int l, int r)
{
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++)
for (int j = i + 1; j <= r; j++)
if (a[j] < a[i])
swap(a[i], a[j]);
}
44. 跳台阶 - 函数递归
// 楼梯共有n级台阶
void f(int k)
{
if (k == n) res++;
else if (k < n)
{
f(k + 1);
f(k + 2);
}
}
45. 走方格 - 函数递归
void dfs(int x, int y)
{
if (x == n && y == m) res++;
else
{
if (y < m) dfs(x, y + 1);
if (x < n) dfs(x + 1, y);
}
}
45. 全排列 - 回溯
/*
要存的数:
1. 每个位置填的是哪些数? nums[]
2. 每个数组有没有被用过 st[]
3. u 可以枚举到第几位? u
*/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10;
int n;
void dfs(int u, int nums[], bool st[])
{
if (u > n) // 表示已经填完所有数
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << nums[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
}
else
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (!st[i]) //找到第一个没有被用过的数
{
st[i] = true;
nums[u] = i;
dfs(u + 1, nums, st); //dfs到下一层
st[i] = false; //回溯,恢复现场
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
int nums[N];
bool st[N] = {0};
dfs(1, nums, st); // 从位置1,2,3的第1位开始枚举
return 0;
}
排列函数 next_permutation()
next_permutation(nums.begin(), nums.end()) 函数
/* 输入:[1,2,3]
输出:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> permutation(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
vector<vector<int>> res;
do
{
res.push_back(nums);
} while (next_permutation(nums.begin(), nums.end()));
return res;
}
};
第七讲 结构体、类、指针、引用
01. class 和 struct 基本相同
class 和 struct 基本相同。里面的 private 和 public 可以不写,在 class 中,不写默认是 private,但子啊 struct 中不写默认是 public。
02. 构造函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Person
{
int age, height;
double money;
Person() {} // 没有参数的构造函数
Person(int _age, int _height) {}
Person(int _age, int _height, double _money) //有参数的构造函数
{
age = _age;
height = _height;
money = _money;
}
//简短的写法,效率会更快一些
Person(int _age, int _height, double _money) : age(_age), height(_height), money(_money) {}
};
int main()
{
Person p = {18, 180};
cout << p.money << endl;
return 0;
}
03. 堆栈空间
-
代码是存到内存空间里的,所有的函数调用都是在栈空间里,局部变量都是定义到栈空间里的,静态变量和数组全部定义到堆空间里。
-
局部变量是随机的,全局变量全是
0;这是因为开到栈里的空间变量没有赋值,所以是不确定的;开到堆里的空间变量全部默认为0。
04. & 和 *
引用、取地址符;指针、解引用符
关键概念:某些符号有多重含义:
像 & 和 * 这样的符号,既能用作表达式里的运算符,也能作为声明的一部分出现,符号的上下文决定了符号的意义。
- 在声明语句中,
&和*用于组成复合类型;(&引用,*指针) - 在表达式中,它们的角色又转变成运算符。(
&取地址符,*解引用符)
int i = 42;
int &r = i; // & 紧随类型名出现,因此是声明的一部分,r 是一个引用
int* p; // * 紧随类型名出现,因此是声明的一部分,p 是一个指针
p = &i; // & 出现在表达式中,是一个取地址符
*p = i; // * 出现在表达式中,是一个解引用符
int &r2 = *p; // & 是声明的一部分,* 是一个解引用符
05. 指针
- 指针指向存放变量的值的地址。因此我们可以通过指针来修改变量的值。
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int *p = &a;
*p += 5;
cout << *p << endl; //输出15
return 0;
}
- 数组名是一种特殊的指针。指针可以做运算:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
char a, b;
int main()
{
char c;
int a[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) cout << *(a + i) << ' '; //输出1 2 3 4 5
cout << endl;
cout << (void*) &c << endl; //0x61ff07
cout << a << endl;//0x61fef0
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
cout << (void*)&a[i] << endl;
/*
0x61fef0
0x61fef4
0x61fef8
0x61fefc
0x61ff00
隔了4个字节是因为每个int型变量有4个字节
如果是char类型的字符数组,则每个地址差1而不是4*/
return 0;
}
06. 链表
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4;
