题目描述
There are n cities numbered from 0 to n-1 and n-1 roads such that there is only one way to travel between two different cities (this network form a tree). Last year, The ministry of transport decided to orient the roads in one direction because they are too narrow.
Roads are represented by connections where connections[i] = [a, b] represents a road from city a to b.
This year, there will be a big event in the capital (city 0), and many people want to travel to this city.
Your task consists of reorienting some roads such that each city can visit the city 0. Return the minimum number of edges changed.
It’s guaranteed that each city can reach the city 0 after reorder.
样例
Example 1:
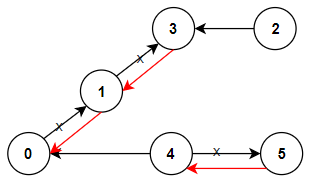
Input: n = 6, connections = [[0,1],[1,3],[2,3],[4,0],[4,5]]
Output: 3
Explanation: Change the direction of edges show in red such that each node can reach the node 0 (capital).
Example 2:
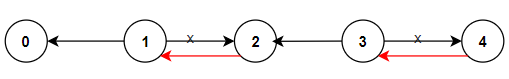
Input: n = 5, connections = [[1,0],[1,2],[3,2],[3,4]]
Output: 2
Explanation: Change the direction of edges show in red such that each node can reach the node 0 (capital).
Example 3:
Input: n = 3, connections = [[1,0],[2,0]]
Output: 0
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 5 * 10^4connections.length == n-1connections[i].length == 20 <= connections[i][0], connections[i][1] <= n-1connections[i][0] != connections[i][1]
算法
(BFS) $O(n)$
建立两个unordered_map,start存储以节点i作为起始点的边,end存储以节点i为终止点的边,根据题意,我们只需要从0开始,依次搜索start和end,那么意味着和0直接相连,并且边从0出发,那么就是需要被修改的。所以真正让计数器+1的,一定是在start里计算。
于是我们可以利用一个队列存储下一个作为搜索的起点,然后用一个数组used来记录每个节点是否被使用过,对于used的理解,可以从第一个样例的节点1来理解。
每个节点最多被访问两次,时间复杂度$O(n)$.
C++ 代码
class Solution {
public:
int minReorder(int n, vector<vector<int>>& connections) {
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> start, end;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
const int & from = connections[i][0];
const int & to = connections[i][1];
start[from].push_back(to);
end[to].push_back(from);
}
int res = 0;
queue<int> q;
q.push(0);
vector<bool> used(n, false);
used[0] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
int tmp = q.front(); q.pop();
if (start.find(tmp) != start.end()) {
auto & vec1 = start[tmp];
for (auto & e: vec1) {
if (!used[e]) {
++res;
used[e] = true;
q.push(e);
}
}
}
if (end.find(tmp) != end.end()) {
auto & vec2 = end[tmp];
for (auto & e : vec2) {
if (!used[e]) {
used[e] = true;
q.push(e);
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
};

