分析
使用tarjan求出所有连通图,然后遍历所有点,将所有连通图的大小计算出来,如果该连通图内有至少两个点x,那么使用公式$$ans+=C_{x}^{2} $$
计算出所有的连通对的总个数。
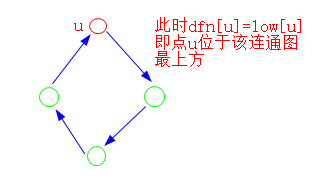
dfn[u]==low[u]时:
C++ 代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 1e4+10,M = 1e5+10;
int h[N],e[M],ne[M],idx; //邻接表存储边
int stk[N],top; //tarjan栈stk,top:栈大小
int dfn[N],low[N],timestamp; //dfn[u]:遍历到u的时间戳;low[u]:从u开始走能遍历到的最小时间戳;timestamp:时间戳
int id[N],scc_cnt; //id[i]表示第i个点处于哪个强连通图,scc_cnt:强联通分量个数
bool in_stk[N]; //判断当前点是否在栈stk中。
int n,m;
LL ans;
unordered_map<int,int> mp; //哈希表用于统计同一个联通图中一共有几个点
void add(int a,int b)
{
e[idx]=b,ne[idx]=h[a],h[a]=idx++;
}
void tarjan(int u) //tarjan算法求连通图
{
dfn[u]=low[u]=++timestamp;
stk[++top]=u,in_stk[u]=true;
for(int i=h[u];~i;i=ne[i])
{
int j=e[i];
if(!dfn[j])
{
tarjan(j);
low[u]=min(low[u],low[j]);
}
else if(in_stk[j])
{
low[u]=min(low[u],dfn[j]);
}
}
if(dfn[u]==low[u]) //此时说明该点位于一个联通图的最上方
{
++scc_cnt;
int y;
do{
y=stk[top--];
in_stk[y]=false;
id[y]=scc_cnt; //下标为y的点所在的联通图标号为scc_cnt
}while(y!=u);
}
}
int main()
{
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
cin>>n>>m;
int a,b;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
cin>>a>>b;
add(a,b);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!dfn[i])
tarjan(i);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) //遍历所有点,统计每个强联通图的大小
{
mp[id[i]]++;
}
for(auto x:mp)
{
if(x.second>1)
{
ans+=(LL)(x.second*(x.second-1))/2; //组合公式求和
}
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}

