数据已经更新
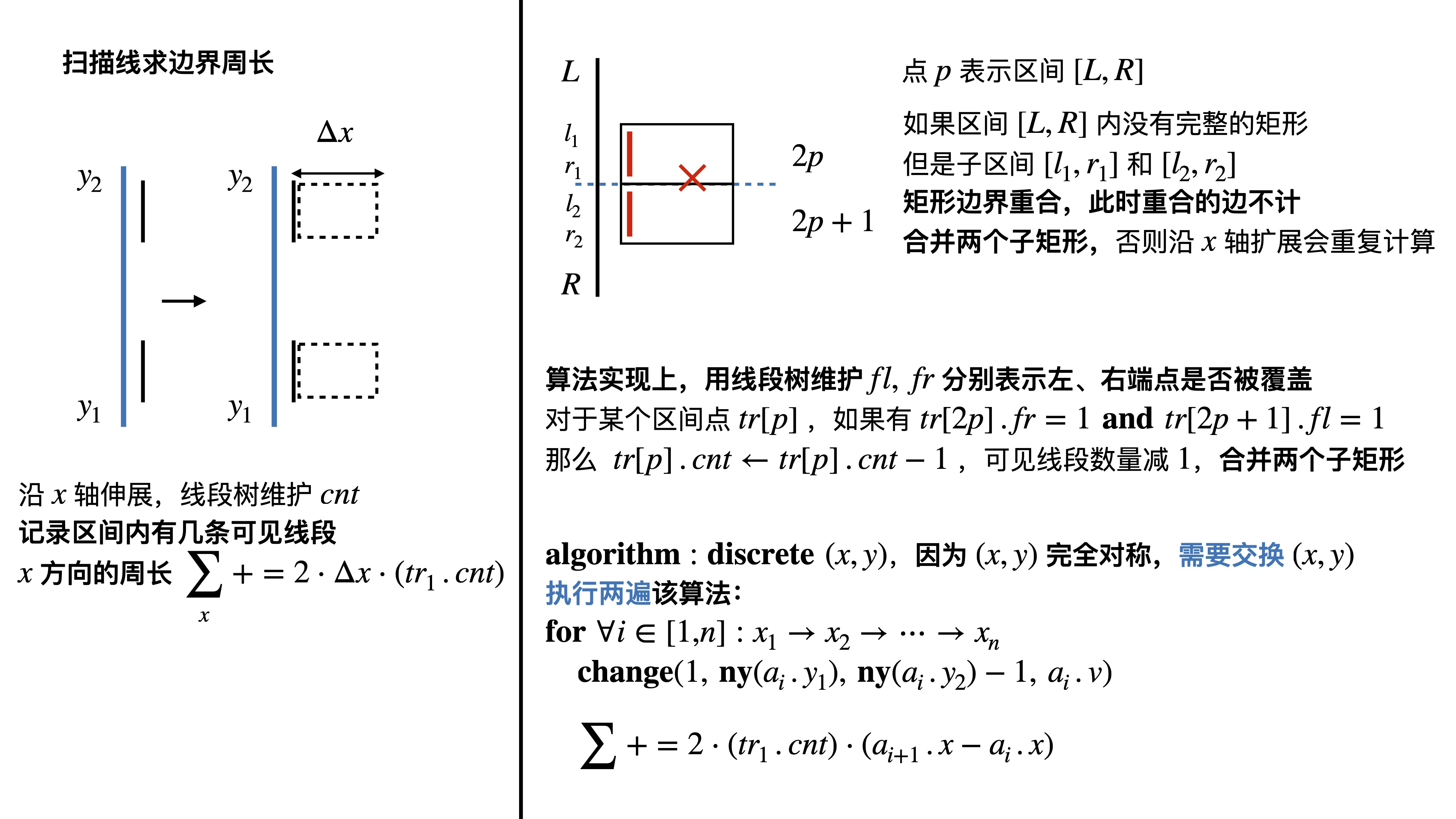
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <sstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cmath>
#include <bitset>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef set<int>::iterator ssii;
#define Cmp(a, b) memcmp(a, b, sizeof(b))
#define Cpy(a, b) memcpy(a, b, sizeof(b))
#define Set(a, v) memset(a, v, sizeof(a))
#define debug(x) cout << #x << ": " << x << endl
#define _forS(i, l, r) for(set<int>::iterator i = (l); i != (r); i++)
#define _rep(i, l, r) for(int i = (l); i <= (r); i++)
#define _for(i, l, r) for(int i = (l); i < (r); i++)
#define _forDown(i, l, r) for(int i = (l); i >= r; i--)
#define debug_(ch, i) printf(#ch"[%d]: %d\n", i, ch[i])
#define debug_m(mp, p) printf(#mp"[%d]: %d\n", p->first, p->second)
#define debugS(str) cout << "dbg: " << str << endl;
#define debugArr(arr, x, y) _for(i, 0, x) { _for(j, 0, y) printf("%c", arr[i][j]); printf("\n"); }
#define _forPlus(i, l, d, r) for(int i = (l); i + d < (r); i++)
#define lowbit(i) (i & (-i))
#define MPR(a, b) make_pair(a, b)
pair<int, int> crack(int n) {
int st = sqrt(n);
int fac = n / st;
while (n % st) {
st += 1;
fac = n / st;
}
return make_pair(st, fac);
}
inline ll qpow(ll a, int n) {
ll ans = 1;
for(; n; n >>= 1) {
if(n & 1) ans *= 1ll * a;
a *= a;
}
return ans;
}
template <class T>
inline bool chmax(T& a, T b) {
if(a < b) {
a = b;
return true;
}
return false;
}
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
ll ksc(ll a, ll b, ll mod) {
ll ans = 0;
for(; b; b >>= 1) {
if (b & 1) ans = (ans + a) % mod;
a = (a * 2) % mod;
}
return ans;
}
ll ksm(ll a, ll b, ll mod) {
ll ans = 1 % mod;
a %= mod;
for(; b; b >>= 1) {
if (b & 1) ans = ksc(ans, a, mod);
a = ksc(a, a, mod);
}
return ans;
}
template <class T>
inline bool chmin(T& a, T b) {
if(a > b) {
a = b;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool _check(int x) {
//
return true;
}
int bsearch1(int l, int r) {
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(_check(mid)) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
int bsearch2(int l, int r) {
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r + 1) >> 1;
if(_check(mid)) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
return l;
}
template<class T>
bool lexSmaller(vector<T> a, vector<T> b) {
int n = a.size(), m = b.size();
int i;
for(i = 0; i < n && i < m; i++) {
if (a[i] < b[i]) return true;
else if (b[i] < a[i]) return false;
}
return (i == n && i < m);
}
// ============================================================== //
