题解 : https://xiaoxiaoh.blog.csdn.net/article/details/104266806
一、内容
Yixght is a manager of the company called SzqNetwork(SN). Now she's very worried because she has just received a bad news which denotes that DxtNetwork(DN), the SN's business rival, intents to attack the network of SN. More unfortunately, the original network of SN is so weak that we can just treat it as a tree. Formally, there are N nodes in SN's network, N-1 bidirectional channels to connect the nodes, and there always exists a route from any node to another. In order to protect the network from the attack, Yixght builds M new bidirectional channels between some of the nodes.
As the DN's best hacker, you can exactly destory two channels, one in the original network and the other among the M new channels. Now your higher-up wants to know how many ways you can divide the network of SN into at least two parts.
Input
The first line of the input file contains two integers: N (1 ≤ N ≤ 100 000), M (1 ≤ M ≤ 100 000) — the number of the nodes and the number of the new channels.
Following N-1 lines represent the channels in the original network of SN, each pair (a,b) denote that there is a channel between node a and node b.
Following M lines represent the new channels in the network, each pair (a,b) denote that a new channel between node a and node b is added to the network of SN.
Output
Output a single integer — the number of ways to divide the network into at least two parts.
Sample Input
4 1
1 2
2 3
1 4
3 4
Sample Output
3
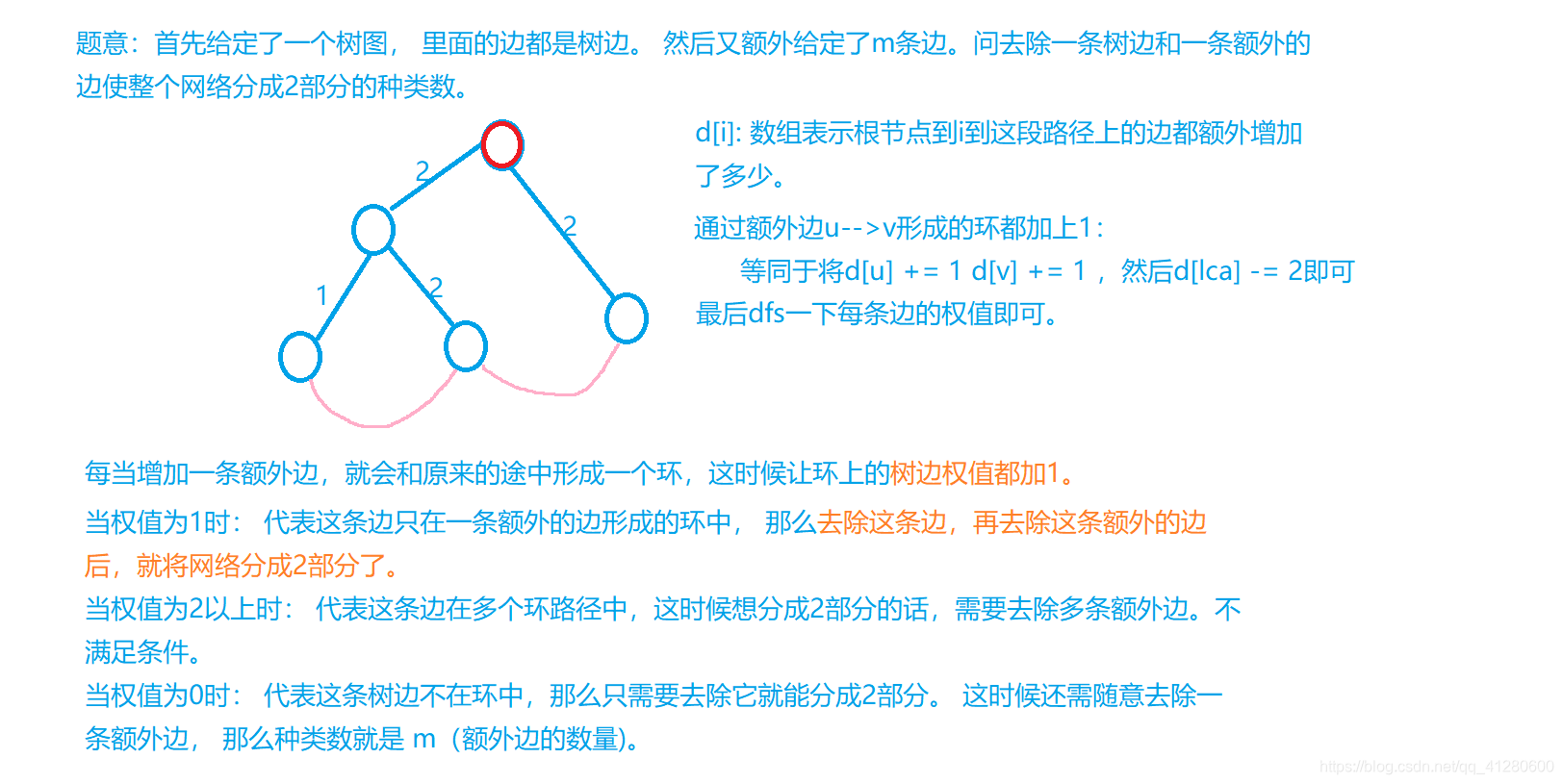
二、思路
三、代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5, M = N * 2;
struct E { int v, next;} e[M];
int n, m, u, v, len, ans, lg, h[N], f[N][20], dep[N], d[N]; //d[i]代表根节点到i的这条路径上每条边加的次数
queue<int> q;
void add(int u, int v) {e[++len].v = v; e[len].next = h[u]; h[u] = len;}
void bfs() {
dep[1] = 1; q.push(1);
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for (int j = h[u]; j; j = e[j].next) {
int v = e[j].v;
if (dep[v]) continue;
dep[v] = dep[u] + 1;
q.push(v);
f[v][0] = u;
for (int k = 1; k <= lg; k++) f[v][k] = f[f[v][k - 1]][k - 1];
}
}
}
int lca(int x, int y) {
if (dep[y] > dep[x]) swap(x, y);
for (int k = lg; k >= 0; k--) {
if (dep[f[x][k]] >= dep[y]) x = f[x][k];
}
if (x == y) return x;
for (int k = lg; k >= 0; k--) {
if (f[x][k] != f[y][k]) x = f[x][k], y = f[y][k];
}
return f[x][0];
}
void dfs(int u, int fa) {
for (int j = h[u]; j; j = e[j].next) {
int v = e[j].v;
if (v == fa) continue;
dfs(v, u);
if (d[v] == 0) ans += m;
else if (d[v] == 1) ans += 1;
d[u] += d[v];
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
lg = int(log(n) / log(2)) + 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
add(u, v); add(v, u);
}
bfs();
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
int Lca = lca(u, v);
d[Lca] -= 2; d[u] += 1; d[v] += 1;
}
dfs(1, 0);
printf("%d", ans);
return 0;
}