题目描述
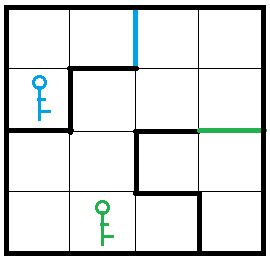
输入样例
4 4 9
9
1 2 1 3 2
1 2 2 2 0
2 1 2 2 0
2 1 3 1 0
2 3 3 3 0
2 4 3 4 1
3 2 3 3 0
3 3 4 3 0
4 3 4 4 0
2
2 1 2
4 2 1
输出样例
14
算法
(拆点+BFS) $O(nm)$
- 将迷宫中的二维坐标压缩成一维数组方便枚举,即$n$行$m$列的迷宫中点$(x, y)$的下标为$t = (x - 1) * n + y$
- 设$dist[t][state]$表示所有从起点走到$t$这个格子,且当前已经拥有的钥匙是$state$的所有路线的集合中的最短距离
- 用一个10位的二进制数$state$存储每一类🔑的存放情况
- 初始时,对于没有🔑的单元,只有一种状态$dist[t][0]$;对于包含🔑的单元,有两种状态$dist[t][0]$和$dist[t][state]$(因为只要有钥匙一定是全部带着,否则有可能走回头路)
- 状态转移的方式分以下2种情况:
- 拿起所有钥匙(花费时间0):$dist[t][state] = min(dist[t][state], dist[t][0])$
- 向四周移动,只有以下2种情况能走(花费时间1):$dist[t1][state] = min(dist[t1][state], dist[t2][state] + 1)$
(1)没有门和墙
(2)有门,且有匹配的钥匙
- 状态转移过程中花费时间只有0或者1,因此考虑使用双端队列BFS
时间复杂度
整个过程分为建图和双端队列广搜,每个单元至多只会入队和出队一次,因此时间复杂度是$O(nm)$
C++ 代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <deque>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define x first
#define y second
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 11, M = N * N, E = 400, P = 1 << N;
int n, m, p, k;
int h[M], e[E], w[E], ne[E], idx;
int g[N][N], keys[M], dist[M][P];
bool st[M][P];
set<PII> edges;
void add(int a, int b, int c) {
e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
void build() {
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1}, dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ )
for (int u = 0; u < 4; u ++ ) {
int x = i + dx[u], y = j + dy[u];
if (x <= 0 || y <= 0 || x > n || y > m) continue;
int a = g[i][j], b = g[x][y];
if (!edges.count({a, b})) add(a, b, 0);
}
}
int bfs() {
memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist);
dist[1][0] = 0;
deque<PII> q;
q.push_back({1, 0});
while (q.size()) {
PII t = q.front(); q.pop_front();
if (st[t.x][t.y]) continue;
st[t.x][t.y] = true;
if (t.x == n * m) return dist[t.x][t.y];
if (keys[t.x]) {
int state = t.y | keys[t.x];
if (dist[t.x][state] > dist[t.x][t.y]) {
dist[t.x][state] = dist[t.x][t.y];
q.push_front({t.x, state});
}
}
for (int i = h[t.x]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int j = e[i];
if (w[i] && !(t.y >> w[i] - 1 & 1)) continue;
if (dist[j][t.y] > dist[t.x][t.y] + 1) {
dist[j][t.y] = dist[t.x][t.y] + 1;
q.push_back({j, t.y});
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int main() {
cin >> n >> m >> p >> k;
int cnt = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ )
g[i][j] = cnt ++ ;
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i ++ ) {
int x1, x2, y1, y2, c; cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2 >> c;
int a = g[x1][y1], b = g[x2][y2];
if (c) add(a, b, c), add(b, a, c);
edges.insert({a, b}), edges.insert({b, a});
}
build();
cin >> p;
for (int i = 0; i < p; i ++ ) {
int x, y, c; cin >> x >> y >> c;
keys[g[x][y]] |= 1 << c - 1;
}
cout << bfs();
return 0;
}

tql