const int maxn = 1e4 + 10;
int n, m[2];
class A {
public:
int x, y1, y2, c;
A() = default;
A(int x, int y1, int y2, int c) : x(x), y1(y1), y2(y2), c(c) {}
bool operator< (const A &rhs) const {
return x < rhs.x || (x == rhs.x && c < rhs.c);
}
} a[2][maxn];
vector<int> B[2];
map<int, int> ny[2];
void prework() {
_for(i, 0, 2) {
sort(a[i]+1, a[i]+1+m[i]);
sort(B[i].begin(), B[i].end());
B[i].erase(unique(B[i].begin(), B[i].end()), B[i].end());
for (auto x : B[i]) ny[i][x] = lower_bound(B[i].begin(), B[i].end(), x) - B[i].begin();
}
}
class segTree {
public:
int l, r;
int cnt;
bool fl, fr;
int cover;
void clear() {
l = r = 0;
cnt = 0;
fl = fr = false;
cover = 0;
}
} tr[maxn * 4];
void build(int p, int l, int r) {
tr[p].clear();
tr[p].l = l; tr[p].r = r;
if (l == r) return;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(p<<1, l, mid);
build(p<<1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
}
void pushup(int p, int sgn) {
if (tr[p].cover) {
tr[p].cnt = 1;
tr[p].fl = tr[p].fr = 1;
}
else {
if (tr[p].l == tr[p].r) {
tr[p].fl = tr[p].fr = 0;
tr[p].cnt = 0;
}
else {
tr[p].fl = tr[p<<1].fl;
tr[p].fr = tr[p<<1 | 1].fr;
tr[p].cnt = tr[p<<1].cnt + tr[p<<1 | 1].cnt;
if (tr[p<<1].fr && tr[p<<1 | 1].fl) tr[p].cnt--;
}
}
}
void change(int p, int l, int r, int v, int sgn) {
if (l <= tr[p].l && tr[p].r <= r) {
tr[p].cover += v;
pushup(p, sgn);
return;
}
int mid = (tr[p].l + tr[p].r) >> 1;
if (l <= mid) change(p<<1, l, r, v, sgn);
if (r > mid) change(p<<1 | 1, l, r, v, sgn);
pushup(p, sgn);
}
int solve(int sgn) {
build(1, 0, B[sgn].size() - 2);
int ans = 0;
_rep(i, 1, m[sgn]) {
change(1, ny[sgn][a[sgn][i].y1], ny[sgn][a[sgn][i].y2]-1, a[sgn][i].c, sgn);
//debug(ny[a[i].y1]);
ans += 2 * tr[1].cnt * (a[sgn][i+1].x - a[sgn][i].x);
}
return ans;
}
int ans = 0;
void init() {
memset(m, 0, sizeof(m));
_for(i, 0, 2) {
B[i].clear();
ny[i].clear();
}
ans = 0;
}
int main() {
//freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
while (~scanf("%d", &n)) {
init();
_rep(i, 1, n) {
int x1, y1, x2, y2;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &y1, &x1, &y2, &x2);
a[0][++m[0]] = A(x1, y1, y2, 1);
a[0][++m[0]] = A(x2, y1, y2, -1);
B[0].push_back(y1);
B[0].push_back(y2);
a[1][++m[1]] = A(y1, x1, x2, 1);
a[1][++m[1]] = A(y2, x1, x2, -1);
B[1].push_back(x1);
B[1].push_back(x2);
}
assert(m[0] == n*2 && m[1] == n*2);
// prework
prework();
_for(i, 0, 2) ans += solve(i);
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}


请问大佬为什么要按照y轴从小到大处理?我按照x从小到大处理acwing上面wa了但是poj上面A了
我也是…,按照x和按照y好像得出的答案不一样,不知道怎么回事
线段树是怎么理解的?