题目描述
地上有一个 m 行和 n 列的方格,横纵坐标范围分别是 0∼m−1 和 0∼n−1。
一个机器人从坐标0,0的格子开始移动,每一次只能向左,右,上,下四个方向移动一格。
但是不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于 k 的格子。
请问该机器人能够达到多少个格子?
样例
输入:k=7, m=4, n=5
输出:20
输入:k=18, m=40, n=40
输出:1484
解释:当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格(35,37),因为3+5+3+7 = 18。
但是,它不能进入方格(35,38),因为3+5+3+8 = 19。
注意:
0<=m<=50
0<=n<=50
0<=k<=100
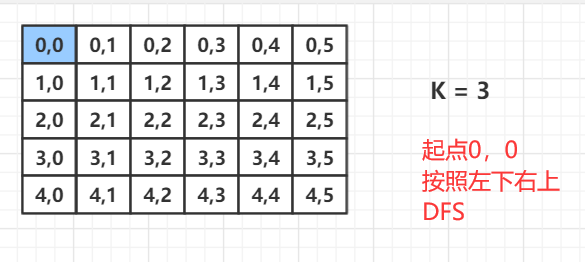
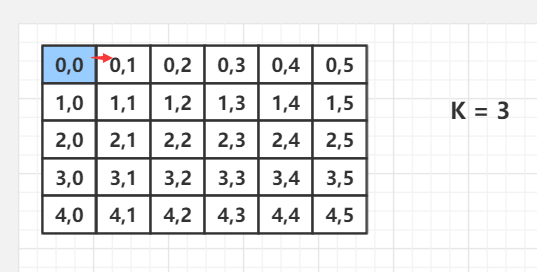
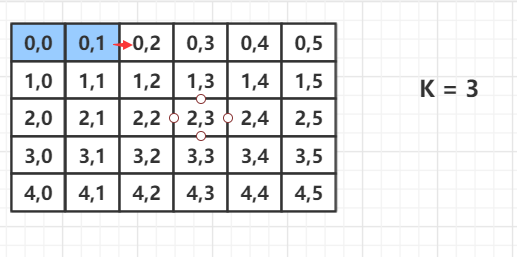
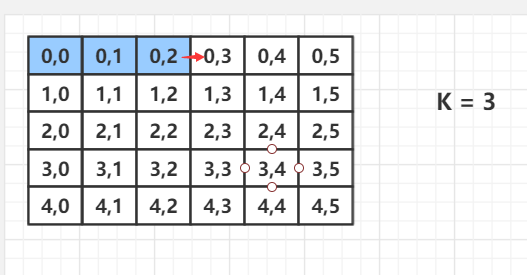
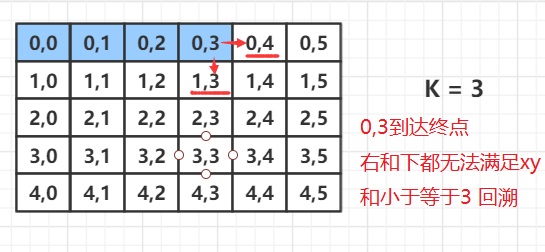
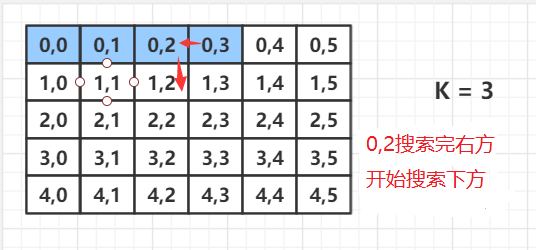
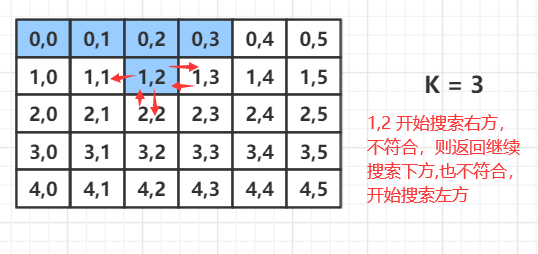
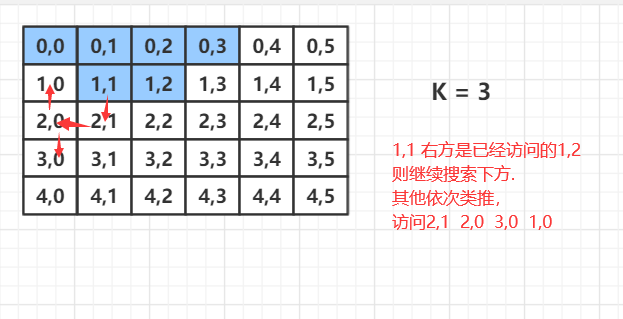
算法1
x y的+- 1 的搜索模板
在添加上检测每个格子是否符合要求的代码
与递归回溯搜索代码结合
C++ 代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<bool>> vis;
int count = 0;
bool Check(int x, int y, int rows, int cols, int limit) {
if (x <0 || y < 0 || x > rows - 1 || y > cols - 1)
return false;
int sum = 0;
while (x != 0) {
sum += x % 10;
x = x / 10;
if (sum > limit)
return false;
}
while (y != 0) {
sum += y % 10;
y = y / 10;
if (sum > limit)
return false;
}
return true;
}
void dfs(int x, int y, int rows, int cols, int limit)
{
//坐标位置不对 或者已经访问过 即可返回
if (x <0 || y < 0 || x > rows - 1 || y > cols - 1 || vis[x][y])
return;
//标记是否访问 然后检查该坐标是否符合要求 计数是否加1
if (vis[x][y] == false) {
vis[x][y] = true;
if (Check(x, y, rows, cols, limit) == true) {