struct Node
{
int val;
Node* next;
Node(int _val) : val(_val), next(NULL) {};
};
int main()
{
Node* p = new Node(1);
Node* q = new Node(2);
Node* o = new Node(3);
p->next = q;
q->next = o;
Node* head = p;
// 在头节点前面添加节点 (4) 1 2 3
Node* u = new Node(4);
u->next = head;
head = u;
// 删除节点 head指向节点2,跳过节点1
head->next = head->next->next;
//链表的遍历方式
for (Node* i = head; i; i = i->next) // i是指针,运行条件是 i != NULL;
cout << i->val << endl;
return 0;
}
遍历链表,将值存到 vector 中
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printListReversingly(ListNode* head) {
vector<int> res;
for (auto p = head; p; p = p->next) res.push_back(p->val);
return res;
}
};
46. 链表:删除链表节点本身
输入:链表 1->4->6->8
删掉节点:第2个节点即6(头节点为第0个节点)
方法:先让该节点伪装成其next节点6变成8,再把next节点干掉(真正的8被干掉)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void deleteNode(ListNode* node) {
node->val = node->next->val; // 伪装成下一个点(将下个点的值拿过来)
node->next = node->next->next; // 将下一个点删掉
}
};
47. 链表:归并链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1), tail = dummy;
while (l1 && l2)
if (l1->val < l2->val) //l1小
{
tail = tail->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else //l2小
{
tail = tail->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
if (l1) tail->next = l1;
if (l2) tail->next = l2;
return dummy->next;
}
};
48. 链表:翻转链表/反转链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head || !head->next) return head; // 如果节点为空或只有一个头结点,返回头结点
auto p = head, q = p->next;
while (q) // 当q还没走到空节点
{
auto o = q->next;
q->next = p;
p = q, q = o;
}
head->next = nullptr;
return p; // p 是新的头结点
}
};
49. ### 链表:两个链表的第一个公共结点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *findFirstCommonNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
auto p = headA, q = headB;
while (p != q)
{
if (p) p = p->next;
else p = headB;
if (q) q = q->next;
else q = headA;
}
return p;
}
};
50. 链表:删除链表中重复的节点
AcWing 29. 删除链表中重复的节点
听下视频讲解
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* head) {
auto dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next = head;
auto p = dummy;
while (p->next)
{
auto q = p->next;
while (q->next && q->next->val == p->next->val) q = q->next;
if (q == p->next) p = q;
else p->next = q->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
第八章 C++ STL
01 #include <vector>
vector 是变长数组,支持随机访问,不支持在任意位置 $O(1)$ 插入。为了保证效率,元素的增删一般应该在末尾进行。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> a({1, 2, 3});
// 方式一
for (int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++) cout << a[i] << ' ';
cout << endl;
// 方式二 vector<int>::iterator 迭代器类型
for (auto it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++) cout << *it << ' ';
cout << endl;
// 方式三
for (int x : a) cout << x << ' ';
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
02 #include <queue>
头文件 queue 主要包括循环队列 queue 和优先队列 priority_queue 两个容器。
声明:
queue<int> q;
struct rec{…}; queue<rec> q; //结构体rec中必须重载小于号
priority_queue<int> q; //大根堆
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> q; //小根堆
priority_queue<pair<int, int>>q;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
queue<int> q; //队列
