题目描述
Given a string num representing the digits of a very large integer and an integer k.
You are allowed to swap any two adjacent digits of the integer at most k times.
Return the minimum integer you can obtain also as a string.
样例
Example 1:
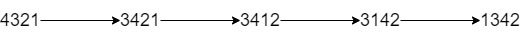
Input: num = "4321", k = 4
Output: "1342"
Explanation: The steps to obtain the minimum integer from 4321 with 4 adjacent swaps are shown.
Example 2:
Input: num = "100", k = 1
Output: "010"
Explanation: It's ok for the output to have leading zeros, but the input is guaranteed not to have any leading zeros.
Example 3:
Input: num = "36789", k = 1000
Output: "36789"
Explanation: We can keep the number without any swaps.
Example 4:
Input: num = "22", k = 22
Output: "22"
Example 5:
Input: num = "9438957234785635408", k = 23
Output: "0345989723478563548"
Constraints:
1 <= num.length <= 30000numcontains digits only and doesn’t have leading zeros.1 <= k <= 10^9
一般涉及由数字组成的字符串,经过一系列操作让其最大/最小,往往涉及两个主题:贪心和逆序对。比如本题,洛谷 P1106 删数问题和洛谷P1323 删数问题。
本题最好想的思路是从贪心角度来思考,为了让最后的数字最小,那么肯定是数字越小,位置应该越靠前。从字符串的首部开始遍历,标记为left,每次找从left + 1到right的最小值,假设最小值的位置是pos,就需要将left到pos - 1的元素整体后移一个位置,将pos的元素移到left。
flag用来标记是否发生了数字交换(有点冒泡排序的意思),如果没有发生交换,并且已经到了字符串的末尾,就可以退出循环。时间复杂度$O(n^2)$,从数据范围推断,按理来说过不了。
这题的数据很迷,写了一个归并排序来计算逆序对的个数,其实就是冒泡排序交换的次数,如果k超过了cnt,直接排序返回即可。这种方法能过是计算cnt排除掉了最耗时的倒数两个测试数据,比赛时侥幸过关。这种思路对应解法一。
那么可以从上面思路的反方向考虑,因为字符串num里面的数字只能是0-9这十个数字中的一个,类似于分桶的思想,每个桶用队列来维护,总共十个桶,存储对应数字在num里出现的下标,显然每个桶里的下标值都是单调上升的。
现在假如k趋于无穷大,以num = "43031"为例,类似于分桶的思想,构建十个桶,每个桶用队列维护,存储对应数字的下标,显然每个桶(队列)里的(从队首看向队尾)下标是单调上升的。
| 桶号 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下标 | 2 | 4 | 空 | 1,3 | 0 | 空 | 空 | 空 | 空 | 空 |
已经假设k是无穷大,那么构建最小数的方法是:从所有非空桶里面选择最小的桶号(意味着每次选择了num里能够选择的最小数字),这个最小的数字放在位数越高的位置,显然得到数字会越小。也就是第一次我们取出了下标2,对应num里的0,此时他前面还没有数字被选择,肯定放在最高位最好,那么交换后num变成04331。
因为下标2对应的数字已经被使用过了,我们用一个数组used来记录下标对应的数字是否被使用过了,初始为0,被使用了标记为1。继续上面的思路,接下来该选择桶1里面的4,对应num里的1,此时最高位已经被占据了,他只能占据第二高的位置,变换后num为01433。
上面是假设k趋于无穷大,但是显然k是有限的,这意味着上面忽略了交换的代价。现在考虑存在交换代价时产生的影响。现在假设k = 1,num不变,此时如果最先选择下标2,它交换到最高位的代价是2,很显然是不满足条件的,接下来考虑下标4,也不满足。考虑下标1,它交换到最高位的代价是1,恰好满足。
此时规律不太明显,现在设k = 5,按照上面的思路,第一次将下标2对应的0换到最高位,代价为2;第二次将下标4对应的1换到第二高的位置,代价是3,现在考虑这个代价3是怎么得到的。在交换之前,used数组是:
下标i |
0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
used[i] |
0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
在移动前,我们可以把当前位置的前面的结构描述成:
[A] [B] [curPos]
curPos:当前需要被移动的位置
[A]里面的数字都被是从某个位置移动过来的,并且都小于curPos对应的数字
[B]里面包含的是介于curPos和[A]之间没有被移动的数字
那么curPos移动到合适位置的代价就是移动到[B]里面的最高位,恰好就是curPos减去[A]的长度,此时used数组派上用场,计算[A]的长度,其实就是从0到curPos之间被使用过的位置的数量。
这样问题的主要矛盾在于如何解决一个数字使用后标记为1(单点修改),计算区间内的总和(查询区间和)。所以只要能解决前面两个矛盾的方法都可以采用,于是有线段树,树状数组,数列分块,依次对应第2,3,4种解法。
解法一:贪心 + 归并排序
时间复杂度$O(n^2)$,实际运行速度竟然还不错……
class Solution {
string help;
int cnt;
int n;
string s;
public:
string minInteger(string num, int k) {
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
cnt = 0;
n = num.size();
calculate(num);
if (cnt <= k) {
sort(num.begin(), num.end());
return num;
}
int left = 0, right, pos;
bool flag = false;
if (k >= n - 1) right = n - 1;
else right = k;
while (k) {
flag = false;
pos = left;
for (int i = left; i <= right; ++i) {
if (num[pos] > num[i]) pos = i;
}
