题目描述
把 1~n 这 n
个整数排成一行后随机打乱顺序,输出所有可能的次序。
输入格式
一个整数n。
输出格式
按照从小到大的顺序输出所有方案,每行1个。
首先,同一行相邻两个数用一个空格隔开。
其次,对于两个不同的行,对应下标的数一一比较,字典序较小的排在前面。
数据范围
1≤n≤9
样例
输入样例:
3
输出样例:
1 2 3
1 3 2
2 1 3
2 3 1
3 1 2
3 2 1
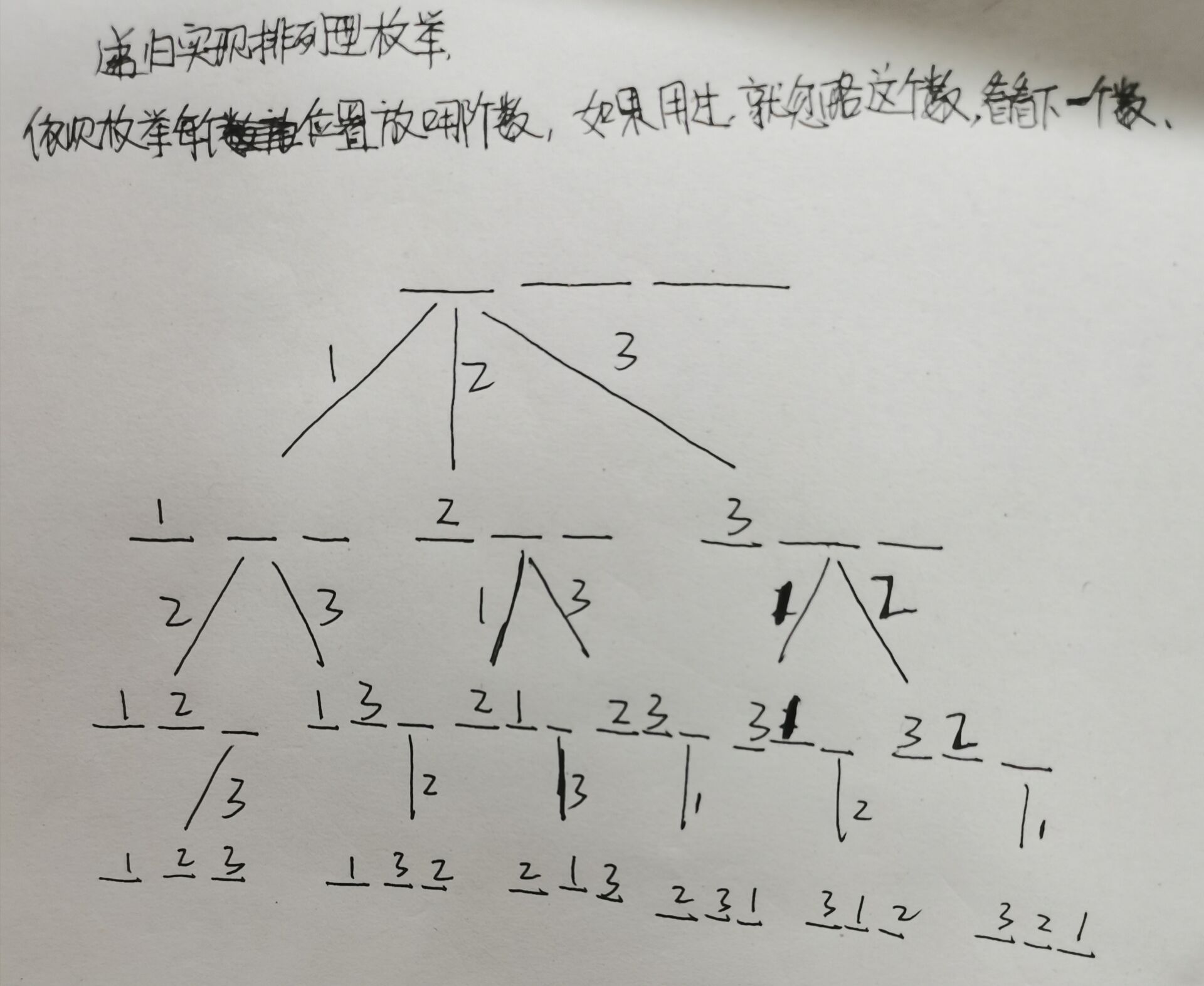
算法1
非STL
画个二叉树有助于理解,由于刚开始写题解,不会插入图片,
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <cstdio>
int n;
int order[30];//表示此数的值
bool st[30];//表示此数是否被使用过
void dfs(int x){//枚举第x个位置
if(x>n){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
printf("%d ",order[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return;
}
else{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(st[i]) continue;
st[i]=1;
order[x]=i;//注意是第x个位置上的数是i
dfs(x+1);
st[i]=0;//恢复现场
order[x]=0;//恢复现场,可省略
}
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
dfs(1);
return 0;
}
算法2
STL
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int> num;
bool isUsed[100];
int n;
void dfs(int k) {
if (k>=n) {
for (int x : num) {
cout << x << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
if (isUsed[i])
continue;
num.push_back(i);
isUsed[i] = true;
dfs(k + 1);
num.pop_back();
isUsed[i] = false;
}
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
dfs(0);
return 0;
}

