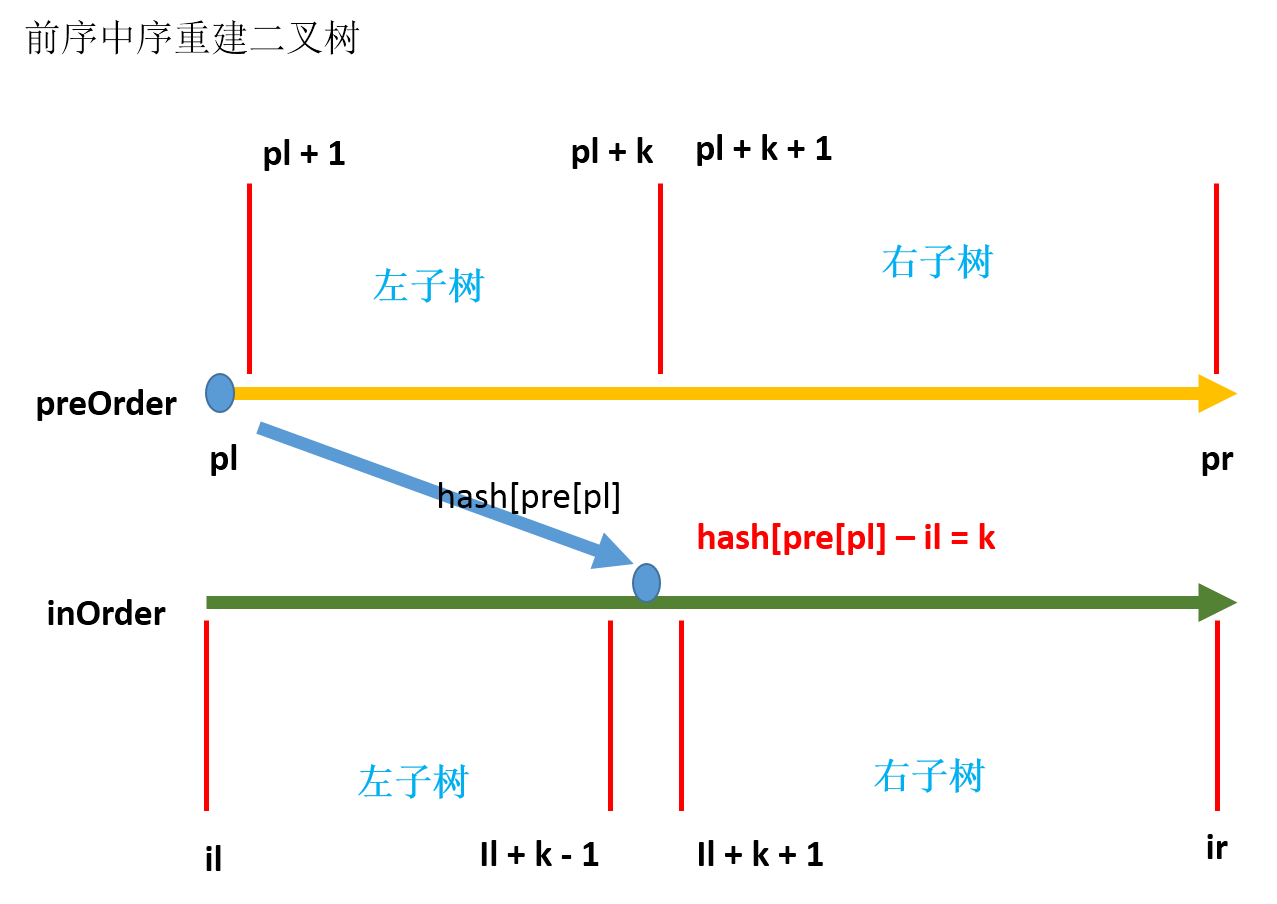
在Y总的基础上,增加了图示,便于理解区间的变化。
题目描述
输入一棵二叉树前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请重建该二叉树。
样例
给定:
前序遍历是:[3, 9, 20, 15, 7]
中序遍历是:[9, 3, 15, 20, 7]
返回:[3, 9, 20, null, null, 15, 7, null, null, null, null]
返回的二叉树如下所示:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
算法
(递归) $O(n)$
哈希预处理,首先保存中序遍历每个节点的下标,这样方便递归每次求根节点在中序遍历时的下标。
找到了根节点在中序遍历的位置,那么左右子树的中序遍历也随之确定。
进一步的,知道的左子树的节点数量,其对应的前序遍历也确定了下来,随之右子树的前序遍历也确定。
参考文献
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/706/
C++ 代码
// 前序 + 中序
// 前序 -> 根节点 中序 -> 左右子树各有多少分节点
// 哈希表(unordered_map<int,int>)记录每个值在中序遍历中的位置
// 这样我们在递归到每个节点时,在中序遍历中查找根节点位置的操作,只需要O(1)
class Solution {
public:
//快速的找到根节点的位置
unordered_map<int, int> pos;
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int n = preorder.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) pos[inorder[i]] = i;
return dfs(preorder, inorder, 0, n - 1, 0, n - 1);
}
TreeNode* dfs(vector<int>&pre, vector<int>&in, int pl, int pr, int il, int ir)
{
if (pl > pr) return NULL;
// 当前区间【pl, pr】所表示的树的根节点 前序遍历的第一个节点就是根节点
// 找到改区间根节点在中序遍历的位置 以及左子树的元素个数
// 左前 :【pl + 1, pl + k】 左中【il, il + k - 1】
// 右前 :【pl + k + 1, pr】 右中【il + k + 1, ir】
int k = pos[pre[pl]] - il;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(pre[pl]);
root->left = dfs(pre, in, pl + 1, pl + k, il, il + k - 1);
root->right = dfs(pre, in, pl + k + 1, pr, il + k + 1, ir);
return root;
}
};