for (int i = pos; i > left; --i) {
std::swap(num[i], num[i - 1]);
--k;
flag = true;
}
if (!flag && left == n - 1) break;
++left;
if (left + k < n - 1) right = left + k;
}
return num;
}
void calculate(string & num)
{
s = help = num;
mergeSort(0, n - 1);
}
void mergeSort(int left, int right)
{
if (left < right) {
int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1);
mergeSort(left, mid);
mergeSort(mid + 1, right);
merge(left, mid + 1, right);
}
}
void merge(int leftPos, int rightPos, int rightEnd)
{
int num = rightEnd - leftPos + 1; //需要归并的元素的数量
int leftEnd = rightPos - 1; //前半部分的最右端的下标
int tmp = leftPos;
while (leftPos <= leftEnd && rightPos <= rightEnd) {
if (s[leftPos] <= s[rightPos]) {
help[tmp++] = s[leftPos++];
}
else {
cnt += leftEnd - leftPos + 1;
help[tmp++] = s[rightPos++];
}
}
while (leftPos <= leftEnd) {
help[tmp++] = s[leftPos++];
}
while (rightPos <= rightEnd) {
help[tmp++] = s[rightPos++];
}
for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) {
s[rightEnd] = help[rightEnd];
--rightEnd;
}
}
};
解法二:线段树
构建带延迟标记的线段树,来实现单点修改和查询区间和。每次查询和修改都是$O(\log n)$,时间复杂度$O(n \log n)$。关于线段树的解释可以参见《算法竞赛进阶指南》0x43部分。
class Solution {
struct SegmentTree
{
int left, right;
long long sum, lazy;
//SegmentTree(): left(0), right(0), sum(0), lazy(0) {}
};
vector<SegmentTree> tree;
int n;
#define left(x) tree[x].left
#define right(x) tree[x].right
#define sum(x) tree[x].sum
#define lazy(x) tree[x].lazy
inline int leftChild(int x) { return x << 1; }
inline int rightChild(int x) { return x << 1 | 1; }
inline int length(int x) { return right(x) - left(x) + 1; }
inline void update(int root)
{
sum(root) = sum(leftChild(root)) + sum(rightChild(root));
}
void build(int root, int l, int r)
{
left(root) = l;
right(root) = r;
if (l == r) { sum(root) = 0; return; }
int mid = l + ((r - l) >> 1);
build(leftChild(root), l, mid);
build(rightChild(root), mid + 1, r);
update(root);
}
void pushDown(int root)
{
if (lazy(root)) {
sum(leftChild(root)) += lazy(root) * length(leftChild(root));
sum(rightChild(root)) += lazy(root) * length(rightChild(root));
lazy(leftChild(root)) += lazy(root);
lazy(rightChild(root)) += lazy(root);
lazy(root) = 0;
}
}
void change(int root, int pos, long long val)
{
if (left(root) == right(root)) { sum(root) = val; return; }
int mid = left(root) + ((right(root) - left(root)) >> 1);
if (pos <= mid) change(leftChild(root), pos, val);
else change(rightChild(root), pos, val);
update(root);
}
long long query(int root, int l, int r)
{
if (left(root) == l && right(root) == r) return sum(root);
pushDown(root); //延迟标记下传
int mid = left(root) + ((right(root) - left(root)) >> 1);
if (r <= mid) return query(leftChild(root), l, r);
else if (l > mid) return query(rightChild(root), l, r);
return query(leftChild(root), l, mid) + query(rightChild(root), mid + 1, r);
}
public:
string minInteger(string num, int k) {
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
n = num.size();
string res;
tree.resize((n + 5) * 4);
build(1, 1, n);
vector<queue<int>> digit(10);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) digit[num[i] - '0'].push(i);
while (res.size() < n) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
