问题描述
You are given coins of different denominations and a total amount of money amount. Write a function to compute the fewest number of coins that you need to make up that amount. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return -1.
提供给你一些不同面值的硬币,每种硬币均可无限量使用,计算出可凑出金额Amount的最少硬币数量。
举个例子:
Example 1:
Input: coins = [1, 2, 5], amount = 11
Output: 3
Explanation: 11 = 5 + 5 + 1
Example 2:
Input: coins = [2], amount = 3
Output: -1
Update at 2020_0915
典型的完全背包问题。
先来看下朴素做法:
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int l = coins.length;
var dp = new int[l + 1][amount + 1];
// 将第一行的所有元素设置为一个较大值,为了后续求Min。
Arrays.fill(dp[0], amount + 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= l; i++){
for (int j = 1; j <= amount; j++){
// 选择了第i件物品,并求在金额j范围内满足要求的最小数量。
if (j - coins[i - 1] >= 0){
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - coins[i - 1]] + 1);
} else {
// 不选第i件物品。
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
}
}
}
// eg. coins = [2], amount = 3
return dp[l][amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[l][amount];
}
}
然后对空间进行降维:
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int l = coins.length;
var dp = new int[amount + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++){
dp[i] = amount + 1;
}
for (int c: coins){
for (int j = c; j <= amount; j++){
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - c] + 1);
}
}
return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
}
解法1
先看下我最初的实现方法:
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int len = coins.length;
int[][] dp = new int[len + 1][amount + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
for (int j = 1; j <= amount; j++){
// Bag has rest.
if (j - coins[i - 1] >= 0){
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - coins[i - 1]] + 1;
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
}
}
}
return dp[len][amount];
}
}
但是当提供硬币无法凑出Amount金额时,就会出现问题。
那么问题到底出在哪里?
我们应该明确定义无法凑出Amount金额这种情况,并将其表示成dp[i][j] = -1。
来调整下实现:
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int len = coins.length;
int[][] dp = new int[len + 1][amount + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp[0], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
int min;
for (int j = 1; j <= amount; j++){
int coin = coins[i - 1];
int top = dp[i - 1][j];
int jump = dp[i][j - coin];
// Bag has rest.
if (j - coin >= 0){
if (top == -1 && jump == -1){
min = -1;
} else if (top == -1){
min = jump + 1;
} else if (jump == -1){
min = top;
} else {
min = Math.min(top, jump + 1);
}
} else {
min = top;
}
min = (min == Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? -1 : min;
dp[i][j] = min;
}
}
return dp[len][amount];
}
}
还是挺复杂的。
我们调整一下策略,在遍历过程中不处理其最大值,而在最后获取结果的时候再处理:
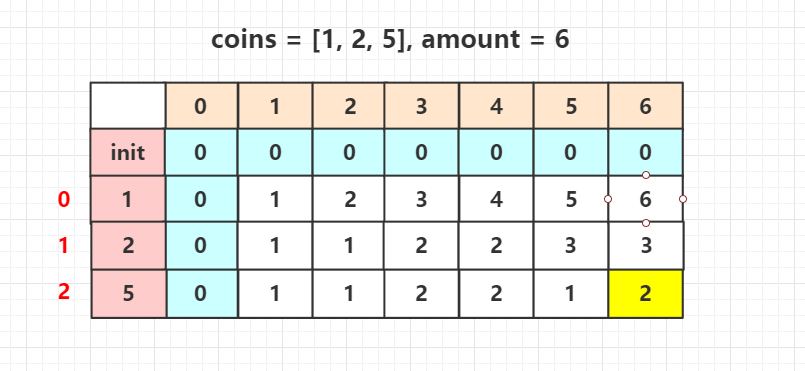
先来看下示意图:
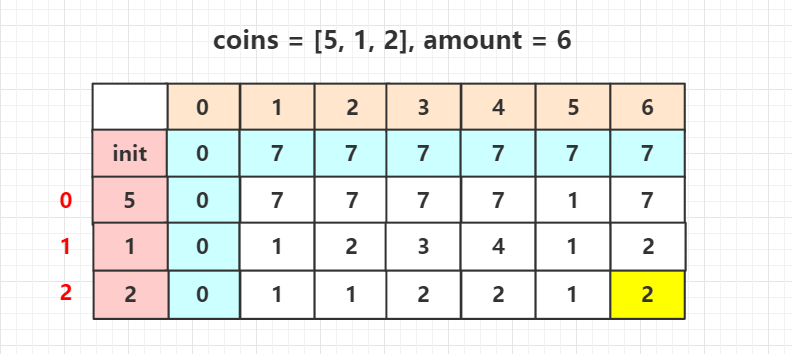
这里有个小技巧,一开始我们初始化的最大值,可以选择amount + 1,而不是Integer.MAX_VALUE,防止整数溢出。
再考虑下无法凑出Amount金额的场景:
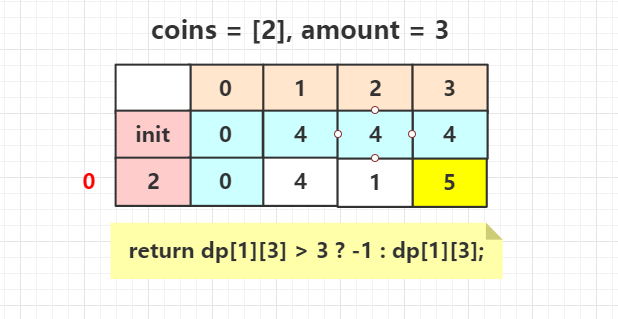
Let's code:
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int len = coins.length;
int[][] dp = new int[len + 1][amount + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp[0], amount + 1);
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
for (int j = 1; j <= amount; j++){
int coin = coins[i - 1];
int top = dp[i - 1][j];
// Bag has rest.
if (j - coin >= 0){
dp[i][j] = Math.min(top, dp[i][j - coin] + 1);
} else {
dp[i][j] = top;
}
}
}
return dp[len][amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[len][amount];
}
}
老规矩,压缩成一维数组:
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int len = coins.length;
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, amount + 1);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++){
for (int j = 1; j <= amount; j++){
int coin = coins[i - 1];
// Bag has rest.
if (j - coin >= 0){
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - coin] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
}
再来,合并内层循环条件:
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, amount + 1);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int c: coins){
for (int j = c; j <= amount; j++){
// Bag has rest.
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - c] + 1);
}
}
return dp[amount] > amount ? -1 : dp[amount];
}
}
Enjoy it !


很棒,终于看到二维数组做的了,