题目描述
给定一个字符串 s 和一个 长度相同 的整数数组 indices。
请你重新排列字符串 s,其中第 i 个字符需要移动到 indices[i] 指示的位置。
返回重新排列后的字符串。
样例
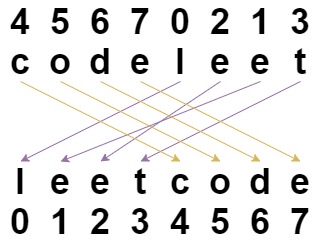
输入:s = "codeleet", indices = [4,5,6,7,0,2,1,3]
输出:"leetcode"
解释:如图所示,"codeleet" 重新排列后变为 "leetcode" 。
输入:s = "abc", indices = [0,1,2]
输出:"abc"
解释:重新排列后,每个字符都还留在原来的位置上。
输入:s = "aiohn", indices = [3,1,4,2,0]
输出:"nihao"
输入:s = "aaiougrt", indices = [4,0,2,6,7,3,1,5]
输出:"arigatou"
输入:s = "art", indices = [1,0,2]
输出:"rat"
限制
s.length == indices.length == n1 <= n <= 100s仅包含小写英文字母。0 <= indices[i] < nindices的所有的值都是唯一的(也就是说,indices是整数0到n - 1形成的一组排列)。
算法
(原地算法) $O(1)$
- 由数学定理知,一个置换必定由若干个不重叠的子置换构成。
- 从一个没有访问过的位置开始,遍历其一个子置换,然后在子置换上进行原地平移。
时间复杂度
- 每个位置仅访问一次,故时间复杂度为 $O(n)$。
空间复杂度
- 仅需要常数的额外空间。
C++ 代码
class Solution {
public:
string restoreString(string s, vector<int>& indices) {
const int n = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int j = indices[i];
while (j != i) {
swap(s[i], s[j]);
swap(indices[i], indices[j]);
j = indices[i];
}
}
return s;
}
};