count++;
}
else {
return;
}
}
//本坐标符合要求 则进行上下左右的扩展
dfs(x + 1, y, rows, cols, limit);
dfs(x - 1, y, rows, cols, limit);
dfs(x, y + 1, rows, cols, limit);
dfs(x, y - 1, rows, cols, limit);
}
int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols)
{
int x = 0, y = 0; count = 0;
//创建标注是否搜索到的标记数组
vis = vector<vector<bool>>(rows, vector<bool>(cols, false));
//开始 递归回溯搜索
dfs(0, 0, rows, cols, threshold);
return count;
}
};
算法1
BFS
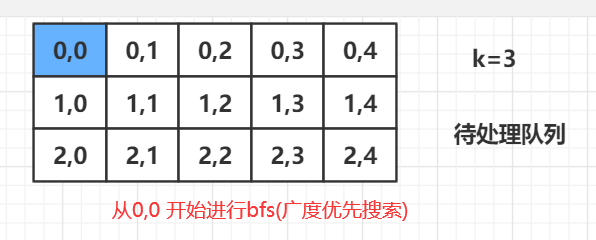
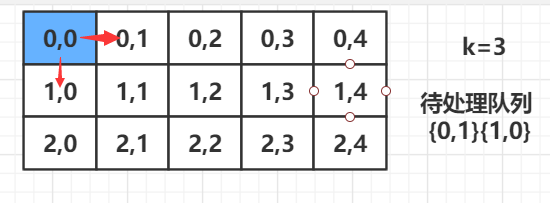
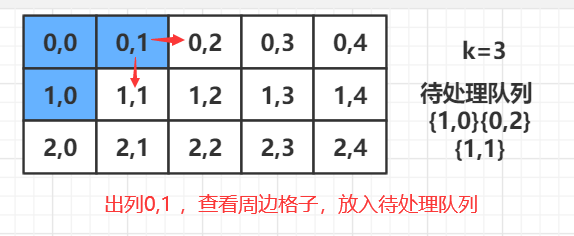
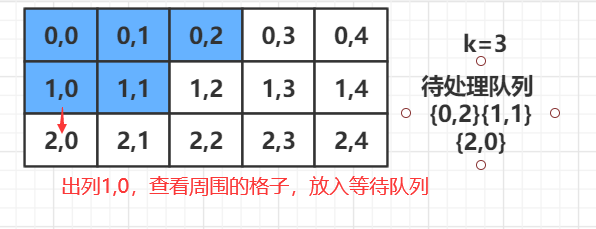
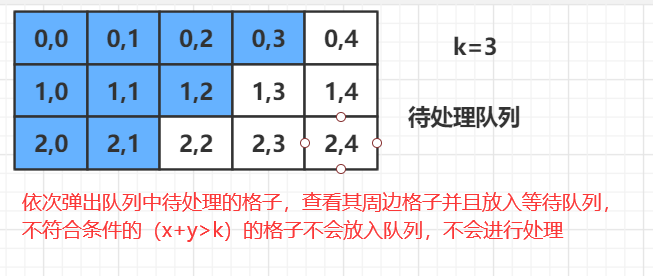
C++ 代码
class Solution {
public:
queue<pair<int,int>> q;
int addx[4] = {1,-1,0,0};
int addy[4] = {0,0,1,-1};
vector<vector<int>> vis;
int ans;
int Sumxy(int a){
int ret = 0;
while(a!=0){
ret += a%10;
a=a/10;
}
return ret;
}
int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {
q.push({0,0});
vis = vector<vector<int>>(m,vector<int>(n));
vis[0][0]= 1;
while(!q.empty()){
pair<int,int> XY = q.front();q.pop();
if(Sumxy(XY.first)+Sumxy(XY.second) >k) continue;
ans++;
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i++){
int newx = XY.first+addx[i];
int newy = XY.second+addy[i];
if(newx>=0 && newx<m && newy>=0 && newy<n && 0 == vis[newx][newy]){
vis[newx][newy] = 1;
q.push({newx,newy});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};