priority_queue<int> a; //大根堆,重载<小于号
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> b; //小根堆,重载>大于号
struct Rec
{
int a, b;
bool operator< (const Rec& t) const
{
return a < t.a;
}
};
priority_queue<Rec> d;
d.push({1, 2});
}
clear除了队列、优先队列、栈之外,其他所有的STL容器都有clear函数。- 重新初始化队列可以清空:
q = queue<int>();
03 #include <set>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
set<int> a; //元素不能重复
multiset<int> b; //元素可以重复
set<int>::iterator it = a.begin();
++it, --it;
a.find(x); //会返回值等于x的迭代器
if (a.find(x) == a.end()) //判断x在a中是否存在
a.lower_bound(x); //找到大于等于x的最小的元素的迭代器
a.upper_bound(x); //找到大于 x的最小的元素的迭代器
a.erase(x); //从a中删除所有等于x的元素 O(k+logn),k是被删元素的个数
a.erase(it); // 从a中删除迭代器 it 指向的元素, O(logn)
a.count(x); //x在a里的个数
struct Rec
{
int x, y;
bool operator< (const Rec& t) const
{
return x < t.x;
}
};
set<Rec> c;
}
04 #include <map>
map 容器是一个键值对 $key-value$ 的映射,其内部实现是一棵以 $key$ 为关键码的红黑树。$Map$ 的 $key$ 和 $value$ 可以是任意类型,其中 $key$ 必须定义小于号运算符。
#include <map>
int main()
{
map<string, vector<int>> a;
a["yxc"] = vector<int>({1, 2, 3, 4});
cout << a["yxc"][2] << endl;
cout << (a.find("yxc") == a.end()) << endl;
return 0;
}
05 #include <bitset>
#include <bitset>
int main()
{
bitset<1000> a; //定义了长度为1000位的01串
a[0] = 1;
a[1] = 1;
cout << a[2] << endl; //没有赋过值的是0
cout << a.count() << endl; //返回里面1的个数
return 0;
}
06 pair
int main()
{
pair<int, string> a;
a = {3, "yxc"};
cout << a.first << ' ' << a.second << endl;
a = make_pair(4, "abc");
cout << a.first << ' ' << a.second << endl;
return 0;
}
51. 用两个栈实现队列
int pop() {
while (s1.size() > 1) s2.push(s1.top()), s1.pop();
int t = s1.top(); s1.pop();
while (s2.size()) s1.push(s2.top()), s2.pop();
return t;
}
52. Two-Sum变体 用到 unordered_set
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findNumbersWithSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered_set<int> S;
for (auto x : nums)
{
if (S.count(target - x)) return {x, target - x};
S.insert(x);
}
}
};
53. 位运算:求二进制中1的个数
n >> i & 1
class Solution {
public:
int NumberOf1(int n) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++)
if (n >> i & 1) res++;
return res;
}
};
lowbit做法
class Solution {
public:
int NumberOf1(int n) {
int res = 0;
while (n) n -= n & -n, res ++;
return res;
}
};
54. 结构体排序 + string字符串 printf输出时要注意加.c_str()
//结构体排序
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
struct Data
{
int x;
double y;
string z;
bool operator< (const Data &t) const
{
return x < t.x;
}
}a[N];
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> a[i].x >> a[i].y >> a[i].z;
sort(a, a + n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%d %.2lf %s\n", a[i].x, a[i].y, a[i].z.c_str()); //printf输出string字符串时要用到 .c_str()
return 0;
}
55. 0x3f3f3f3f
-
0x3f3f3f3f的十进制是 $1061109567$,也就是 $10^{9}$ 级别的(和0x7fffffff一个数量级),而一般场合下的数据都是小于 $10^{9}$ 的,所以它可以作为无穷大使用而不致出现数据大于无穷大的情形。 -
另一方面,由于一般的数据都不会大于 $10^{9}$,所以当我们把无穷大加上一个数据时,它并不会溢出(这就满足了“无穷大加一个有穷的数依然是无穷大”),事实上
0x3f3f3f3f+0x3f3f3f3f$= 2122219134$,这非常大但却没有超过 32-bit int的表示范围,所以0x3f3f3f3f还满足了我们“无穷大加无穷大还是无穷大”的需求。 -
最后,
