题目描述
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
样例
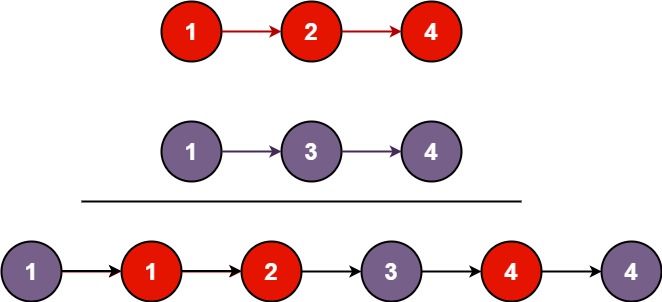
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
限制
- 两个链表的节点数目范围是
[0, 50]。 -100 <= Node.val <= 100l1和l2均按 非递减顺序 排列。
算法
(线性合并) $O(n)$
- 新建头部的保护结点 $dummy$,设置 $cur$ 指针指向 $dummy$。
- 若当前 $list1$ 指针指向的结点的值比 $list2$ 指针指向的结点的值小,则令 $cur$ 的 $next$ 指针指向 $list1$,且 $list1$ 后移;否则指向 $list2$,且 $list2$ 后移。
- 然后 $cur$ 指针按照上一部设置好的位置后移。
- 循环以上步骤直到 $list1$ 或 $list2$ 为空。
- 将剩余的 $list1$ 或 $list2$ 接到 $cur$ 指针后边。
时间复杂度
- 两个链表各遍历一次,所以时间复杂度为 $O(n)$。
C++ 代码
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode();
ListNode *cur = dummy;
while (list1 != NULL && list2 != NULL) {
if (list1 -> val < list2 -> val) {
cur -> next = list1;
list1 = list1 -> next;
}
else {
cur -> next = list2;
list2 = list2 -> next;
}
cur = cur -> next;
}
cur -> next = (list1 ? list1 : list2);
return dummy -> next;
}
};