if (digit[i].empty()) continue;
int curPos = digit[i].front();
int cost = curPos - query(1, 1, curPos + 1);
if (cost <= k) {
k -= cost;
res.push_back('0' + i);
digit[i].pop();
change(1, curPos + 1, 1);
break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
解法三:树状数组
涉及lowbit运算,可以参考《算法竞赛进阶指南》0x01位运算部分。树状数组可参考0x42部分。
每次查询和修改的时间复杂度$O(\log n)$,时间复杂度$O(n \log n)$。
class Solution {
vector<int> preSum;
int n;
inline int lowbit(int x) { return x & (-x); }
//查询[1, pos]内前缀和
int query(int pos)
{
int res = 0;
while (pos) {
res += preSum[pos];
pos -= lowbit(pos);
}
return res;
}
//修改位于pos位置的数值为val
void change(int pos, int val)
{
while (pos <= n) {
preSum[pos] += val;
pos += lowbit(pos);
}
}
public:
string minInteger(string num, int k) {
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
n = num.size();
preSum.resize(n + 1, 0);
vector<queue<int>> digit(10);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) digit[num[i] - '0'].push(i);
string res;
while (res.size() < n) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
if (digit[i].empty()) continue;
int curPos = digit[i].front();
int cost = curPos - query(curPos + 1);
if (cost <= k) {
k -= cost;
res.push_back('0' + i);
digit[i].pop();
change(curPos + 1, 1);
break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
解法四:数列分块
其实就是hzwer数列分块九题里的区间加法,区间查询。单点修改可以看成长度为1的区间加法。
数列分块是将数组分成$\sqrt{n}$块,维护一个加法标记,同时维护每个块的和,完整的块进行标记,不完整的块直接暴力修改。查询和修改的时间复杂度是$O(\sqrt{n})$,时间复杂度$O(n \sqrt{n})$。
class Solution {
vector<int> seq, sum, addTag, belong;
int n, blockNum;
void init()
{
seq.resize(n + 1, 0);
sum.resize(n + 1, 0);
belong.resize(n + 1);
addTag.resize(n + 1);
blockNum = sqrt(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) belong[i] = (i - 1) / blockNum + 1;
}
//查询[left, right]内前缀和
int query(int left, int right)
{
int res = 0;
for (int i = left; i <= min(belong[left] * blockNum, right); ++i)
res += seq[i] + addTag[belong[left]];
if (belong[left] != belong[right]) {
for (int i = (belong[right] - 1) * blockNum + 1; i <= right; ++i)
res += seq[i] + addTag[belong[right]];
}
for (int i = belong[left] + 1; i <= belong[right] - 1; ++i)
res += sum[i] + blockNum * addTag[i];
return res;
}
//[left, right]的区间增加val
void change(int left, int right, int val)
{
for (int i = left; i <= min(belong[left] * blockNum, right); ++i) {
seq[i] += val;
sum[belong[left]] += val;
}
if (belong[left] != belong[right]) {
for (int i = (belong[right] - 1) * blockNum + 1; i <= right; ++i) {
seq[i] += val;
sum[belong[right]] += val;
}
}
for (int i = belong[left] + 1; i <= belong[right] - 1; ++i) {
addTag[i] += val;
}
}
public:
string minInteger(string num, int k) {
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
n = num.size();
init();
vector<queue<int>> digit(10);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) digit[num[i] - '0'].push(i);
string res;
while (res.size() < n) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
if (digit[i].empty()) continue;
int curPos = digit[i].front();
int cost = curPos - query(1, curPos + 1);
if (cost <= k) {
k -= cost;
res.push_back('0' + i);
digit[i].pop();
change(curPos + 1, curPos + 1, 1);
break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
};


youxiu