0x3f3f3f3f还能给我们带来一个意想不到的额外好处:如果我们想要将某个数组清零,我们通常会使 用memset(a, 0, sizeof a)这样的代码来实现(方便而高效),但是当我们想将某个数组全部赋值为无穷大时(例如解决图论问题时邻接矩阵的初始化),就不能使用memset函数而得自己写循环了,我们知道这是因为memset是按字节操作的,它能够对数组清零是因为 $0$ 的每个字节都是 $0$,现在好了,如果我们将无穷大设为0x3f3f3f3f,那么奇迹就发生了,0x3f3f3f3f的每个字节都是0x3f!所以要把一段内存全部置为无穷大,我们只需要memset(a, 0x3f, sizeof a)。所以在通常的场合下,const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;真的是一个非常棒的选择。 -
另外两种常见的方式:
memset(a, 0, sizeof a);和memset(a, -1, sizeof a);$memset$ 是按字节赋值的,$int$ 是四个字节的。前者,往每个字节赋值 $0$,那每个字节就是 $0$;后者,$-1$ 在 C++ 表示的时候,表示每个位上的数字都是 $1$,把每个字节赋值成 $-1$,那整个就是 $-1$。
56. STL 函数
vector(变长数组),倍增的思想,支持比较运算(按字典序)
定义::
vector <int> a; 定义:一个vector数组a
vector <int> a(10); 定义:一个长度为10的vector数组a
vector <int> a(10,3); 定义:一个长度为10的vector数组a,并且所有元素都为3
常用函数::
size(); 返回元素个数
empty(); 返回是否是空
clear(); 清空
front(); 返回vector的第一个数
back(); 返回vector的最后一个数
push_back(); 向vector的最后插入一个数
pop_back(); 把vector的最后一个数删掉
begin(); vector的第0个数
end(); vector的最后一个的数的后面一个数
倍增的思想:
系统为某一程序分配空间是,所需时间,与空间大小无关,与申请次数有关
遍历方法
假设有个vector <int> a;
第一种:
for(int i = 0;i < a.size();i ++) cout<<a[i]<<" ";
第二种:
for(vector <int>::iterator i = a.begin();i != a.end();i ++) cout<<*i<<" "; vector <int>::iterator可以写为auto
第三种:
for(auto x : a) cout<<x<<" ";
pair,支持比较运算,以first为第一关键字,以second为第二关键字(按字典序)
定义::
pair <类型,类型> 变量名; 两个类型可以不同
初始化方式:
假设有个pair <int,string> p;
第一种:
p = make_pair(10,"abc");
第二种:
p = {10,"abc");
常用函数::
first(); 第一个元素
second(); 第二个元素
string(字符串)
常用函数::
substr(); 返回每一个子串
c_str(); 返回这个string对应的字符数组的头指针
size(); 返回字母个数
length(); 返回字母个数
empty(); 返回字符串是否为空
clear(); 把字符串清空
queue(队列)
定义::
queue <类型> 变量名;
常用函数::
size(); 这个队列的长度
empty(); 返回这个队列是否为空
push(); 往队尾插入一个元素
front(); 返回队头元素
back(); 返回队尾元素
pop(); 把队头弹出
注意:队列没有clear函数!!!
清空:
变量名 = queue <int> ();
priority_queue(优先队列,堆)
注意:默认是大根堆!!!
定义::
大根堆:priority_queue <类型> 变量名;
小根堆:priority_queue <类型,vecotr <类型>,greater <类型>> 变量名
常用函数:
size(); 这个堆的长度
empty(); 返回这个堆是否为空
push();往堆里插入一个元素
top(); 返回堆顶元素
pop(); 弹出堆顶元素
注意:堆没有clear函数!!!
stack(栈)
常用函数:
size(); 这个栈的长度
empty(); 返回这个栈是否为空
push(); 向栈顶插入一个元素
top(); 返回栈顶元素
pop(); 弹出栈顶元素
deque(双端队列)
常用函数:
size(); 这个双端队列的长度
empty(); 返回这个双端队列是否为空
clear(); 清空这个双端队列
front(); 返回第一个元素
back(); 返回最后一个元素
push_back(); 向最后插入一个元素
pop_back(); 弹出最后一个元素
push_front(); 向队首插入一个元素
pop_front(); 弹出第一个元素
begin(); 双端队列的第0个数
end(); 双端队列的最后一个的数的后面一个数
set,map,multiset,multimap 基于平衡二叉树(红黑树),动态维护有序序列
set/multiset
注意:set不允许元素重复,如果有重复就会被忽略,但multiset允许!!!
常用函数:
size(); 返回元素个数
empty(); 返回set是否是空的
clear(); 清空
begin(); 第0个数,支持++或--,返回前驱和后继
end(); 最后一个的数的后面一个数,支持++或--,返回前驱和后继
insert(); 插入一个数
find(); 查找一个数
count(); 返回某一个数的个数
erase();
(1)输入是一个数x,删除所有x O(k + log n)
(2)输入一个迭代器,删除这个迭代器
lower_bound(x); 返回大于等于x的最小的数的迭代器
upper_bound(x); 返回大于x的最小的数的迭代器
map/multimap
常用函数:
insert(); 插入一个数,插入的数是一个pair
erase();
(1)输入是pair
(2)输入一个迭代器,删除这个迭代器
find(); 查找一个数
lower_bound(x); 返回大于等于x的最小的数的迭代器
upper_bound(x); 返回大于x的最小的数的迭代器
unordered_set,unordered_map,unordered_muliset,unordered_multimap 基于哈希表
和上面类似,增删改查的时间复杂度是O(1)
不支持lower_bound()和upper_bound()
bitset 压位
定义:
bitset <个数> 变量名;
支持:
~,&,|,^
>>,<<
==,!=
[]
常用函数:
count(); 返回某一个数的个数
any(); 判断是否至少有一个1
none(); 判断是否全为0
set(); 把所有位置赋值为1
set(k,v); 将第k位变成v
reset(); 把所有位变成0
flip(); 把所有位取反,等价于~
flip(k); 把第k位取反


大佬
三目运算符不能这样用吗
?”字符串” : int
两边一定要相同数据类型吗?
tql
%%%
orz
大佬太厉害了!